Title Page
-
Plant Name
-
Plant Manager
-
Date
-
Location
-
Audit Number
-
Auditor
SAFETY CHECKLIST
Hazard Communication
-
Hazard Communication Standard
The hazard communication program is intended to inform employees about the chemical hazards they may encounter at the ready mixed concrete facility. It includes provisions for employee training, labeling of hazardous chemicals, maintaining material safety data sheets (MDSs), and developing a written hazard communication plan. A written hazard communication program must be in place and include the following:
• a list of hazardous chemicals present in the ready mixed concrete facility
• how the employer will label primary and secondary chemical containers in the ready mixed concrete facility
• how the facility collects and maintains SDSs for each chemical
• training programs regarding chemical hazards and protective measures
• proof of employee training
Items to look for include:
• The Hazard Communication Program
• List and location of chemicals present at the facility
• Training records
• Site's SOP for chemical handling
• Spot check a couple of SDS with chemicals -
1. A written hazard communication program is developed, implemented, and maintained at the ready mixed concrete facility. (29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(1) and (3) — (5))
-
2. Ready mixed concrete facilities that produce, use, or store hazardous chemicals at a ready mixed concrete facility where employees of other employer(s) (contractors) may be exposed must include additional provisions in their hazard communication program. (29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(2))
-
Note:
• Verify that employees are notified of the locations of SDS. NOTE: this area may be found in a separate SOP or in the Safety Orientation -
3. Each container of chemicals present in the ready mixed concrete facility must be labeled or marked. (29 CFR 1910.1200(f)(5) — (11))
-
4. Each SDS must be in English. (29 CFR 1910.1200(g)(2))
-
5. Copies of the required SDS for each chemical must be maintained in the ready mixed concrete facility and must be readily accessible during each work shift to employees when they are in their work area(s). (29 CFR 1910.1200(g)(8))
-
Note:
• Electronic access and other alternatives to maintaining paper copies of the SDS are permitted as long as such options do not create any barriers to immediate employee access in each ready mixed concrete facility. -
6. SDSs must be made readily available, upon request, to employee-designated representatives, OSHA and to emergency responders. (29 CFR 1910.1200(g)(11)
-
7. Employees must be provided with information on the hazardous chemicals in their work areas at the time of their initial assignment and whenever a new hazard is introduced into their work areas. (29 CFR 1910.1200(h)(1) and (2)
-
8. Hazard communication training must include ways for employees to detect the presence of hazardous chemicals, relevant physical and health hazards, measures employees can take to protect themselves and the details of the facility's hazard communication program. (29 CFR 1910.1200(h)(3)
-
9. Verify that everyone at the site has been trained in Hazard Communication and all training records are available for immediate inspection.
Fire Protection
-
This section covers portable fire extinguishers and fire protection equipment found at the ready mixed concrete facility and the administration offices. Applicable 29 CFR 1910 sections include:
29 CFR 1910.157 Portable Fire Extinguishers
29 CFR 1910.159 Automatic Sprinkler Systems
29 CFR 1910.164 Fire Detection Systems
29 CFR 1910.165 Employee Alarm Systems
Items to look for include:
• Fire protection SOP
• Monthly inspection records for portable fire extinguishers
• Annual portable fire extinguisher inspection records
• Facility fire detection equipment maintenance records
• Employee portable fire extinguisher training records -
10. Only approved portable fire extinguishers may be used. They must be mounted and identified so they can be readily located and obtained without injury. (29 CFR 1910.157(c))
-
11. Portable fire extinguishers must be selected based on the fire hazard class present. (29 CFR 1910.157(d))
-
Notes:
• extinguishers for Class A and D fires must be located within 75 ft of employees
• extinguishers for Class B fires must be within 50 ft of employees
• extinguishers for Class C hazards must be distributed on the basis of the appropriate pattern for existing Class A or Class B hazards -
12. The facility is responsible to inspect, maintain, and test all portable fire extinguishers in the ready mixed concrete facility. (29 CFR 1910.157(e))
-
Note:
• Verify that procedures are in place to conduct and record maintenance checks on portable fire extinguishers -
13. All portable extinguishers must be tested annually by a<br><br>• portable fire extinguisher servicing company
-
14. The company must train employees in the proper use of all portable fire extinguishers present in the ready mixed concrete facility that employees are expected to use. (29 CFR 1910.157(g))
-
Fire Detection Systems:
-
20. Fire detection systems and components must be restored to normal operating condition as soon as possible after each test or alarm. (29 CFR 1910.164(b)(1)—(2))
-
21. Fire detection systems must be protected from damaging substances or conditions. (29 CFR 1910.164(d)(1)—(3))
-
Employee Alarm Systems:
-
22. Employee alarm systems must provide sufficient warning time to allow employees to implement the emergency actions called for in the facility's Emergency Action Plan. (29 CFR 1910.165(b)(1)—(5))
-
Note:
For employers with 10 or fewer employees in a "particular ready mixed concrete facility," (defined as an entirely separate building) direct voice communication is an acceptable procedure for sounding the alarm provided all employees can hear the alarm. Such ready mixed concrete facilities need not have a back-up system. -
23. Manually-operated actuation devices for use in conjunction with employee alarms must be kept unobstructed, conspicuous, and readily accessible. (29 CFR 1910.165(e))
Medical Services and First Aid
-
This section covers medical services and first aid at the facility. Reference 29 CFR 1910.151 for more details. Items to look for include:
• Fire aid kits and supplies
• Employee training of first aid
• Restocking plan of first aid supplies -
The ready mixed concrete facility has stocked First-Aid Kit.
-
24. The ready mixed concrete facility has a first-aid kit restocking plan
-
25. In the absence of an infirmary, clinic, or hospital in near proximity to the ready mixed concrete facility which is used for the treatment of all injured employees, a person or persons must be adequately trained to render first aid. Adequate first aid supplies must be readily available. (29 CFR 1910.151(b))
-
26. Where the eyes or body of any person may be exposed to injurious corrosive materials, suitable facilities for quick drenching or flushing of the eyes and body must be provided within the work area for immediate emergency use. (29 CFR 1910.151(c))
Emergency Action Plans
-
This section covers emergency action plans at the facility. Reference 29 CFR 1910.38 for more details. Items to look for include:
• Facility Emergency Action Plan
• Training documents -
27. An Emergency Action Plan must contain minimum requirements found at 29 CFR 1910.38(c) (see notes below)
-
Notes:
• If the facility has 10 or fewer employees, interview employees to verify that the information required in the plan has been communicated orally to employees
• Emergency Action Plan requirements:
o Procedures for reporting a fire or other emergency
o Procedures for emergency evacuation, including type evacuation and exit route assignments
o Procedures to be followed by employees who remain to operate critical plant operations before they evacuate
o Procedures to account for all employees after an evacuation
o Procedures to be followed by employees performing rescue or medical duties
o The name or job title of every employee who may be contacted for more information on the Emergency Action Plan -
28. The company must designate and train employees to assist in a safe and orderly evacuation of other employees. (29 CFR 1910.38(e))
-
The site specific Emergency Action Plan must be posted in a common place and in plain view.
-
29. The Employee Action Plan must be covered with each employee upon initial assignment, change of duties, or the plan changes. (29 CFR 1910.38(f)).
-
The onsite storm shelter shall be unlocked during normal hours of operation.
Confined Spaces
-
This section covers confined spaces (permit required and non-permit required) at the facility. Reference 29 CFR 1910.146 for more details. Items to look for include:
• Permit Required Confined Space SOP
o How the facility evaluated a permit vs. non-permit confined spaces
• Training documents
• Air Monitoring equipment
• Ventilation equipment
• Review the previous years confined space permits -
30. The company must evaluate the plant to determine if any spaces are permit-required confined spaces. (29 CFR 1910.146(c)(1) and (c)(6))
-
31. Permit-required confined spaces must be identified by posting warning signs or some other effective measures to inform employees of the existence and dangers of confined spaces (29 CFR 1910.146(c)(2))
-
32. If the company allows employees to enter permit required spaces, they must develop and implement a written permit program. (29 CFR 1910.146(c)(4) and (d)(1) — (d)(2))
-
33. The company must provide and maintain the equipment required to safely enter the permit spaces. (29 CFR 1910.146(d)(4))
-
34. The confined space entry program requires monitoring of the atmosphere in the space prior to entry to ensure safe entry conditions exist before entry is authorized, and during entry to ensure safe entry conditions are maintained. (29 CFR 1910.146(d)(5))
-
35. The company may use an alternate program in lieu of a permit- required confined space program. (29 CFR 1910.146 (c)(5))
-
36. When using an alternate entry technique, the company must conduct operations according to certain specified procedures. (29 CFR 1910.146 (c)(5)(ii))
-
37. The facility can reclassify a permit space as a non-permit space under certain conditions. (29 CFR 1910.146(c)(7))
-
38. Before entry into a permit space is authorized, the company must, prior to entry, prepare and issue an entry permit that has certain required components. (29 CFR
-
39. Before entry is authorized, the company must, prior to entry, document the completion of certain measures required in the program. (29 CFR 1910.146(e)(1) — (e)(4))
-
40. Procedures must be in place to terminate entry permits. (29 CFR 1910.146(e)(5))
-
41. Canceled entry permits must be retained for at least one yr. (29 CFR 1910.146(e)(6))
-
42. Training must be conducted for employees who act as attendants, entrants, supervisors issuing permits, and rescue personnel. (29 CFR 1910.146(g))
-
43. The company must ensure that authorized entrants know certain duties. (29 CFR 1910.146(h))
-
44. The company must ensure that attendants understand certain duties. (29 CFR 1910.146(i))
-
45. The company must ensure that the entry supervisor understands certain duties. (29 CFR 1910.146(j))
-
46. If the company permits its employees to enter permit spaces to perform rescue services, these employees must be provided with certain PPE, trained, and must practice their assigned duties. (29 CFR 1910.146(k)(1) and (i)(4))
-
47.If the facility uses an outside response group to provide rescue services, the facility must inform the rescue service of all hazards and provide access to all permit spaces. (29 CFR 1910.146(k)(2))
-
48. The facility must use retrieval equipment that can be operated by attendants from outside of the confined space, unless the retrieval equipment would increase the overall risk of entry. (29 CFR 1910.146(k)(3))
-
49. Safety data sheets (SDSs) or other similar written information must be made available to the medical facility treating exposed entrants. (29 CFR 1910.146(k)(4))
-
50. The written permit-required confined space entry program must be reviewed. (29 CFR 1910.146(d)(13) - (d)(14))
Electrical
-
All outlets and switches must be covered with a protective plate.
-
Receptacles installed on 15- and 20-amprere circuits shall be of the grounding type. (29 CFR 1910.3104(b)(2)(i))
-
Receptacles installed in a bathroom shall have a ground-fault circuit-interupter protection for personnel. (29 CFR 1910.304(b)(3)(ii)(A))
-
Breaker panels should be tagged with appropriate ARC FLASH WARNING labels. (29 CFR 1910.335(b)(1))
-
All electrical equipment shall be firmly secured to the surface on which it is mounted. (29 CFR 1910.303(b)(8)(i))
-
Breaker panels should be securely closed when not being serviced.
-
All switches in breaker panel boxes should be clearly labeled.
-
There should be no gaps or missing switches in a breaker panel.
-
Breaker Panels shall have installed a "Dead Front" panel which prevents exposure to any live parts of the breaker panel. (29 CFR 1910.305(d))
-
All electrical components shall be properly grounded.
-
There shall be no broken, damaged, or cut extension cords in use on the plant facility. (29 CFR 1910.334(a)(2)(ii))
-
All extension cords shall be 3-wire type so they may be grounded, no grounding prong may be missing (29 CFR 1926
-
All cables and enclosures should be in good working condition (not damaged, not broken) and kept out of any water.
-
A minimum of three (3) feet of clearance in front of any electrical panel must be maintained for electrical equipment servicing 600 volts or less. The width of the clear working space in front shall be thirty (30) inches minimum or width if the equipment, whichever is greater. (29 CFR 1910.303(g), NFPA 70 110.26)
Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout)
-
This section covers the control of hazardous energy (Lockout/Tagout) at the facility. Reference 29 CFR 1910.147 for more details. Items to look for include:
• LO/TO SOP
• LO/TO training records
• Equipment Specific LO/TO documents
• Applicable LO/TO equipment -
51. Program consisting of energy-control procedures, employee training, and periodic inspections must be established. 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(1) and (2))
-
52. Procedures must be developed, documented, and used to control potentially hazardous energy when employees are engaged in the activities covered by the lockout/tagout standard. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(4))
-
53. When a tagout device is used on an energy-isolating device that is not capable of being locked out, the tagout device must be Latched at the same location the lockout device would have been attached. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(3)(i))
-
54. The level of safety achieved in the tagout program must be quivalent to the level of safety obtained by using a lockout ilrogram. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(3)(ii))
-
55. Protective materials and hardware (locks, tags, chains, etc.) must be provided (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(i) and (ii))
-
56. Lockout/tagout devices must be durable and meet certain requirements. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(ii) and (iii))
-
57. Periodic inspections must be conducted at least annually to ensure that requirements are being followed. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(6)(i)and(ii))
-
58. Training must be provided to ensure that employees understand the purpose and functions of the energy control program and that they acquire the knowledge and skills required for the safe application, usage, and removal of energy controls. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(7 (i), (ii) and (iv))
-
59. All authorized and affected employees must be retrained whenever their job assignments change, whenever there is a change in equipment, machines or processes in which a new liazard or whenever there is a change in the energy-control procedures. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(7)(iii))
-
60. Lockout or tagout procedures must be performed only by the authorized employees who are performing the servicing or maintenance. (29 CFR 1910147(c)(8))
-
61. Affected employees must be notified by the employer or authorized employee of the application and removal of lockout devices or tagout devices. (29 CFR 1910.147(c)(9))
-
62. Procedures must be followed whenever lockout or tagout devices must be temporarily removed from the energy-isolating device, and the machine or equipment is energized to test or position the machine, equipment, or component thereof. (29CFR1910.147(f)(l))
-
63. When outside personnel is engaged in lockout/tagout procedures, the facility, and the outside employer must inform each other of their respective lockout or tag-out procedures. (29CFR1910.147(f)(2))
-
64. When lockout/tagout procedures are performed by a crew, department or other group, they must utilize a procedure which affords the employees a level of protection equivalent to that provided by the implementation of a personal lockout or tagout device. (29CFR1910.147(f)(3))
-
65. Procedures must be utilized during shift or personnel changes to ensure the continuity of lockout or tagout protection. (29CFR1910.147(f)(4))
-
66. Procedures must be established to apply energy controls. (29CFR1910.147(d))
-
67. Before lockout or tagout devices are removed and energy is restored to the equipment and machine, appropriate procedures must be followed and actions taken by the authorized employee(s). (29 CFR 1910.147(e))
Hand Tools, Portable Power Tools and Jacks
-
This section covers the hand tools, power tools and jacks used at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.242 Hand and Portable Powered Tools
• 29 CFR 1910.243 Guarding of Portable Powered Tools
• 29 CFR 1910.244 Jacks
Items to look for include:
• Tool SOP
• Training records
• Verify by walking around and spot checking tools -
68. Hand and portable powered tools and equipment must be maintained in such a manner that they are safe to use. (29 CFR 1910.242(a))
-
69. Compressed air used for cleaning purposes must be below 30 psig, and must be used with effective chip guarding and personal protective equipment (PPE). (29 CFR 1910.242(b))
-
70. Portable circular saws must be equipped with appropriate guarding. (29 CFR 1910.243(a)(l))
-
71. Switches and controls on certain handheld tools must be designed to shut off when pressure is released (commonly called "dead man" controls). (29 CFR 1910.243(a)(2))
-
72. Portable electrically-powered hand tools must be properly grounded. (29 CFR 1910.243(a)(5))
-
73 .Pneumatic powered tools and hoses must meet specific installation and design criteria. (29 CFR 1910.243(b))
-
74. Right angle head or vertical portable grinders must be provided with safety guards. (29 CFR 1910.243(c)(3))
Machine Guarding
-
This section covers the machine guarding at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.212 General Requirements for All Machines
• 29 CFR 1910.215 Abrasive Wheel Machinery
• 29 CFR 1910.219 Mechanical Power-Transmission Apparatus
Items to look for include:
• Machine Guarding SOP
• Training records
• Verify by walking around and spot checking tools -
76. Machine guards must be provided to protect people from machine hazards. (29 CFR 1910.212(a)(l)-(2))
-
77. Points of operation that expose an employee to injury must be guarded. (29 CFR 1910.212(a)(3)(ii) and (iv))
-
78. Special hand tools designed to place and remove material must allow for the safe handling of material. (29 CFR 1910.212(a)(3)(iii))
-
79. Fan blades must be guarded under certain circumstances. (29 CFR 1910.212(a)(5))
-
80. Machines designed for a fixed location must be secured in place. (29 CFR 1910.212(b))
-
81. Abrasive wheel safety guards must meet certain requirements. (29 CFR 1910.215(a)(2)-(3))
-
82. Work rests must be used to support the work. (29 CFR 1910.215(a)(4))
-
83. Maximum guard exposure angles must not be exceeded. (29 CFR 1910.21 5(b)(2)), (b)(3) - (b)(8)
Walking and Working Surfaces
-
This section covers the walking and working surfaces at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.22 Walking and Working Surfaces - General Requirements
• 29 CFR 1910.23 Guarding Floors, wall openings and holes
• 29 CFR 1910.24 Fixed Industrial Stairs
• 29 CFR 1910.25 Portable Wood Ladders
Items to look for include:
• Housekeeping
• Training records -
87. Proper housekeeping is maintained in all work facilities. 29CFR1910.22(a)(l)-(3))
-
88. Where mechanical handling equipment is used, aisles and passageways must be properly maintained, clear of materials, in good repair, and marked. (29 CFR 1910.22(b)(l) and (2))
-
89. Covers and guardrails must be provided to protect employees from hazards of open pits & tanks (29 CFR 1910.22(c))
-
90. Floor loading areas must be marked and proper floor loading procedures must be maintained. (29 CFR 1910.22(d)(l) and (2))
-
91. Every stairway and ladder way floor opening or platform must be guarded by a standard railing. (29 CFR 1910.23(a)(l) and (2))
-
92. Every hatchway, chute, pit, manhole, and temporary floor opening must be guarded. (29 CFR 1910.23(a)(3)-(10))
-
93. Wall openings and holes must be guarded if there is a drop of more than 4 ft. (29 CFR 1910.23(b)(l)
-
94. Every window wall opening at a stairway landing, floor, platform, or balcony from which there is a drop of more than 4 ft and where the bottom of the opening is less than 3 ft above the platform or landing must be guarded. (29 CFR 1910.23(b)(3))
-
95. Every temporary wall opening must have adequate guards. (29 CFR 1910.23(b)(4))
-
96. Every open-sided floor or platform 4 ft or more above adjacent floor or ground level must be guarded by a standard railing. (29CFR1910.23(c)(l))
-
97. Railings and toeboards must be provided for certain structures. (29CFR1910.23(c)(3))
-
98. Every flight of stairs having 4 or more risers must be equipped with standard stair railings or standard handrails. (29 CFR 1910.23(d)(l)and(2))
-
99. A standard railing must consist of a top rail, intermediate rail, and posts, and have a vertical height of 42 inches nominal from upper surface to top rail to floor, platform, runway, or ramp level. (29 CFR 1910.23(e)(l))
-
100. A standard toeboard must be 4 inches nominal in vertical height from its top edge to the level of the floor, platform, runway, or ramp. (29 CFR 1910.23(e)(4))
-
101 Floor coverings must meet specific strength requirements. (29 CFR 1910.23(e)(7))
-
102. Fixed stairs must be provided for access from one structure level to another where operations necessitate regular travel between levels. (29 CFR 1910.24(b))
-
103. Fixed stairways must be designed to support 5 times the normal live load anticipated. (29 CFR 1910.24(c))
-
104. Fixed stairways must have a minimum width of 22 inches. (29 CFR 1910.24(d
-
105. All stair treads must be reasonably slip-resistant and the nosings must have a nonslip finish. (29 CFR 1910.24(f))
-
106. Portable step ladders longer than 20 ft must not be used. (29 CFR 1910.25(c)(2))
-
107. Ladders must be in good condition and assembled to meet certain safety requirements. (29 CFR 1910.25(d)(2))
-
108. Rungs and steps of portable metal ladders must be treated to minimize the possibility of slipping. (29 CFR 1910.26(a)(l)(v))
-
109. The bottoms of the 4 rails of a step ladder "feet" must be covered with an insulating non-slip material. (29 CFR 1910.26(a)(3)(vii))
-
110. Step ladders must be fitted with a metal spreader or locking device to hold the front and back sections in open position. (29 CFR 1910.26(a)(3)(viii))
-
111. Ladders must be designed to meet load requirements. (29 CFR 1910.27(a)(l) and (2)
-
112. Fixed ladders must meet certain requirements for clearance. (29 CFR 1910.27(c))
-
113. Ladders with cages or baskets must meet certain specific requirements for clearances. (29 CFR 1910.27(c)(3) and (d)(l)(v)
-
114. When ladders are used to ascend to heights exceeding 20 ft, landing platforms must be provided. (29 CFR 191 0.27 (d)(2))
-
115. Ladder safety devices may be used on tower or silo over 20 ft in unbroken length in lieu of cage protection. (29 CFR 1910.27(d)(5))
-
116. Fixed ladders must be maintained in a safe condition. (29 CFR 1910.27(f))
Welding and Cutting
-
Does the plant location participate in any Welding or Gas Cutting activities?
-
This section covers welding and cutting at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.252 Welding, Cutting and Brazing - General Requirements
• 29 CFR 1910.253 Oxygen-Fuel Gas welding and cutting
. 29 CFR 1910.254 Arc Welding and Cutting
Items to look for include:
• Housekeeping
• Training records
• Compressed Gas Storage
• Hot work permits -
117. Basic fire prevention and protection procedures for welding and cutting operations are followed. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(l)(i)-(ii))
-
118. Where sparks can pass through floor or wall openings Including cracks or holes, etc.) precautions must be taken to prevent contact with combustible materials on the floor below. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(i))
-
119. Suitable fire extinguishing equipment must be maintained for immediate use whenever operations cannot be isolated from combustible materials. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(ii))
-
120. Fire watch must be used when required in situations where combustible materials are present or a fire might develop. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(A))
-
121. Fire watch must have specific basic training requirements and adhere to facility fire watch requirements. (29 CFR1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(B))
-
122. Areas, where cutting and welding are to take place, must be inspected by the authorizing person prior. The authorizing person must designate appropriate precautions to proceed. (29CFR1910.252(a)(2)(iv))
-
123. Floors, where cutting and welding are performed, must meet specific fire prevention requirements. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(v))
-
124. Welding or cutting must be prohibited in certain areas. [29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(vi))
-
125. Where practicable, all combustible materials must be relocated at least 35 ft away. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(vii))
-
126. Conveyor systems that might carry sparks must be protected or shut down. (29 CFR 1910.252 (a)(2)(viii))
-
127. Combustible walls, partitions or roofs must be protected by shields or guards to prevent possible ignition. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(ix))
-
128. Welding performed on a noncombustible metal wall, partition or roof requires additional precautions. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(x)
-
129. Welding is prohibited on a metal partition, wall, ceiling, or roof that has a combustible covering. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(xi))
-
130. Management must uphold its responsibility for safe usage of cutting and welding equipment on its property. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(xiii))
-
131. Cutting or welding is only permitted in areas that are or have been made fire safe. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(xv))
-
132. Cutting or welding or other hot work is prohibited on used drums, tanks or other similar containers unless they are thoroughly cleaned of any flammable materials. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(3)(i)-(ii))
-
133. For cutting and welding in confined spaces, specific confined space precautions must be followed. (29 CFR 1910.252(a)(4)(i)-(ii)
-
134. Proper eye protection is required for cutting and welding operations. (29 CFR 1910.252(b)(2)(i))
-
135. Helmets and hand shields must meet protection level specifications. (29 CFR 1910.252(b)(2)(ii))
-
136. Protective clothing is required during welding, cutting, or brazing operations. (29 CFR 1910.252(b)(3))
-
137. Confined spaces such as a boiler, bin, silo, mixer drum must be provided with proper ventilation and equipment. (29 CFR 1910.252(b)(4)(i)-(vii))
-
138. Local exhaust or general ventilation must be provided to keep concentrations of toxic fumes, gases or dusts below established limits. (29 CFR 1910.252(c)(l)(iii))
-
139. Oxygen cutting using either a chemical flux, iron powder, or gas-shielded arc cutting of stainless steel must be conducted using adequate mechanical ventilation. (29 CFR 1910.252(c)(12))
-
140. First aid equipment must be available for use at all times. (29CFR1910.252(c)(13))
-
Oxygen-Fuel Gas Welding
-
141. Only approved devices and apparatus such as manifolds, torches, and regulators may be used for oxygen-fuel gas welding and cutting. (29 CFR 1910.253(a)(3))
-
142 Acetylene must not be used at a pressure in excess of 15 pounds per square inch gauge (psig) or 30 pounds per square Mich absolute (psia). (29 CFR 1910.253(a)(2))
-
143. Gas cylinders must be stored appropriately. (29 CFR1910.253(b)(2)-(3))
-
144. Oxygen and fuel gas hose and hose connections must meet certain safe use requirements. (29 CFR 1910.253(e)(5)(i)-(v))
Material Handling
-
This section covers Material Handling at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.178 Powered Industrial Trucks
• 29 CFR 1910.184 Slings
Items to look for include:
• Pre-trip inspections
• Training records -
149.Powered industrial trucks must comply with certain design requirements. (29 CFR 1910.178(a))
-
150. Powered industrial trucks must be designated into one of 11 different categories as follows: D, DS, DY, E, ES, EE, EX, G, GS, LP, and LPS. (29 CFR 1910.178(b))
-
151. Safe operating procedures must be followed when using powered industrial trucks. (29 CFR 1910.178(m))
-
152. When traveling, powered industrial trucks must adhere to safe practices. (29 CFR 1910.178(n))
-
153. Powered industrial trucks must be loaded safely. (29 CFR 1910.178(o))
-
154. Areas where powered industrial trucks are used must be managed to reduce hazards. (29 CFR 1910.178(h), (i), and (k))
-
155. Fuel handling and storage associated with use of powered industrial trucks must meet appropriate requirements. (29 CFR 1910.178(f)and(p)(2)-(5))
-
156.Powered industrial trucks must be properly maintained. (29CFR1910.178(q))
-
157. Powered industrial trucks must be examined prior to being placed into service. (29 CFR 1910.178(q)(7))
-
159. Powered industrial track operators must receive training. (29 CFR 1910.178(1)(1))
-
160. The training program must cover specified elements. (29 CFR 1910.178(1)(2) and (3))
-
161. Refresher training and evaluations of the effectiveness of operator training must be conducted. (29 CFR 1910.1 78(1)(4))
-
Slings
-
Are Nylon, Synthetic round, chain, or wire rope slings used or stored at the plant facility?
-
162. Slings must be operated safely. (29 CFR 1910.184(c)
-
163. Each sling and all fastenings and attachments must undergo a thorough inspection each day prior to use. (29 CFR 1910.184(d))
-
164. Loads must be operated in accordance with rated capacities for slings and chains contained in Tables N- 184-1 through N- 184- pin 29 CFR 1910.184. (29CFR1910.184(e)-(i))
-
165. Alloy steel chain slings must be designed and used appropriately. (29 CFR 1910.184(e)(l) - (e)(3))
-
166. Repaired, reconditioned or new alloy steel chain slings must be proof tested by the manufacturer or equivalent entity before use. (29 CFR 1910.1 84(e)(4)) - (7)
-
167. Wire rope slings must be designed in accordance with specific length requirements and must be used in accordance with safe operating temperatures. (29 CFR 1910.1 84(f)(2) and (3))
-
168. Wire rope slings must be immediately removed from service when certain conditions are present. (29 CFR 1910.184(f)(5))
-
169. Natural and synthetic fiber rope slings must be removed from service when certain conditions are present. (29 CFR 1910.184(h)(5))
-
170. Synthetic web slings must be designed and used appropriately. (29 CFR 1910.1 84(i)(2) - (4) and (7))
-
171. Synthetic web slings must be removed from service when certain criteria are met. (29 CFR 1910.1 84(i)(9))
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
-
This section covers PPE use at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.132 PPE General Requirements
• 29 CFR 1910.133 Eye and Face Protection
• 29 CFR 1910.134 Respiratory Protection
• 29CFR1910.135Head Protection
• 29 CFR 1910.136 Foot Protection
Items to look for include:
• PPE Hazard Assessment
• Training records
• PPE SOP
• PPE in use
• Verify by walking around -
172. The company must provide and maintain safe undamaged PPE for employees when there is a need for protection from physical and/or health hazards. (29 CFR 1910.132(a), (c), (e))
-
173. The company must assess the ready mixed concrete facility to determine if hazards are present or are likely to be present (29 CFR 1910.132 (d))
-
174. The company must provide adequate and appropriate training to employees required to use PPE. (29 CFR 1910.132(f))
-
175. The training program must be documented in writing. (29 CFR 1910.132(f)(4))
-
Eye and Face Protection
-
176. The company must ensure that every employee uses appropriate eye or face protection when exposed to eye or face hazards. (29 CFR 1910.133(a)
-
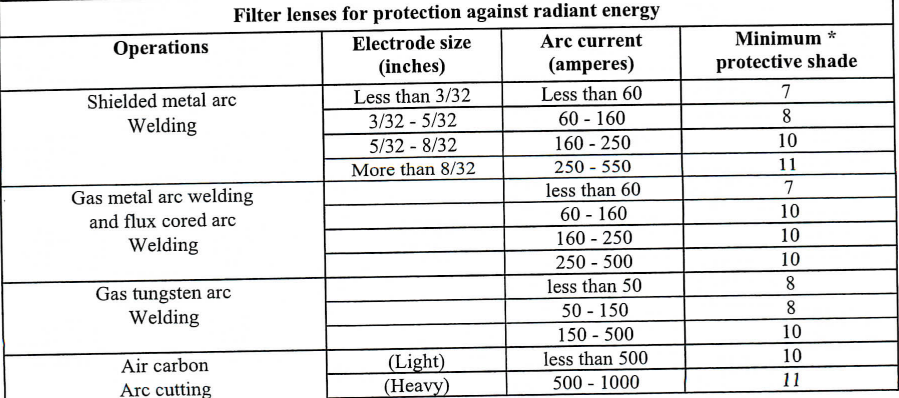
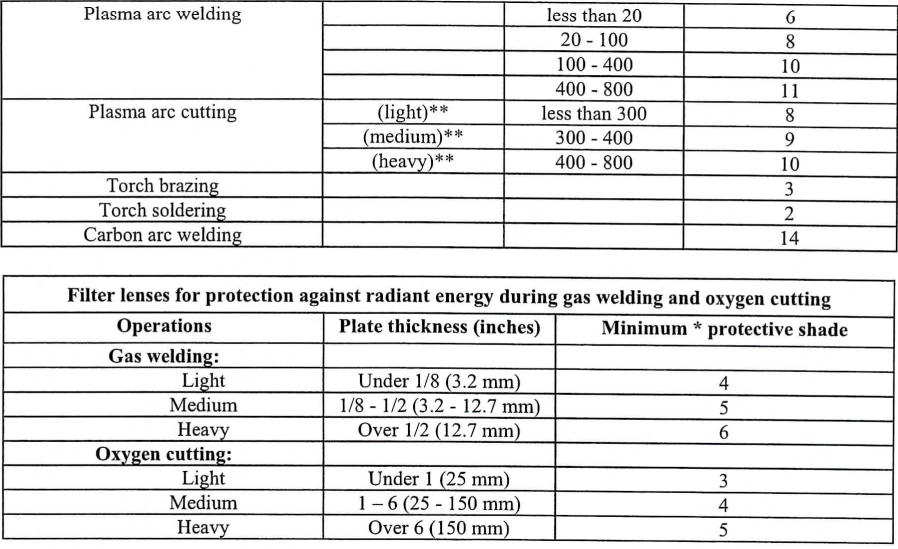
177. The company must ensure that each employee uses eye protection with filter lenses that have a shade number appropriate for the work being performed for protection from injurious light radiation. (29 CFR 1910.133(a)(5)) - see table below
-
-
-
178. Head Protection<br><br>The company must ensure that each employee wears a protective helmet when working in areas posing a risk of injury to the head. (29 CFR 1910.135(a)(l)-(2))
-
179. Foot Protection<br><br>The company must ensure that each affected employee uses a protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries. (29 CFR 1910.136(a)
-
180. Hand Protection<br><br>The company must select and require employees to use appropriate hand protection when employees' hands are exposed to hazards. (29 CFR 1910.138)
-
Respiratory Protection
-
181. Respirators must be provided when such equipment is necessary to protect employee health. (29 CFR 1910.134(a)(2))
-
182. If respirators are required by the company, a written respiratory protection program must be developed and implemented. f29CFR1910.134(c)(l)).
-
183. The respiratory protection program must be administered by a qualified individual. (29 CFR 1910.134(c)(3))
-
184. Respirators, training and medical evaluations must be provided at no cost to the employee. (29 CFR 1910.134(c)(4))
-
185. Respirator selection must be based on an evaluation of respiratory hazard(s) in the ready mixed concrete facility and identification of the relevant ready mixed concrete facility and user factors. (29CFR1910.134(d)(l))
-
186. Minimum requirements for medical evaluation must be implemented to determine the employee's ability to use a respirator. (29 CFR 1910.134(e)(l) - (2)
-
187. The follow-up medical examination must be given under specific circumstances and must include any medical tests, consultations, or diagnostic procedures that the PLHCP deems necessary. (29 CFR 1910.134(e)(3)
-
188. The medical questionnaire must be administered confidentially. (29CFR1910.134(e)(4)
-
189. Supplemental information must be provided to the PLHCP before the PLHCP makes a recommendation concerning an employee's ability to use a respirator. (29 CFR 1910.134(e)(5))
-
190. The company must determine the employee's ability to use a respirator. (29 CFR 1910.134(e)(6))
-
191. Before an employee may be required to use any respirator with a negative or positive pressure tight-fitting facepiece, the employee must be fit tested with the same make, model, style, and size of respirator that will be used. (29 CFR 1910.134(f)(l)-(7))
-
192. Procedures must be established and implemented to prevent facepiece seal leakage. (29 CFR 1910.134(g)(l))
-
193. Accommodations must be provided for the cleaning and disinfecting of respirators used by employees. (29 CFR 1910.134(h)(l)
-
194. Accommodations must be provided for the storage of respirators used by employees. (29 CFR 1910.1 34(h)(2))
-
195. Accommodations must be provided for inspections of respirators used by employees. (29 CFR 1910.134(h)(3))
-
196. Filters and cartridges must be identified with the appropriate NIOSH approval label. (29 CFR 1910.134(j))
-
197. Effective training must be provided to employees who are required to use respirators. (29 CFR 1910.134(k))
-
198. The respirator training program must test the employee's knowledge of proper respirator fit, usage and maintenance (29 CFR 1910.134(k)(l) and (k)(4))
-
199. The employer must provide the training that is understandable to the employee prior to requiring the employee to use a respirator in the ready mixed concrete facility. (29 CFR 1910.134(k)(2)-(3))
-
200. Retraining must be administered annually. (29 CFR 1910.134(k)(5)
Compressed Gasses
-
Are compressed gasses used and/or stored at the plant facility?
-
This section covers the compressed gas storage at the facility. Applicable CFR sections include:
• 29 CFR 1910.101 Compressed Gasses - General Requirements
• 29 CFR 1910.102 Acetylene
Items to look for include:
• Training records
• Gas Cart
• PPE in use
• Verify by walking around -
201. Valve protection and outlet caps must be used properly. (29CFR1910.101(b)
-
202. Warning signs must be posted in the compressed gas storage area. (29 CFR 191 0.101 (b)
-
203. Compressed gas cylinders must be stored by hazard class. (29CFR1910.101(b)
-
204. Flammable gases must be protected from sources of ignition. (29CFR1910.101(b)
-
205. Gas cylinders must be properly secured and stored. (29 CFR 1910.101(b)
-
206. Gas apparatus for withdrawing contents from containers must be properly connected and used. (29 CFR 1910.101(b)
Flammable and Combustible Liquids
-
This section covers the flammable and combustible storage at the facility. Applicable CFR sections
include:
• 29 CFR 1910.106 Flammable and Combustible Liquids
Items to look for include:
• Training records
• Self closing flammables storage
• Ask "how are flammables and combustibles stored?"
• Verify by walking around -
208. Proper fire control equipment must be provided in areas where flammable and combustible liquids are handled. (29 CFR 1910.106(d)(7)(i)-(m))
-
209. Sources of ignition must be controlled in areas where flammable and combustible liquids are handled. (29 CFR 1910.106(b)(6))
-
210. Repairs conducted in areas where flammable and combustible liquids are stored must follow proper hot work procedures. (29CFR1910.106(e)(8))
-
211. Adequate housekeeping and access must be maintained. (29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(i) and (ii))
-
212. Waste materials and residues must be stored and removed appropriately. (29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(iii))
-
213. Requirements must be met for separation and protection of flammable and combustible liquids in incidental storage (29 CFR 1910.106(eX2)(iii))
-
214. Flammable and combustible liquids in incidental storage must be handled properly at point of use. (29 CFR 1910.106(e)(2)(iv))
HOUSEKEEPING CHECKLIST
-
General plant property should be generally clean and free of debris.
-
Parking areas are clean and free of debris.
-
Walkways and paths are clean and free of debris.
-
Landscaping should be regularly maintained.
-
If installed, video surveillance system should be functioning properly.
-
Exterior building, property, and security lighting should be properly functioning.
-
Interior lighting should be functioning properly.
-
Entry/Exit points should be clear of any debris.
-
Customer Service and Contractor Supply display areas are clean, tidy, and presentable.
-
Security fencing is maintained.
-
Exterior waste bins are in satisfactory condition.
-
Interior waste bins are in satisfactory condition.
-
Company Logo should be in satisfactory condition.
-
Tobacco and Vape Free sign should be posted in plain view and legible.
-
No Trespassing sign should be posted in plain view and legible.
-
Weapon Free sign should be posted in plain view and legible.
-
Video Surveillance sign should be posted in plain view and legible.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Additional Comments and Observations
-
Additional comments and observations
AUDIT SIGN OFF
-
DATE & TIME
-
Auditor Name and Signature