Title Page
-
Site conducted
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
Untitled Page
-
-
Office Ergonomics Data Collection and Assessment
-
Client Name & Epic Code
-
Client Contact name and contact info
-
Employee Name & contact info
-
Target Employee direct supervisor & contact info
-
Is an employee under the care of a medical professional? Do they want a copy of report
-
Contact details: Note: If under the care of a medical professional, inquire whether an ergonomic assessment has been ordered by the medical professional. Also, inquire as to whether an ergonomic assessment is being offered by the medical professional. If a diagnosis has been provided, ask the employee if they are willing to share as the diagnosis is relevant to recommendations that are offered and any further treatment for improvement, such as stretching exercises. Finally, share our report with the account contact, not directly with the employee
-
Is this an injury claim – Type – WC, non-work related
-
Injury description
-
Symptoms & complaint summary
-
What symptoms & where
-
When are symptoms noticed
-
Is medical provider involved
-
RTW, Modified duty, ADA, other
-
This evaluation is being provided to offer recommendations for “best practice” recommendations for proper computer workstation set-up and design. It is universally recognized that minimizing postural stresses while working at office computer workstations can help prevent work related injuries and avoid or reduce symptoms of discomfort. Should you experience any new or increases in symptoms subsequent to any modifications or changes to your workstation following this evaluation, please report immediately to your direct supervisor. You should also return to the workstation design that minimizes those symptoms
-
Read disclaimer and have employee sign
-
Data Intake
-
Is this a telephonic assessment, a zoom assessment or an in-person assessment? (Instruction If telephonic, or zoom, have employee provide photos prior to the assessment. Also, if zoom, screen shot photos can be taken). Take pictures of the employee from side, behind, hands on keyboard, hand on pointing device, phone and any other significant tasks
-
Describe typical work tasks (i.e., data entry, word processing, “hunt and peck”, etc
-
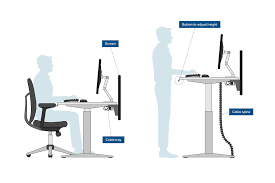
Is this a standing workstation, a sit and stand workstation or is it a standard desk? How much time per day on tasks how long before breaks/change in posture
-
Typing
-
Sitting
-
Standing
-
Pen & paper
-
Number and length of breaks per day
-
Current seat pan height
-
Are hip joints and knee joints aligned horizontally
-
Is pressure on back of thigh even or more at knee or buttocks
-
Is seat pan horizontal, tilted backwards or forwards
-
Torso
-
Are hip joint, shoulder and ear in vertical alignment… describe discrepancies
-
Leaning forward or backward
-
Is there a normal/neutral lumbar curve
-
Increased/decreased lordosis Slight – Minimal – moderate - severe
-
Slight – Minimal – moderate severe
-
Rotation
-
Is there normal/neutral l thoracic curve
-
Increased/decreased kyphosis Slight – Minimal – moderate - severe
-
Slight – Minimal – moderate severe
-
Rotation
-
Is there normal/neutral cervical curve
-
Increased/decreased cervical curve
-
Slight – Minimal – moderate severe
-
Forward head posture
-
Head tilt front back, side to side
-
Arm postures & movement patterns
-
Are shoulders in alignment with spine, hunched forward or arched back
-
Are shoulders as low as possible, (i.e., “hanging on ligaments”) or elevated up toward ears
-
Are elbows below shoulders or forward (flexion) of torso
-
Degrees of shoulder angle with hands at keyboard
-
At pointing device
-
Are elbows out to the side (abduction)
-
Degree of shoulder flexion at keyboard
-
At pointing device
-
Degree of elbow flexion
-
At keyboard
-
At pointing device
-
Hand wrist posture
-
Keyboard Palms flat, rotated outwards (thumbs toward ceiling)
-
degrees
-
Pointing device Palm flat, rotated outwards (thumb toward ceiling)
-
Keyboard Hands tilted inwards (radial deviation)
-
outwards (Ulnar deviation)
-
Pointing device Hand tilted inwards (radial deviation)
-
outwards (Ulnar deviation)
-
Keyboard Are hands in line with forearms bent downward (flexion)
-
degrees
-
degrees upward extension
-
degrees
-
Pointing device Are hands in line with forearms bent downward (flexion)
-
degrees upward (extension
-
Are hands in natural “curl” or stretched flat
-
Describe any frequent/awkward movements
-
Shoulders
-
Movement Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction
-
degrees
-
hours/day
-
times/hour for
-
Activity performed
-
Hands/wrists
-
Movement – flexion, extension, radial deviation, ulnar deviation, rotation (in/out)
-
degrees
-
times/hour for
-
hours/day
-
Activity performed
-
Head/neck
-
Movement – flexion, extension, rotation, side tilt
-
degrees
-
times/hour for
-
hours/day
-
Activity performed
-
Torso
-
Movement– flexion, extension, rotation, side tilt
-
degrees
-
times/hour for
-
hours/day
-
Activity performed
-
Work Pace and duration
-
How fast is work/typing pace – fast, average, slow, intermittent, constant
-
How frequent are breaks/changes of posture
-
Get up from desk
-
Walk around
-
Stretches
-
Hours/day
-
, days/wk
-
Workstation Measurements
-
standing desk top height (if applicable) Keyboard thickness
-
Desktop height
-
sitting desk top height
-
Front/back angle
-
Adjustability of keyboard tray HT
-
degrees
-
length
-
height
-
is there a mouse tray on keyboard Y/N, HT
-
Pointing device type
-
, width
-
from seat pan
-
, Seat pan angle y/n, lumbar support Y/N, backrest height Y/N, Arm rests height
-
Chair adjustability – Height
-
Top of monitor height from desk top
-
, Depth from front of desk
-
, Number of monitors
-
Number keypad placement
-
Is the monitor free of lighting glare Y/N. Is there sufficient lighting
-
depth from front of desk
-
Desktop reach envelope width
-
Workstation Modifications
-
Turn the worker away from the work desk to make all appropriate seat adjustments (note: have the employee mirror me as I discuss the proper ergonomic sitting, or standing, position. I then discuss the proper heights for the keyboard/mouse, chair and monitors and make adjustments for the employee while doing so
-
Adjust the seat pan of the chair to keep the knee joint slightly below the hip joint with feet firmly on the floor or on a footrest (slightly open hip joint angle). There should be even pressure on the upper leg from the knee to the hip
-
Measurement of top of seat pan to floor
-
Keep the low back curve supported by adjusting the backrest of the chair or using a lumbar support pad (i.e., rolled-up towel). The pelvis should not be angled toward the back of the chair (but slightly forward). The low back curve should match the position that is used when standing with good neutral posture
-
Encourage the worker to sit erect (vertically) with the hip joint, shoulder and ears in approximately a straight line
-
Take Picture
-
Note degrees from vertical
-
Encourage the worker to relax and lower the shoulders as much as possible. You may need to lower or remove the arm rests
-
Distance of bottom elbow to floor
-
Turn the worker back toward the computer and work desk
-
Place the keyboard just slightly below the elbow (~110 – 120-degree elbow angle). The keyboard should be angled to elicit a straight wrist posture
-
Keyboard angle from horizontal (I.e., tilted forward or backward)
-
Distance of top of keyboard to floor
-
The keyboard should be close enough to the torso to allow the elbows to be at the sides or just in front of the torso (not held out to the front) with shoulders depressed
-
Take picture
-
Shoulder angle from vertical
-
Notice the inward angle of the forearm (horizontal) (>45 degrees)
-
Take picture
-
Forearm angle from 90 degrees from straight ahead
-
If the angle is severe consider using a curved keyboard to limit wrist deviation
-
Keep the mouse close to the keyboard and on the same horizontal plane (i.e., on the keyboard tray). Consider using a mouse bridge (placed over the number pad) for workers with narrow shoulder span to help avoid external shoulder rotation and excessive reaching
-
distance from center of keyboard
-
Recommended pointing device
-
Height from floor
-
Use a paper document with the same size font as the VDT screen to identify the optimal distance from the eyes for the individual’s visual acuity and monitor distance placement (usually 18” – 24”)
-
Distance from eyes
-
Keep the monitor at a height to allow the worker to maintain a level head position (typically top of screen at eye height). Please remember that workers using bifocals may be looking at the screen with a different viewing angle. For workers using the bottom part of a bifocal lens the monitor should be slightly lower to help maintain a level had position. The head/neck posture should match Neutral posture for the individual being evaluated
-
Top of monitor height from desk top
-
Take picture
-
Keep any documents used at an angle facing the worker and not flat on the table
-
Recommended “originals” placement location
-
Take picture while using / reading this document
-
Recommendation - Get up every 20 minutes
-
Recommendation - Stretch regularly
-
Recommendation – drink water routinely, stay hydrated
-
NOTE: Reference the attached links and resources for further information on wellness techniques
-
Follow-up in 2 weeks