Information
-
Facility
-
Add media
-
District
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Report Issued To:
Employer's Obligations and Rights
-
The Occupational Safety and Health Act requires employers to comply with hazard-specific safety and health standards. In addition, employers must provide their employees with a workplace free from recognized hazards likely to cause death or serious physical harm under Section 5(a)(1), the General Duty Clause of the Act.
The employer must correct imminent danger situations immediately or remove employees from the danger area. The employer must correct all hazards in accordance with correction due dates and provide documentation of the action taken to eliminate or control the hazards.
The recommended abatement action and interim protection recommendations in this report are intended as advisory in nature, informational in content, and are intended to assist employers in identifying potential engineering controls, administrative controls, work practice controls and personnel protective equipment to reduce employee exposure to the hazard. It is the employer's responsibility to evaluate the work place and the controls necessary for their particular operation in order to reduce employee exposure.
Deficiency Abatement Requirements
-
Once a deficiency has been identified, the senior management official for the facility must ensure that corrective action is completed in a timely manner. Operating plans and budgets must include funds for proper resources to correct safety and health deficiencies according to a priority based upon the degree of the hazard.
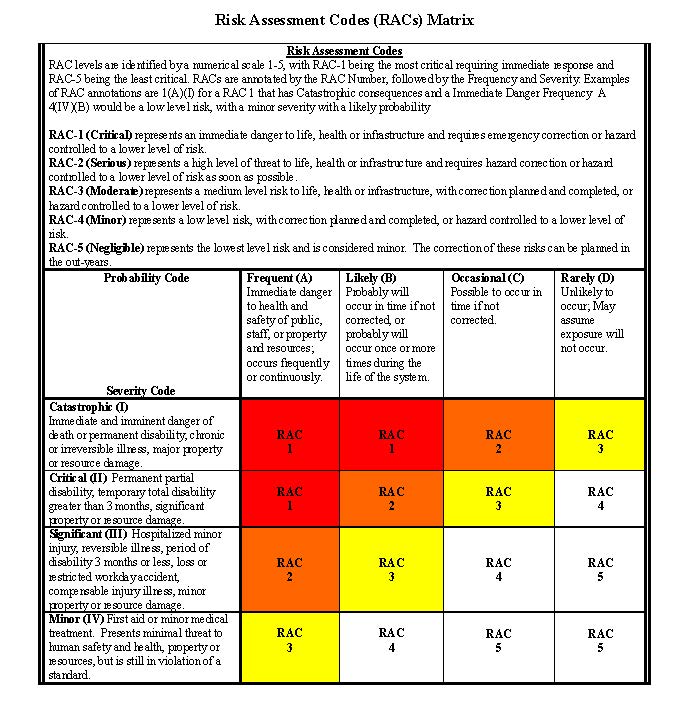
The degree of hazard for each physical deficiency is determined by using the risk assessment code matrix to compare the probability of an accident occurring with the severity if it does occur. The degree of hazard is assigned a risk assessment code based on the hazard classification section of this report.
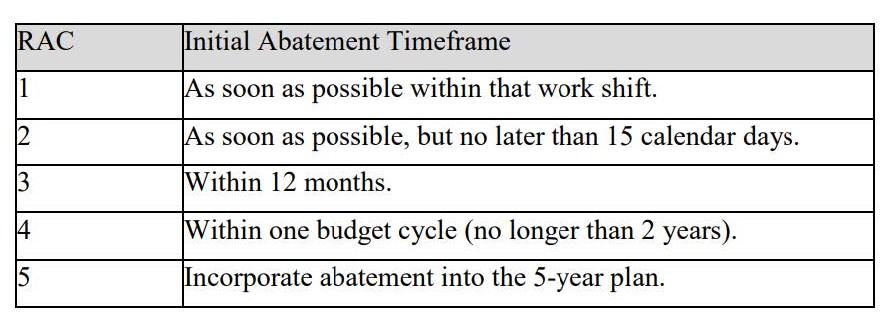
Abatement timeframes for all identified hazards are outlined in the figure below. If the hazard cannot be abated within 30 days, a written abatement plan must be submitted to the safety officer who conducted the inspection. The abatement plan must include any interim actions taken to reduce the hazard until it can be fully corrected. Abatement plans must be submitted using BLM Form 1112-8, “Hazard Abatement Plan.”
Interim Protection for Employees
-
Where a serious hazard(s) is identified and is not immediately corrected in the presence of NIFC EHS, the employer must provide interim protections for affected employees at the worksite while the identified hazard(s) are being corrected. Interim protections include but are not limited to the following:
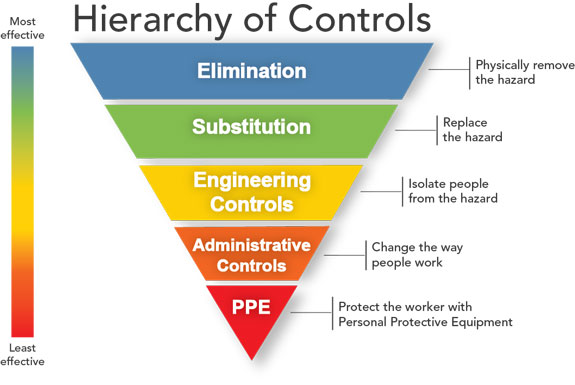
Engineering Controls: Engineering controls consist of, but not limited to, substitution, isolation, ventilation and equipment modification.
Administrative Controls: Any procedure that significantly limits daily exposure by control or manipulation of the work schedule or manner in which work is performed is considered a means of administrative control. The use of personal protective equipment is not considered a means of administrative control.
Work Practice Controls: Work practice controls are one type of administrative control in which the employer modifies the manner in which the employee performs assigned work. Such modification may result in a reduction of exposure through such methods as changing work procedures, improving sanitation and hygiene practices, or making other changes in the way the employee performs the job.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and/or Clothing: Providing the proper personal protective equipment (PPE) to all affected employees and training affected employees in the proper selection, use and maintenance of the PPE.
Hazard Correction/Extension
-
If you are unable to correct the hazard(s) by the date specified, you may request an extension. An extension request must be in writing and include the following requirements for each item:
1. The reason for requesting the extension,
2. Actions taken to correct the hazard,
3. Interim steps to safeguard employees against the hazard during the correction period,
4. The amount of time needed to correct the item.
The enclosed report presents recommendations for correcting identified hazards and for preventing their recurrence. If you have any questions regarding the hazards identified or methods of abatement, feel free to contact NIFC EHS.
1. Hazard Classification
-
A hazard class rating will be assigned by the inspector in accordance with H-1112-1. Hazards found during an inspection shall be classified so that managers can allocate the appropriate time and resources for abatement/mitigation. These hazards should be addressed in order of priority, based on the degree of risk posed by the hazard. Hazards shall be classified as: Critical (imminent danger), Serious, Moderate, Minor, and Negligible - based on the following criteria:
1) Critical Risk (RAC 1). Represents an immediate danger of death or permanent disability, system loss, or major property damage.
Requires state director or associate state director approval.
2) Serious Risk (RAC 2). Represents a high level of threat of permanent partial disability, temporary total disability in excess of 3 months, major system damage, or significant property damage. Requires district manager or equivalent approval.
3) Moderate Risk (RAC 3). Represents a moderate level of risk of minor injury, lost workday accident, compensable injury/illness,
minor system damage, or minor property damage. Requires field office manager or equivalent approval.
4) Minor Risk (RAC 4). Represents a low level of risk of the need for first aid, minor medical treatment, or minor system repair. Requires branch chief or equivalent approval 5) Negligible Risk (RAC 5). While there remains a risk of injury or property damage, it is unlikely to occur. Requires line supervisor
approval.
Imminent danger is defined as a situation posing the threat of immediate death or serious physical injury. Imminent danger situations discovered during any safety and health inspection must be brought immediately to the attention of supervisory personnel. Affected work must be stopped by local management personnel or by the inspector. Personnel not required for abating the hazard must be evacuated from the affected area. Immediate abatement actions must be initiated, or the operation must be terminated
2. POSTINGS
-
Is the Summary of Occupational Illnesses and Injuries posted February thru April? 29 CFR 1904.35
-
Is the required OSHA workplace poster displayed in a prominent location where all employees are likely to see it? OSH Act 1970
-
Are emergency telephone numbers posted where they can be readily found in case of emergency? 29 CFR 1910.38
3. WALKING-WORKING SURFACES
-
Are all area's kept organized and clean? Is good housekeeping maintained? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are walking surfaces kept dry or appropriate means taken to ensure that surfaces are slip-resistant? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are non-slip materials available in areas with wet surfaces? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are materials or equipment stored so sharp objects can not obstruct the walkway? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are signs posted, when appropriate, showing elevated floor load capacity? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Where stairs or stairways exit directly into any area where vehicles may be operated, are adequate barriers and warnings provided to prevent employees from stepping into the path of traffic? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(c)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are openings or holes in the floors or other treading surfaces repaired or otherwise made safe? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are changes of direction or elevations readily identifiable? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are walking-working surfaces inspected regularly and maintained in a safe condition? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.22(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all ladders inspected for defects before use each day and after any occurrence that could damage the ladder? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.23(b)(9)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do portable ladders have a visible label affixed so that the user can determine the manufacturers load rated capacity prior to use? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.23(c)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
When portable rung ladders are used to access elevated surfaces, does the ladder always extend at least 3 feet above that surface? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.23(c)(11)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are mobile ladder stands and platforms capable of supporting at least four times their maximum intended load? Does the mobile ladder stand or platform have a visible label affixed so that the user can determine the manufacturers load rated capacity prior to use? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.23(e)(1)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do stairs angle no more than 50 degrees and no less than 30 degrees? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.25(c)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all stairways at least 22 inches wide? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.25(c)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are guards used where openings 4 feet or greater in floors, porches, abrupt edges of loading docks, etc. present? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are standard guardrails, safety net system or personal fall protection systems provided wherever walking-working surfaces are elevated more than 4 feet above a lower level? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are standard stair rails and handrails present on all stairways having four or more risers? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(11)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are stairway handrails located between 30-38 inches above the leading edge of stair treads? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.29(f)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do stairway handrails have at least 2.25 inches clearance between handrails and the wall or surface they are mounted on? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.29(f)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are stairway handrails capable of withstanding a load of 200 pounds applied in any direction? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.29(f)(7)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are toe boards (minimum 3.5 inches) installed around the edges of a permanent floor opening (where persons may pass below the opening)? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.29(k)(1)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees who use personal fall protection systems receiving fall hazard training? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.30(a)(1) and 29 CFR 1910.132(f)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees who use ladders trained on ladder inspection? Are employees inspecting ladders prior to use? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.30(b)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
4. EXIT DOORS AND ROUTES
-
Is a permanent means of access/egress provided to elevated work surfaces? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.36(a)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are there sufficient exit routes to permit prompt escape in case of emergency? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.36(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit doors able to open from the direction of exit travel without the use of a key or any special knowledge or effort? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.36(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit doors free from any device or alarm that would restrict emergency use if the alarm or device fails? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.36(d)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit doors side-hinged? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.36(e)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit accesses at least 28 inches in width? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.36(g)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are flammable and combustible items stored under stairs? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.37(a)(1), 29 CFR 1910.37)a)(4) and NFPA 101 (2018) para 7.1.3.2.3
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit routes free of obstructions? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.37(a)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit routes adequately lighted? Are exit lights functioning and tested monthly? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are the directions to exits, if not immediately apparent, marked with visible signs? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are doors, passageways, or stairways that are neither exits nor access to exits, and which could be mistaken for exits, appropriately marked “NOT AN EXIT,” or “TO BASEMENT,” “STOREROOM,” etc.? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exit signs provided with the word “EXIT” in lettering at least 6 inches high and the stroke of the lettering at least 3⁄4-inch wide? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(7)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is an evacuation plan prepared for the site? Is an appropriately detailed scale plan of the site posted in conspicuous location(s) at the site? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.38(c)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees trained on the occupant emergency guide and facility specific evacuation? Is training documented? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.38(e)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is a fire prevention plan prepared for the site? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.39(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all personnel familiar with the plan, and are fire drills conducted at least once per year? Ref: NFPA 101 (2018) para 4.7
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
5. OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL
-
Is dust permitted to accumulate on the floor or on ledged outside of an abrasive-blasting enclosure? Cleaned up promptly? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.94(a)(7)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees receiving baseline and then annual audiometric testing? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.95(g)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees trained annually on the NIFC campus hearing conservation program? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.95(k)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
undefined
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
6. HAZARDOUS MATERIALS
-
Is gasoline kept in Safety Cans? Plastic cans are not allowed for any amount over 1 gallon unless you are with the fire crews. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(2)(iii)(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are flammable storage cabinets securely closed with a 3 point locking mechanism? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(3)(ii)(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are liquid petroleum gas (LPG) cylinders re-certified at the 12 year mark from date of manufacture and every 7 years thereafter? Are LPG cylinders free from corrosion? Ref: 49 CFR 180.209(e)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all flammable liquids kept in closed containers when not in use? 29 CFR 1910.106(d)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all flammable and combustible liquids stored in labeled, approved containers, tanks, or drums? 29 CFR 1910.1200(f)(5) 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are flammable and combustible liquids stored in approved cabinets or storage buildings? 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are bulk drums of flammable liquids grounded and bonded to containers during dispensing? 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(6)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are covered metal waste cans used for oily and paint-soaked waste? 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is combustible scrap, debris, and waste stored safely and removed from the worksite promptly? 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9) (iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are storage cabinets labeled “Flammable- Keep Fire Away”? H&SC 61.51d.4.a
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are “NO SMOKING” signs posted in areas where flammable or combustible materials are used/or stored? H&SC 39.64
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are “NO SMOKING” signs posted on liquefied petroleum gas tanks? Everyday HazMat Training Guide pg. 89 NFPA 58 5.2.8.1(A)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are liquefied petroleum storage tanks guarded to prevent damage from vehicles? 29 CFR 1910.110(d)(10)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are grates or similar covers over floor openings, such as floor drains, of such design that the grate spacing will not catch foot traffic or rolling equipment? 29 CFR 1910.123(a)(9)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
7. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
-
Is personal protective equipment maintained in a sanitary condition to prevent injury or impairment of the body through absorption, inhalation or physical contact? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.132(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Has the employer identified and maintain written certification of all required workplace personal protective equipment? Is the identification and certification documented on a Risk Management Worksheet (BLM Form 1112-5)? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.132(d)(2) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 19
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees trained on the use, wear, limitations, care, maintenance and life of all required personal protective equipment? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.132(f)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees provided Appendix D of the standard? Is a signed copy of the Appendix D kept by the supervisor as documentation? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.134(c)(2) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 22
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees receiving training on disposable respirator use? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.134(k)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are voluntary use N95 respirators properly disposed of after use? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.134(k)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are hard hats/helmets/head protection taken out of service when damaged or 10 years from date of manufacture? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.135(b)(1), ANSI Z89.1 and NFPA 1977
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees wearing protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries due to falling or rolling objects, or objects piercing the sole, or when the use of protective footwear will protect the affected employee from an electrical hazard? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.136(a)091
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees inspecting personal fall protection systems prior to use during each workshift? Are damaged personal fall protection systems removed from service? Are all personal fall protection system components inspected per manufacturer requirements and those inspections documented on inspection tags? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.140(c)(18) and manufacturers instructions.
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is a rescue plan in place so that an employee is promptly rescued should a fall occur? Are employees trained on the rescue plan and fall suspension trauma? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.140(c)(21)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
8. ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROLS
-
Are enclosed workplaces constructed, equipped, and maintained, so far as reasonably practicable, as to prevent the entrance or harbor age of rodents, insects, and other vermin? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.141(a)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is all water provided for drinking, washing, and cooking potable? Include copies of latest required water test(s). Ref: 29 CFR 1910.141(b)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are toilets and washing facilities sanitary? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.141(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees allowed to eat and drink in areas where they would be exposed to a toxic material? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.141(g)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are hazardous materials prohibited from being stored in refrigerators used for storing food? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.141(g)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are safety instruction signs in place where there is a need for general instructions and suggestions relative to safety measures? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.145(c)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the work area’s ventilation system appropriate for the work being performed? H&SC 39.74a.1
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
9. CONFINED SPACE
-
Has the employer evaluated the workplace to determine if any spaces are permit-required confined spaces. Do you have an inventory list of all of your permit and non-permit spaces? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.146(c)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Has a written confined space program been established where applicable? and training. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.146(c)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees receiving confined space training where applicable? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.146(g)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Have you posted danger signs or by any other equally effective means, of the existence and location of and the danger posed by the permit spaces. 29 CFR 1910.146(c)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
In the last year have you had to reclassify a non-permit space to a permit required space, due to changes in the use or configuration that might increase the hazards to entrants? 29 CFR 1910.146(c)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
10. LOCKOUT/TAGOUT PROCEDURES
-
Has a hazardous energy control (lockout/tagout) program been established where applicable? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(1), BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 13 and the NIFC campus Lockout/Tagout program
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Have energy control procedures been developed, documented and utilized for the control of hazardous energy? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(4)(i) and 29 CFR 1910.147 Appendix A
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Has appropriate training been provided to authorized, affected and "other" employees? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(7)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are lockout devices used only for lockout/tagout purposes when servicing or maintenance is being conducted? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is all machinery or equipment (capable of movement) required to be de-energized or disengaged and locked out during cleaning, servicing, adjusting, or setting-up operations? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(1) 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(2)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Does the lockout/tagout procedure require stored energy (i.e., mechanical, hydraulic, air) be released or blocked before equipment is locked out for repairs? 29 CFR 1910.147(d)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are appropriate employees provided with protective materials and hardware for control of hazardous energy? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are lockout and tagout devices identifiable to the employee applying them? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(ii)(D)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do tagout devices include a legend warning against hazardous conditions if the equipment is energized? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees required to check the safety of the lockout by attempting to start up after making sure no one is exposed? 29 CFR 1910.147(d)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do tagout devices include a legend warning against hazardous conditions if the equipment is energized? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees required to check the safety of the lockout by attempting to start up after making sure no one is exposed? 29 CFR 1910.147(d)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
11. MEDICAL AND FIRST AID
-
Are eye wash stations provided (15 min./ min flow) in areas where caustics (battery charging or corrosive liquids) are used? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.151(c)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are eye wash stations provided and inspected as required per manufacturer instructions? Fluid expired? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.151(c) and ANSI Z358.1
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are first aid kits maintained in the work area? Are items single use only? Are items expired? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.151(b), 29 CFR 1910.151 Appendix A and ANSI Z308.1
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
12. FIRE PROTECTION
-
Are portable fire extinguishers located, mounted, and readily accessible to employees at each work location? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.157(c)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are fire extinguishers mounted 4 inches minimum off the ground maximum of 5 feet from the top of extinguisher weighing less then 40 lbs. and 3.5 feet from the top of extinguisher weighing more then 40 lbs. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.157(c)(1) and NFPA 10
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are portable fire extinguishers visually inspected monthly? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.157(e)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees who are expected to use portable fire extinguisher trained? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.157(g)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the minimum vertical clearance between fire suppression sprinkler systems and material below 18 inches or greater? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.159(c)(10)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are fire extinguishers provided for the type of materials they will extinguish, and placed in areas where they are to be used? CLASS A: Ordinary combustible materials fires; CLASS B: Flammable liquid, gas, or grease fires; CLASS C: Energized-electrical equipment fires. 29 CFR 1910.157(d)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are fire extinguishers mounted so that employees do not have to travel more than 75 feet for a Class A fire or 50 feet for a Class B fire? 29 CFR 1910.157(d)(2) 29 CFR 1910.157(d)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all fire extinguishers serviced, maintained, and tagged at intervals not to exceed one year? 29 CFR 1910.157(e)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
13. COMPRESSORS AND COMPRESSED AIR
-
Are drain valves opened frequently to prevent the accumulation of liquid in the tank? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are compressors equipped with pressure- relief valves and pressure gauges? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are safety devices on compressed-air systems checked frequently? Are records of tank draining's and safety valve checks maintained? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(3)(iv)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the belt drive system totally enclosed to provide protection on the front, back, top, and sides? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.219(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all compressor tanks in compliance with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standard, conform to state laws, and be inspected monthly for leaks and signs of corrosion on surfaces. Clean or replace air filters, replace worn parts, and remove corrosion, as needed. Maintain a service log. Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 42
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are abrasive wheels kept free from oil and properly dressed? H&SC 43.72.10
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are compressor air intakes installed and equipped to ensure that only clean, uncontaminated air enters the compressor? 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are supply lines, hoses, and connections inspected regularly? H&SC 43.31
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are high pressure hoses and connections in good repair? H&SC 43.31
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are compressors operated and lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations? H&SC 43.21
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are signs posted to warn of the automatic starting feature of the compressors? H&SC 43.21
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is it strictly prohibited to direct compressed air toward a person? H&SC 43.31
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees prohibited from using compressed air at over 29 PSI for cleaning purposes unless they use an approved nozzle with pressure relief and chip guard? H&SC 43.31
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
14. MATERIALS HANDLING
-
Are aisles and passageways kept clear and in good repair? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.176(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are aisles or walkways that pass near moving or operating machinery, welding operations, or similar operations arranged so employees will not be subjected to hazards? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.176(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are material storage racks/shelves secured in place and structurally sound? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.176(b), OSH Act of 1970 Section 5(a)(1), ANSI MH16.1: 2012 Section 1.4.7 and manufacturer installation instructions
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are only designated and qualified employees permitted to operate cranes? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.179(b)(8)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are crane frequent and periodic inspection accomplished? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.179(j)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is there safe clearance for walking in aisles where vehicles are operating? 29 CFR 1910.176(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is there safe clearance for equipment through aisles and doorways? Are materials stored so as to allow safe passage of workers? 29 CFR 1910.176(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are materials stored so as to not create hazards to employees? 29 CFR 1910.176(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is material on elevated surfaces piled, stacked, or secured in a manner to prevent it from tipping, falling, collapsing, rolling, or spreading?29 CFR 1910.176(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are load limits conspicuously posted on storage shelves, bins, and racks? H&SC 39.64.3
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are materials stored in a manner to prevent sprain or strain injuries to employees when retrieving them? H&SC 39.64
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are securing chains, ropes, chokers or slings of adequate strength/condition for the job performed? H&SC 39.64.3f
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do your chain, synthetic web, and wire rope slings have permanently affixed ID tags, stating size, grade, rate capacity? 29 CFR 1910.184(e)(1) 29 CFR 1910.184(h)(1) 29 CFR 1910.184(f)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
If hoisting equipment is used for lifting heavy objects, are hoist ratings and conditions appropriate for the task? H&SC 42.1.11
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
15. INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS/FORKLIFTS
-
Modifications and additions which affect capacity and safe operation shall not be performed by the customer or user without manufacturers prior written approval. Capacity, operation, and maintenance instruction plates, tags, or decals shall be changed accordingly. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(a)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
If the truck is equipped with front-end attachments other than factory installed attachments, the user shall request that the truck be marked to identify the attachments and show the approximate weight of the truck and attachment combination at maximum elevation with load laterally centered. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(a)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
The user shall see that all nameplates and markings are in place and are maintained in a legible condition. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(a)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees trained to refuel forklift LP tanks? Is this training documented? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(f)(2) and NFPA 58
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do industrial truck operators meet OSHA's industrial truck operator training requirements? Initial certification and three year refresher training. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(l)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are horns used where vision is obstructed, and backup alarms used when traveling in reverse? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(l)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are persons prohibited from standing or passing under the elevated portion of any truck? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(m)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are unattended industrial trucks shut off, loads lowered, and brakes set? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(m)(5)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are operators prohibited from handling loads exceeding the truck’s rated capacity? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(o)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are industrial trucks taken out of service when found in need of repair, or in any way unsafe? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(p)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are industrial trucks inspected by the operator prior to each shift? Attach copies of latest completed inspection form(s). Ref: 29 CFR 1910.178(q)(7) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 18 Section D(5)(c)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are industrial trucks equipped with a fire extinguisher? Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 18 Section D(5)(c)(12)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
16. MACHINE GUARDING
-
Are employees trained on the use of machinery and the requirements for machine guarding? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.212(a), 29 CFR 1910.242(a) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 42
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is one or more methods of guarding provided to protect the operator and other employees from hazards created by point of operation, ingoing nip points, rotating parts, flying chips and sparks? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are portable fans provided with full guards having openings of 1/2-inch or less? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are machine guards affixed to machines to protect the operator? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is equipment and machinery securely placed and anchored when necessary to prevent tipping or other movement that could result in personal injury? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.212(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is all machinery and equipment clean and properly maintained? H&SC 43.12 H&SC 43.51.19
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is sufficient clearance provided around machines for safe operations, set up and servicing, material handling, and waste removal? 29 CFR 1910.213(s)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is there a power shut-off switch within reach of the operator’s position at each machine? 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are foot-operated switches guarded to prevent accidental actuation by personnel or falling objects? 29 CFR 1910.218(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are foot-operated switches guarded to prevent accidental actuation by personnel or falling objects? 29 CFR 1910.218(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are operating controls clearly identified and readily accessible? 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all belts, pulleys, gears, shafts, and moving parts properly guarded? Are guards and safety devices functional, adjusted, and in place? 29 CFR 1910.213(a) (9) 29 CFR 1910.219(d) 29 CFR 1910.219(e)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are provisions made to prevent machines from automatically starting when power is restored (following a power failure or shut- down)? 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are saws used for ripping equipped with anti-kickback devices and spreaders? 29 CFR 1910.213(c)(2) 29 CFR 1910.213(c)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are effective guards in place over belts, pulleys, chains, and sprockets on equipment such as concrete mixers, air compressors, and the like? 29 CFR 1910.219(d) 29 CFR 1910.219(e)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are radial arm saws guarded and so arranged that the cutting head will gently return to the back of the table when released? 29 CFR 1910.213(h)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
17. ABRASIVE WHEEL EQUIPMENT/GRINDERS
-
Are machines designed for a fixed location permanently mounted? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.212(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the work rest used and kept adjusted to within 1/8-inch of the wheel? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.215(a)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the adjustable tongue on the top side of grinder used and kept adjusted to w/i 1/4- inch of the wheel? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.215(b)(9)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do side guards cover the spindle end, nut, flange projections, and 75 percent of the abrasive wheel diameter? 29 CFR 1910.215(a)(2) 29 CFR 1910.215(b)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is eye and hearing protection always worn when grinding? H&SC 43.71 H&SC 43.72.8
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the maximum RPM rating of each abrasive wheel compatible with the RPM rating of the grinder motor? 29 CFR 1910.
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Before mounting new abrasive wheels, are they visually inspected and ring tested? 29 CFR 1910.215(d)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are abrasive wheels kept free from oil and properly dressed? H&SC 43.72.10
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
18. HAND TOOLS AND EQUIPMENT
-
Are all tools and equipment present on site in good working condition? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.242(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are pneumatic and hydraulic hoses on power-operated tools checked regularly for deterioration or damage? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.242(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all air hoses and connectors used for conducting compressed air designed for the pressure and service they are subjected? Are air hose crimps in use, no worm drive water hose clamps in use? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.243(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all jacks legibly and permanently marked with their rated load? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.244(a)(1)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are jacks inspected periodically to assure that they are in good operating condition? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.244(a)(2)(vi)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are only employees who have been trained in the operation of powder-actuated tools allowed to use them? Do employees who operate powder-actuated tools have a qualified operator's card/license? Ref: 29 CFR 1926.302(e)(1) and ANSI A10.3
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are hand tools such as chisels or punches (that develop mushroomed heads) reconditioned or replaced as necessary? 29 CFR 1910.242(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are broken or fractured handles on hammers, pulaskis, etc. replaced promptly? 29 CFR 1910.242(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are tool handles wedged tightly in the head of all tools? 29 CFR 1910.242(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all cord-connected, electrically- operated tools and equipment effectively grounded or of the approved double- insulated type? 29 CFR 1910.243(a)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are rotating or moving parts of equipment such as sanders guarded at nip points to prevent physical contact? 29 CFR 1910.243(a)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are grinders, saws, and similar equipment provided with appropriate safety guards? 29 CFR 1910.243
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are portable circular saws equipped with guards above and below the base shoe? 29 CFR 1910.243(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are power tools used with the shield or guard recommended by the manufacturer? 29 CFR 1910.243(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are tool-cutting edges kept sharp? H&SC 41.13.2
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
19. CHAINSAWS
-
Are employees trained prior to operating chainsaws? Training course S-212 or equivalent. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.266(i)(1) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 42
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees who operate chainsaws trained and current in first-aid and CPR? Is employee training current? Ref: 29CFR 1910.266(i)(7)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
20. WELDING, CUTTING AND BRAZING
-
Are special precautions to include welding permits in place when objects to be welded cannot be relocated at least 35 ft. away from fire hazards/combustibles? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(1)(ii) and 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all employees who cut and weld suitably trained in the safe operation of their equipment and the safe use of the process? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(xiii)[C] and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 42
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are hoses and hose connections free from damaged and stored so that they are not subjected to damage? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.253(e)(5)(v)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are welding lead terminals protected by covers? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.254(b)(4)(iv)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are welding cables/leads free from splices within 10 feet of the holder/clamp? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.254(d)(8)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are cylinders with water-weight capacity over 30 pounds equipped (with means for connecting a valve protector or device, or with a collar or recess) to protect the valve? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(1)(iv)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are cylinders legibly marked to clearly identify the gas contained? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)1)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are compressed-gas cylinders stored in an area, protected from external heat sources (flames, intense radiant heat, electric arcs or high-temperature lines)? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are cylinders located or stored in well- ventilated dry areas where they will not be damaged by passing or falling objects, struck by vehicles, or be subject to tampering by unauthorized persons? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are fuel-gas and oxygen cylinders securely separated by a minimum 20-foot distance, fire-resistant barriers, or other means when stored? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are cylinders stored or transported in a manner to prevent them from creating a hazard by tipping, falling, or rolling? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(iii)(B)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are valve protectors always placed on cylinders when they are not in use or connected for use? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2) (iv)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all valves closed off before a cylinder is moved/ empty/ at the completion of each job? 29 CFR 1910.101(a)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are low-pressure fuel-gas cylinders checked periodically for corrosion, general distortion, cracks, or any other defect that might indicate a weakness or render them unfit for service? H&SC 61.62
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Readily ignitable material such as weeds and long dry grass shall be removed within 10 feet of any container. 29 CFR 1910.110(b)(6)(vi)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Containers shall be protected by crash rails or guards to prevent physical damage unless they are so protected by virtue of their location. 29 CFR 1910.110(h)(6)(ii)(b)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Piping from tank to building needs to be metal. NFPA 58 6.9.3 and 6.9.4 29 CFR 1910.110(13)(ii)(b)(5) 29 CFR1910.110(h)(9)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
21. ELECTRICAL SAFETY
-
Is electrical equipment free from recognized hazards? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are power strips and extension cords daisy chained together? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are flat 2 or 3 wire extension cords in use? Are household use extension cords used in the workplace? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the space in front of circuit breaker panels, electrical service panels and disconnects used for storage or blocked? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.303(g)(1)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do all 125-volt, single-phase, 15- and 20-ampere receptacles installed in bathrooms or on rooftops have ground-fault circuit-interrupter protection for personnel? Ref: 1910.304(b)(3)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are high amperage electrical items plugged directly into a wall electrical outlet so that the amperage rating on the outlet device is not exceeded? Examples: Microwaves, coffee pots, kettles, refrigerators and space heaters. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.304(b)(4)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is temporary lighting protected by a fixture or guard to prevent bulb breakage? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.305(a)(2)(ix)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are electrical enclosures such as switches, receptacles, and junction boxes provided with undamaged, tight-fitting covers, or plates, including plugged unused opening (knockouts)? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.305(b)(1) and 29 CFR 1910.305(b)(2)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are extension cords used as fixed wiring of a structure? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.305(g)(1)(iv)(A)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are electrical cords free of splices or taps? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.305(g)(2)(ii) and 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(2)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all lights located within 8 feet of the floor, or exposed to being struck or damaged, protected? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.305(j)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are outdoor electrical outlets in wet locations protected by a weatherproof cover? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.305(j)(2)(v)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are unqualified employees trained in and familiar with electrically related safety practices? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.332(b)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are qualified employees trained on electrical installation safety-related work practices? Receiving professional level refresher training every 2 years? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.332(b)(3) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 3
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is portable electric equipment equipped with a flexible cord free from visual external defects? Missing prongs, damage to insulation etc. Ref: 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(2)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do you require all electrical work to be performed by a licensed contractor in compliance with NEC and OSHA rules? 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all disconnecting switches and circuit breakers each labeled to indicate their use or equipment served? 29 CFR 1910.303(f)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do circuit breakers clearly indicate whether they are in the “on” or “off” position? 29 CFR 1910.304(e)(1)(vi)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are electrical appliances such as vacuum cleaners, portable heaters, and vending machines grounded? 29 CFR 1910.304(f)(5)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are exposed wiring and cords with frayed or deteriorated insulation repaired or replaced promptly? 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(2) (I) 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do all extension cords have a grounding conductor? 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(3)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are multiple plug adaptors prohibited? 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(3)(ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are electrical outlets prohibited above permanently installed electric heaters? NEC 424.9
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are extension cords protected from abrasion, crushing, kinking, and pulling? H&SC 36.13.6
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
22. TOXIC AND HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES
-
Has the employer conducted lead exposure monitoring to determine if any employee may be exposed at or above the action level? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.1025(d)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees trained to observe bloodborne pathogens universal precautions? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.1030(d)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees who have an occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens receiving initial and annual refresher training? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.1030(g)(2) and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 24
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the possible presence of asbestos determined prior to the beginning of any repair, demolition, construction, or reconstruction work? 29 CFR 1910.1001(j)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees warned of the presence and hazards of asbestos-containing materials where required? 29 CFR 1910.1001(j)(2)(iii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
23. HAZCOM PROGRAM
-
Is each container for a hazardous substance (vats, bottles, storage tanks) labeled with product identity and a hazard warning that communicates specific health and physical hazards? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.1200(f)(6)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Does the employer maintain a Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for all hazardous chemicals used in the workplace? Are all SDS's populated in the NIFC eBinder? Are SDS's printed and maintained at remote locations that do not have web or cell service access? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.1200(g)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees trained on the NIFC campus hazard communication program? Is this training supplemented with work area specific hazard communication information and training? Ref: 29 CFR 1910.1200(h)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees made aware of hazards involved with the various chemicals they may be exposed to in their work environment, such as ammonia, chlorine, epoxies, and caustics? (Right-to-know) 29 CFR 1910.1200(e) 29 CFR 1910.1200(h)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is there a "Written hazard communication program." that describes labels and other forms of warning, safety data sheets, and employee information and training that will be met? 29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(1)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do you have an inventory list of the chemicals in the work area? 29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(1)(i)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Have employees been informed of the chemicals in their work areas and all non routine tasks? 29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(1) (ii)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do you have a method of informing contractors/contract employees of the chemical hazards in the their work area? 29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(2)
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Do you have a current Hazardous Material Spill Response Plan, as part of a comprehensive Emergency Action Plan, to manage spills in the office and field? FSM 2100, Ch. 2160
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are employees prohibited from handling hazardous chemicals that do not have an SDS? Are SDS’s readily available to employees at all times? H&SC 61.14.2
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
24. PLUMBING, HEATING, VENTILATION, AND AIR CONDITIONING
-
Does your HVAC system provide at least the quantity of outdoor air designed into the system at the time the building was constructed? H&SC 37.12
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is preventive maintenance performed as recommended by the manufacturer, and records kept with the equipment? H&SC 37.12.3
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are chimneys, flues, and masonry inspected at least annually? H&SC 34.33
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are air filters inspected monthly and changed as needed, or as recommended by the manufacturer? H&SC 37.12.7
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are indoor air quality complaints investigated with results effectively communicated to employees? MLA, Article 27.6
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are pipelines transporting hazardous substances through above-ground piping identified? H&SC 38.12b
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are gas appliances accessible for inspection and service? UPC 511.0 H&SC 39.9
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are temperature/pressure relief valves and drains installed on all water heaters? UPC 608.3 and 608.5 H&SC 39.9
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are water heaters anchored or strapped (within upper one-third of tank) for seismic protection? UPC 510.5 H&SC 39.9
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are gas water heaters and connectors protected from physical damage (e.g., in garages)? UPC 510.3 H&SC 39.9
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are gas system shutoffs identified, and readily accessible? UPC 1211.4 and 1211.18 H&SC 37.12.6
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are gas appliances accessible for inspection and service? UPC 511.0 H&SC 39.9
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are water system shutoffs identified, accessible and operable? Local Regulation
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
25. VEHICLE, TRAILER and OFF-HIGHWAY VEHICLES
-
Are vehicle/trailer inspections accomplished prior to use and monthly? Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 15 and 18
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are vehicle operators prohibited from using cell phones, GPS and other electronic devices while vehicle is in motion? Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 15
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Have employees completed Defensive Driving training, initial assignment and every 3 years there after? Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 15
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is the BLM form 1112-11 Vehicle Operator Authorization on file for all employees who operate vehicles? Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 15
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Have employees completed Off-Highway ATV/UTV training, initial assignment and every 3 years there after. Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 17
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all government- owned or -leased vehicles equipped with fire extinguishers that are properly maintained and inspected? Ref: DOI Occupational Safety and Health Program - Field Manual
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
26. HEAVY EQUIPMENT
-
Is a qualified heavy equipment trainer/tester formally designated in writing via a position description or memorandum? Ref: BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 18
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Has a Risk Management Worksheet been completed for heavy equipment operations? Ref: DOI Occupational Safety and Health Program - Field Manual
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are all heavy equipment operators trained prior to operating heavy equipment? Is this training documented? Ref: DOI Occupational Safety and Health Program - Field Manual and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 18
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Does heavy equipment operator training include comprehension of the operator's manual, written test and skills test? Ref: DOI Occupational Safety and Health Program - Field Manual and BLM H-1112-1 Chapter 18
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Is all heavy equipment equipped with an operational backup alarm? Ref: DOI Occupational Safety and Health Program - Field Manual
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
Are operators conducting a complete safety walk-around of the equipment prior to mounting, starting or operating heavy equipment? Ref: DOI Occupational Safety and Health Program - Field Manual
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
27. BEST PRACTICE
-
Lightning Safety
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
28. MISCELLANEOUS
-
undefined
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
undefined
- Critical RAC 1
- Serious RAC 2
- Moderate RAC 3
- Minor RAC 4
- Negligible RAC 5
- N/A
-
INSPECTION CONDUCTED BY