Information
-
Audit Title
-
Client / Site
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Personnel
1.0 Employer Posting
-
Is employer posting going to be inspected?
-
1.1 Is the required OSHA Job Safety and Health Protection Poster displayed in a prominent location where all employees are likely to see it?
-
GPO 1952.10(a)(1) “Labor posters must be posted in common area where they are easily visible to all employees.”
-
1.2 Are signs concerning exit routes, room capacities, floor loading, biohazards, exposures to x-ray, microwave, or other harmful radiation or substances posted where appropriate?<br>
-
1.3 Is the Summary of Work-Related Injuries and Illnesses (OSHA Form 300A) posted during the months of February, March and April?<br>
-
The OSHA 300 log is part of a federal requirement concerning safety in the workplace. It is a form that must be filled out by employers and displayed in a visible area. The log records all applicable injuries or illnesses that occur in the workplace. It must be posted every year between February 1 and April 30.
-
Additional Notes:
2.0 Recordkeeping
-
Is employer recordkeeping going to be inspected?
-
2.1 Are occupational injuries or illnesses, except minor injuries requiring only first aid, recorded as required on the OSHA 300 log?<br>
-
The OSHA Form 300 is a form for employers to record all reportable injuries and illnesses that occur in the workplace, where and when they occur, the nature of the case, the name and job title of the employee injured or made sick, and the number of days away from work or on restricted or light duty, if any.
Employers must record all new cases of work-related fatalities, injuries, and illnesses if
they involve:
death,
days away from work,
restricted work or transfer to another job,
medical treatment beyond first aid,
loss of consciousness, or
a significant injury or illness diagnosed by a physician or other licensed health care professional.
Each recordable injury or illness case must be recorded on the OSHA 300 Log and the Form 301 Incident Report within seven calendar days after the employer receives notice that the injury or illness occurred. -
2.2 Are employee medical records and records of employee exposure to hazardous substances or harmful physical agents up-to-date and in compliance with current OSHA standards?<br>
-
1910.1020(e)(2)(ii)(A) "Each employer shall, upon request, assure the access of each employee to employee medical records of which the employee is the subject, except as provided in paragraph (e)(2)(ii)(D) of this section."
1910.1020(e)(2)(i)(A) "Except as limited by paragraph (f) of this section, each employer shall, upon request, assure the access to each employee and designated representative to employee exposure records relevant to the employee. For the purpose of this section, an exposure record relevant to the employee consists of:" 1910.1020(e)(2)(i)(A)(1) "A record which measures or monitors the amount of a toxic substance or harmful physical agent to which the employee is or has been exposed." -
2.3 Are employee training records kept and accessible for review by employees, as required by OSHA standards?<br>
-
2.4 Are operating permits and records up-to-date for items such as elevators, air pressure tanks, liquefied petroleum gas tanks, etc.?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
3.0 Safety and Health Program
-
Is the company safety and health program going to be inspected?
-
3.1 Does the company have an active safety and health program in operation that includes general safety and health program elements as well as the management of hazards specific to your work-site?
-
3.2 Is one person clearly responsible for the safety and health program?
-
3.3 Does the company have a safety committee or group made up of management and labor representatives that meets regularly and reports in writing on its activities?
-
3.4 Does the company have a working procedure to handle in-house employee complaints regarding safety and health?<br>
-
3.5 Are the employees advised of efforts and accomplishments of the safety and health program made to ensure they will have a workplace that is safe and healthful?
-
3.6 Are employees instructed in proper first aid and other emergency procedures?
-
3.7 Are employees instructed in the proper manner for lifting heavy objects?
-
3.8 Are universal precautions observed where occupational exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials can occur and in all instances where differentiation of types of body fluids or potentially infectious materials is difficult or impossible?
-
3.9 Where heat is a problem, are all employees trained and protected against heat related illnesses?
-
Additional Notes:
4.0 First Aid
-
Is the company first aid going to be inspected?
-
4.1 Have all employees who are expected to respond to medical emergencies as part of their job responsibilities received first aid training; had hepatitis B vaccination made available to them; had appropriate training on procedures to protect them from bloodborne pathogens, including universal precautions; and have available and understand how to use appropriate PPE to protect against exposure to bloodborne diseases?<br>
-
1910.151(b) "In the absence of an infirmary, clinic, or hospital in near proximity to the workplace which is used for the treatment of all injured employees, a person or persons shall be adequately trained to render first aid. Adequate first aid supplies shall be readily available."
-
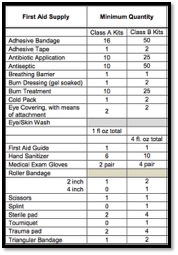
4.2 Are fully supplied first aid kits easily accessible to each work area, periodically inspected and replenished as needed?<br>
-
OSHA requires a minimum amount of first aid items. On an annual basis, or as needed, check the quantity and expiration of your first aid items on hand – Section 1910.151(a): “The employer shall ensure the ready availability of medical personnel for advice and consultation on matters of plant health." ANSI Z308.1-1998 – Minimum requirements for workplace first aid kits).
-
-
4.3 Is there an eye-wash station or sink available for quick drenching or flushing of the eyes and body in areas where corrosive liquids or materials are handled?<br><br>
-
1910.151(c) "Where the eyes or body of any person may be exposed to injurious corrosive materials, suitable facilities for quick drenching or flushing of the eyes and body shall be provided within the work area for immediate emergency use."
-
4.4 Are employees instructed in proper first aid and other emergency procedures?
-
4.5 Are universal precautions observed where occupational exposure to blood or other potentially infectious materials can occur and in all instances where differentiation of types of body fluids or potentially infectious materials is difficult or impossible?
-
Additional Notes:
5.0 Fire Protection
-
Is the company fire protection going to be inspected?
-
5.1 Are portable fire extinguishers provided in adequate number and type and mounted in readily accessible locations?<br>
-
1910.157(c)(1) “The employer shall provide portable fire extinguishers and shall mount, locate and identify them so that they are readily accessible to employees without subjecting the employees to possible injury.”
-
5.2 Are fire extinguishers inspected monthly and recharged annually with this noted on the inspection tag?<br>
-
1910.157(c)(4) “The employer shall assure that portable fire extinguishers are maintained in a fully charged and operable condition and kept in their designated places at all times except during use.”
-
5.3 Are employees periodically instructed in the use of fire extinguishers and fire protection procedures?<br>
-
5.4 Are doors unobstructed and protected against obstructions?<br>
-
1910.37(a)(3) “Exit routes must be free and unobstructed. No materials or equipment may be placed, either permanently or temporarily, within the exit route. The exit access must not go through a room that can be locked, such as a bathroom, to reach an exit or exit discharge, nor may it lead into a dead-end corridor. Stairs or a ramp must be provided where the exit route is not substantially level."
-
5.5 If the company has a fire alarm system, is it certified as required and tested annually?<br>
-
5.6 If there are interior standpipes and valves, are they protected and inspected regularly?<br>
-
1910.158(b) “The employer shall assure that standpipes are located or otherwise protected against mechanical damage. Damaged standpipes shall be repaired promptly.”
1910.159(c)(2) "The employer shall properly maintain an automatic sprinkler system installed to comply with this section. The employer shall assure that a main drain flow test is performed on each system annually. The inspector's test valve shall be opened at least every two years to assure that the sprinkler system operates properly." -
5.7 Are automatic sprinkler system water control valves, air and water pressure checked periodically as required?<br>
-
5.8 Is the maintenance of automatic sprinkler systems assigned to responsible persons or to a sprinkler contractor?<br>
-
5.11 Is proper clearance maintained below sprinkler heads?<br>
-
1910.159(c)(10) "The employer shall assure that sprinklers are spaced to provide a maximum protection area per sprinkler, a minimum of interference to the discharge pattern by building or structural members or building contents and suitable sensitivity to possible fire hazards. The minimum vertical clearance between sprinklers and material below shall be 18 inches (45.7 cm)."
-
Additional Notes:
6.0 Personal Protective Equipment
-
Is PPE going to be inspected?
-
6.1 Has the employer determined whether hazards that require the use of PPE (e.g., head, eye, face, hand, or foot protection) are present or are likely to be present?<br><br>
-
1910.132(d)(1) "The employer shall assess the workplace to determine if hazards are present, or are likely to be present, which necessitate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). If such hazards are present, or likely to be present, the employer shall:" 1910.132(d)(1)(i) "Select, and have each affected employee use, the types of PPE that will protect the affected employee from the hazards identified in the hazard assessment;" 1910.132(d)(1)(ii) "Communicate selection decisions to each affected employee; and," 1910.132(d)(1)(iii) "Select PPE that properly fits each affected employee."
-
6.2 If hazards or the likelihood of hazards are found, are employers selecting appropriate and properly fitted PPE suitable for protection from these hazards and ensuring that affected employees use it?<br><br>
-
1910.132(a) "Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, shall be provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition wherever it is necessary by reason of hazards of processes or environment, chemical hazards, radiological hazards, or mechanical irritants encountered in a manner capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through absorption, inhalation or physical contact."
-
6.3 Have both the employer and the employees been trained on PPE procedures, i.e., what PPE is necessary for job tasks, when workers need it, and how to properly wear and adjust it?<br><br>
-
1910.132(f)(1) "The employer shall provide training to each employee who is required by this section to use PPE. Each such employee shall be trained to know at least the following:" 1910.132(f)(1)(i) "When PPE is necessary;" 1910.132(f)(1)(ii) "What PPE is necessary;" 1910.132(f)(1)(iii) "How to properly don, doff, adjust, and wear PPE;" 1910.132(f)(1)(iv) "The limitations of the PPE; and," 1910.132(f)(1)(v) "The proper care, maintenance, useful life and disposal of the PPE."
-
6.4 Are approved safety glasses or face shields required to be worn at all times in areas where there is a risk of eye injuries such as punctures, abrasions, contusions, or burns?<br><br>
-
1910.133(a)(1) "The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses appropriate eye or face protection when exposed to eye or face hazards from flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation."
-
6.5 Are protective gloves, aprons, shields, or other means provided and required where employees could be cut or where there is reasonably anticipated exposure to corrosive liquids, chemicals, blood, or other potentially infectious materials? See the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens standard, 29 CFR 1910.1030(b), for the definition of "other potentially infectious materials."<br><br>
-
1910.138(a) "Employers shall select and require employees to use appropriate hand protection when employees' hands are exposed to hazards such as those from skin absorption of harmful substances; severe cuts or lacerations; severe abrasions; punctures; chemical burns; thermal burns; and harmful temperature extremes."
-
6.6 Are hard hats required, provided and worn where danger of falling objects exists?<br><br>
-
6.7 Is appropriate foot protection required where there is the risk of foot injuries from hot, corrosive, or poisonous substances, falling objects, crushing, or penetrating actions?<br><br>
-
1910.136(a) "The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries due to falling or rolling objects, or objects piercing the sole, or when the use of protective footwear will protect the affected employee from an electrical hazard, such as a static-discharge or electric-shock hazard, that remains after the employer takes other necessary protective measures."
-
6.8 Are approved respirators provided when needed?
-
1910.134(a)(2) "A respirator shall be provided to each employee when such equipment is necessary to protect the health of such employee. The employer shall provide the respirators which are applicable and suitable for the purpose intended. The employer shall be responsible for the establishment and maintenance of a respiratory protection program, which shall include the requirements outlined in paragraph (c) of this section. The program shall cover each employee required by this section to use a respirator."
-
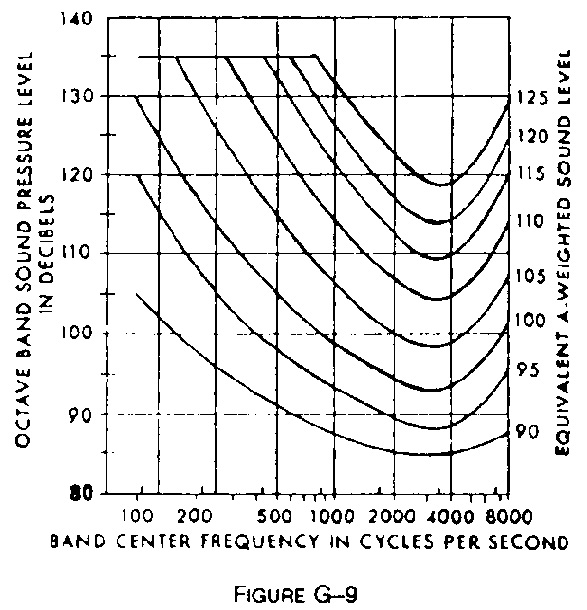
6.9 Is protection against the effects of occupational noise provided when sound levels exceed those of the OSHA Noise standard?<br><br>
-
1910.95(a) "Protection against the effects of noise exposure shall be provided when the sound levels exceed those shown in Table G-16 when measured on the A scale of a standard sound level meter at slow response." -
When noise levels are determined by octave band analysis, the equivalent A-weighted sound level may be determined as follows:
-
6.10 Is all PPE regularly inspected and maintained in a sanitary condition and ready for use?<br><br>
-
1910.132(a) "Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, shall be provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition wherever it is necessary by reason of hazards of processes or environment, chemical hazards, radiological hazards, or mechanical irritants encountered in a manner capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through absorption, inhalation or physical contact."
-
Additional Notes:
7.0 General Work Environment and Housekeeping
-
Is the company general work environment and housekeeping going to be inspected?
-
7.1 Are all work areas clean, sanitary and orderly?<br>
-
1910.141(a)(3)(i) "All places of employment shall be kept clean to the extent that the nature of the work allows."
-
7.2 Are walking and working surfaces kept clear and free of trip and fall hazards?<br>
-
1910.22(a)(1) “All places of employment, passageways, storerooms, service rooms, and walking-working surfaces are kept in a clean, orderly, and sanitary condition.”
1910.22(a)(3) "Walking-working surfaces are maintained free of hazards such as sharp or protruding objects, loose boards, corrosion, leaks, spills, snow, and ice."
1910.22(d)(1) “Walking-working surfaces are inspected, regularly and as necessary, and maintained in a safe condition.” -
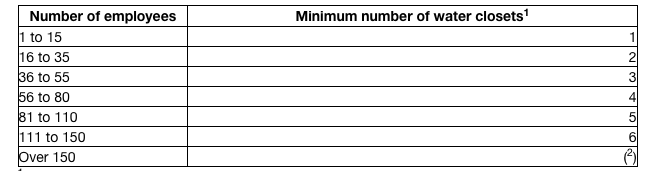
7.3 Are the minimum number of toilets and washing facilities provided and maintained in a clean and sanitary fashion?<br>
-
1910.141(c)(1)(i) "Except as otherwise indicated in this paragraph (c)(1)(i), toilet facilities, in toilet rooms separate for each sex, shall be provided in all places of employment in accordance with table J-1 of this section. The number of facilities to be provided for each sex shall be based on the number of employees of that sex for whom the facilities are furnished. Where toilet rooms will be occupied by no more than one person at a time, can be locked from the inside, and contain at least one water closet, separate toilet rooms for each sex need not be provided. Where such single-occupancy rooms have more than one toilet facility, only one such facility in each toilet room shall be counted for the purpose of table J-1."
-
Where toilet facilities will not be used by women, urinals may be provided instead of water closets, except that the number of water closets in such cases shall not be reduced to less than 2/3 of the minimum specified.
1 additional fixture for each additional 40 employees. -
7.4 Are all work areas adequately illuminated?<br>
-
1915.82(a)(1) “The employer shall ensure that each work area and walkway is adequately lighted whenever an employee is present.”
-
7.5 Are pits and floor openings covered or otherwise guarded?<br>
-
1910.23(a)(8) "Every floor hole into which persons can accidentally walk shall be guarded by either:" 1910.23(a)(8)(i) "A standard railing with standard toeboard on all exposed sides, or" 1910.23(a)(8)(ii) "A floor hole cover of standard strength and construction. While the cover is not in place, the floor hole shall be constantly attended by someone or shall be protected by a removable standard railing."
-
7.6 Have all confined spaces been evaluated for compliance with 29 CFR 1910.146? (Permit required confined spaces.)<br>
-
1910.146(c)(1) “The employer shall evaluate the workplace to determine if any spaces are permit-required confined spaces.
NOTE: Proper application of the decision flow chart in Appendix A to section 1910.146 would facilitate compliance with this requirement.”
1910.146(c)(2) “If the workplace contains permit spaces, the employer shall inform exposed employees, by posting danger signs or by any other equally effective means, of the existence and location of and the danger posed by the permit spaces.
NOTE: A sign reading DANGER -- PERMIT-REQUIRED CONFINED SPACE, DO NOT ENTER or using other similar language would satisfy the requirement for a sign.”
1910.146(c)(3) “If the employer decides that its employees will not enter permit spaces, the employer shall take effective measures to prevent its employees from entering the permit spaces and shall comply with paragraphs (c)(1), (c)(2), (c)(6), and (c)(8) of this section.”
1910.146(c)(4) “If the employer decides that its employees will enter permit spaces, the employer shall develop and implement a written permit space program that complies with this section. The written program shall be available for inspection by employees and their authorized representatives.” -
10.1 Do standard stair rails or handrails on all stairways have at least four risers?<br>
-
1910.25(b) “The employer must ensure:” 1910.25(b)(1) “Handrails, stair rail systems, and guardrail systems are provided in accordance with § 1910.28;” 1910.25(b)(2) “Vertical clearance above any stair tread to any overhead obstruction is at least 6 feet, 8 inches (203 cm), as measured from the leading edge of the tread. Spiral stairs must meet the vertical clearance requirements in paragraph (d)(3) of this section.” 1910.25(b)(3) “Stairs have uniform riser heights and tread depths between landings;” 1910.25(b)(4) “Stairway landings and platforms are at least the width of the stair and at least 30 inches (76 cm) in depth, as measured in the direction of travel;” 1910.25(b)(5) “When a door or a gate opens directly on a stairway, a platform is provided, and the swing of the door or gate does not reduce the platform's effective usable depth to:” 1910.25(b)(5)(i) “Less than 20 inches (51 cm) for platforms installed before January 17, 2017; and” 1910.25(b)(5)(ii) “Less than 22 inches (56 cm) for platforms installed on or after January 17, 2017 (see Figure D-7 of this section);” 1910.25(b)(6) “Each stair can support at least five times the normal anticipated live load, but never less than a concentrated load of 1,000 pounds (454 kg) applied at any point;” 1910.25(b)(7) “Standard stairs are used to provide access from one walking-working surface to another when operations necessitate regular and routine travel between levels, including access to operating platforms for equipment. Winding stairways may be used on tanks and similar round structures when the diameter of the tank or structure is at least 5 feet (1.5 m).”
-
7.8 Is material on elevated surfaces piled, stacked, or racked in a manner to prevent it from tipping, falling, collapsing, rolling, or spreading?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
8.0 Egress
-
Are egresses going to be inspected?
-
8.1 Are all exits kept free of obstructions?<br>
-
1910.37(a)(3) “Exit routes must be free and unobstructed. No materials or equipment may be placed, either permanently or temporarily, within the exit route. The exit access must not go through a room that can be locked, such as a bathroom, to reach an exit or exit discharge, nor may it lead into a dead-end corridor. Stairs or a ramp must be provided where the exit route is not substantially level."
-
8.2 Are all exits marked with an exit sign and illuminated by a reliable light source or meets OSHA requirements?<br>
-
1910.37(b)(2) “Each exit must be clearly visible and marked by a sign reading "Exit."
1910.37(b)(6) "Each exit sign must be illuminated to a surface value of at least five foot-candles (54 lux) by a reliable light source and be distinctive in color. Self-luminous or electroluminescent signs that have a minimum luminance surface value of at least .06 footlamberts (0.21 cd/m2) are permitted."
1910.37(b)(7) "Each exit sign must have the word "Exit" in plainly legible letters not less than six inches (15.2 cm) high, with the principal strokes of the letters in the word "Exit" not less than three-fourths of an inch (1.9 cm) wide."
1910.37(a)(3) "Exit routes must be free and unobstructed. No materials or equipment may be placed, either permanently or temporarily, within the exit route. The exit access must not go through a room that can be locked, such as a bathroom, to reach an exit or exit discharge, nor may it lead into a dead-end corridor. Stairs or a ramp must be provided where the exit route is not substantially level." -
8.3 Are the directions to exits, when not immediately apparent, marked with visible signs?<br>
-
8.4 Are doors, passageways or stairways that are neither exits nor access to exits, but could be mistaken for exits, appropriately marked "NOT AN EXIT," "TO BASEMENT," "STOREROOM," etc.?<br>
-
8.5 Are there sufficient exits to permit prompt escape in case of emergency?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
9.0 Portable Ladders
-
Are company portable ladders to be inspected?
-
9.1 Are all ladders maintained in good condition, joints between steps and side rails tight, all hardware and fittings securely attached, and moveable parts operating freely without binding or undue play?<br>
-
1926.1053(b)(15) "Ladders shall be inspected by a competent person for visible defects on a periodic basis and after any occurrence that could affect their safe use."
-
9.2 Are employees required to properly use ladders and practice ladder safety?<br>
-
From OSHA: "Always maintain a 3-point (two hands and a foot, or two feet and a hand) contact on the ladder when climbing. Keep your body near the middle of the step and always face the ladder while climbing. "
-
9.3 Are ladders stored in a safe manner?<br>
-
1926.1053(b)(8) "Ladders placed in any location where they can be displaced by workplace activities or traffic, such as in passageways, doorways, or driveways, shall be secured to prevent accidental displacement, or a barricade shall be used to keep the activities or traffic away from the ladder."
-
9.4 Are portable ladders labeled with load rating, and are metal ladders legibly marked with signs reading "CAUTION - Do Not Use Around Electrical Equipment" or equivalent wording?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
10.0 Hand Tools
-
Are hand tools going to be inspected?
-
10.1 Are all tools and equipment (both company and employee-owned) used at the workplace in good condition?<br>
-
From OSHA:
"Five basic safety rules can help prevent hazards associated with the use of hand and power tools:
Keep all tools in good condition with regular maintenance.
Use the right tool for the job.
Examine each tool for damage before use and do not use damaged tools.
Operate tools according to the manufacturers' instructions.
Provide and use properly the right personal protectiv equipment." -
10.2 Are all cord-connected, electrically operated tools and equipment effectively grounded or of the approved double insulated type?<br>
-
1910.334(a)(3)(i) "A flexible cord used with grounding type equipment shall contain an equipment grounding conductor."
-
10.3 Are power tools used with proper shields, guards, or attachments, as recommended by the manufacturer?<br>
-
1926.302(e)(11) "All tools shall be used with the correct shield, guard, or attachment recommended by the manufacturer."
-
10.4 Are effective guards in place over belts, pulleys, chains and sprockets on equipment such as concrete mixers, air compressors, etc.?<br>
-
1926.302(e)(11) "All tools shall be used with the correct shield, guard, or attachment recommended by the manufacturer."
-
10.5 Are pneumatic and hydraulic hoses on powder-operated tools checked regularly for deterioration or damage?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
11.0 Grinders
-
Are grinders going to be inspected?
-
11.1 Is the grinder guarded and used according to OSHA standards?<br>
-
1910.215(a)(1) "Abrasive wheels shall be used only on machines provided with safety guards as defined in the following paragraphs of this section."
1910.215(a)(2) "The safety guard shall cover the spindle end, nut, and flange projections. The safety guard shall be mounted so as to maintain proper alignment with the wheel, and the strength of the fastenings shall exceed the strength of the guard, except:" 1910.215(a)(2)(i) "Safety guards on all operations where the work provides a suitable measure of protection to the operator, may be so constructed that the spindle end, nut, and outer flange are exposed; and where the nature of the work is such as to entirely cover the side of the wheel, the side covers of the guard may be omitted; and" 1910.215(a)(2)(ii) "The spindle end, nut, and outer flange may be exposed on machines designed as portable saws." -
11.2 Are bench and pedestal grinders permanently mounted?<br>
-
11.3 Is each electrically operated grinder effectively grounded?<br>
-
1910.334(a)(3)(i) "A flexible cord used with grounding type equipment shall contain an equipment grounding conductor."
-
Additional Notes:
12.0 Machine Guarding
-
Is machine guarding going to be inspected?
-
12.1 Are machine guards secure and arranged so they do not cause a hazard while in use?<br>
-
1910.212(a)(1) "One or more methods of machine guarding shall be provided to protect the operator and other employees in the machine area from hazards such as those created by point of operation, ingoing nip points, rotating parts, flying chips and sparks. Examples of guarding methods are-barrier guards, two-hand tripping devices,electronic safety devices, etc."
1910.212(a)(2) "Guards shall be affixed to the machine where possible and secured elsewhere if for any reason attachment to the machine is not possible. The guard shall be such that it does not offer an accident hazard in itself." -
12.2 Is there a training program to instruct employees on safe methods of machine operation?<br>
-
12.3 Is there adequate supervision to ensure that employees are following safe machine operating procedures?<br>
-
12.4 Is there a regular program of safety inspection of machinery and equipment?<br>
-
12.5 Is all machinery and equipment kept clean and properly maintained?<br>
-
12.6 Is sufficient clearance provided around and between machines to allow for safe operations, set up and servicing, material handling and waste removal?<br>
-
12.7 Is equipment and machinery securely placed and anchored to prevent tipping or other movement that could result in personal injury?<br>
-
12.8 Is there a power shut-off switch within reach of the operator's position at each machine?<br>
-
12.9 Can electric power to each machine be locked out for maintenance, repair, or security?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
13.0 Lockout/Tagout Procedures
-
Are the company lockout/tagout procedures going to be inspected?
-
1910.147(c)(1) "Energy control program. The employer shall establish a program consisting of energy control procedures, employee training and periodic inspections to ensure that before any employee performs any servicing or maintenance on a machine or equipment where the unexpected energizing, startup or release of stored energy could occur and cause injury, the machine or equipment shall be isolated from the energy source and rendered inoperative."
-
13.1 Is all machinery or equipment capable of movement required to be de-energized or disengaged and blocked or locked out during cleaning, servicing, adjusting, or setting up operations?<br>
-
13.2 If the power disconnect for equipment does not also disconnect the electrical control circuit, are the appropriate electrical enclosures identified and is a means provided to ensure that the control circuit can also be disconnected and locked out?<br>
-
13.3 Is the locking out of control circuits instead of locking out main power disconnects prohibited?<br>
-
13.4 Are all equipment control valve handles provided with a means for locking out?<br>
-
13.5 Does the lockout procedure require that stored energy (mechanical, hydraulic, air, etc.) be released or blocked before equipment is locked out for repairs?<br>
-
13.6 Are appropriate employees provided with individually keyed personal safety locks?<br>
-
13.7 Are employees required to keep personal control of their key(s) while they have safety locks in use?<br>
-
13.8 Is it required that only the employee exposed to the hazard can place or remove the safety lock?<br>
-
13.9 Is it required that employees check the safety of the lockout by attempting a startup after making sure no one is exposed?<br>
-
13.10 Are employees instructed to always push the control circuit stop button prior to re-energizing the main power switch?<br>
-
13.11 Is there a means provided to identify any or all employees who are working on locked-out equipment by their locks or accompanying tags?<br>
-
13.12 Are a sufficient number of accident prevention signs or tags and safety padlocks provided for any reasonably foreseeable repair emergency?<br>
-
13.13 When machine operations, configuration, or size require an operator to leave the control station and part of the machine could move if accidentally activated, is the part required to be separately locked out or blocked?<br>
-
13.14 If equipment or lines cannot be shut down, locked out and tagged, is a safe job procedure established and rigidly followed?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
14.0 Welding, Cutting, Brazing
-
Are the company welding, cutting, and brazing procedures going to be inspected?
-
1910.252(a)(1) "For elaboration of these basic precautions and of the special precautions of paragraph (d)(2) of this section as well as a delineation of the fire protection and prevention responsibilities of welders and cutters, their supervisors (including outside contractors) and those in management on whose property cutting and welding is to be performed, see, Standard for Fire Prevention in Use of Cutting and Welding Processes, NFPA Standard 51B,1962, which is incorporated by reference as specified in Sec. 1910.6. The basic precautions for fire prevention in welding or cutting work are:"
1910.252(a)(1)(i) "If the object to be welded or cut cannot readily be moved, all movable fire hazards in the vicinity shall be taken to a safe place."
1910.252(a)(1)(ii) "If the object to be welded or cut cannot be moved and if all the fire hazards cannot be removed, then guards shall be used to confine the heat, sparks, and slag, and to protect the immovable fire hazards."
1910.252(a)(1)(iii) "If the requirements stated in paragraphs(a)(1)(i) and (a)(1)(ii) of this section cannot be followed then welding and cutting shall not be performed." -
14.1 Are only authorized and trained personnel permitted to use welding, cutting, or brazing equipment?<br>
-
14.2 Does each operator have a copy of and follow the appropriate operating instructions?<br>
-
14.3 Are compressed gas cylinders regularly examined for obvious signs of defects, deep rusting, or leakage?<br>
-
14.4 Is care used in handling and storage of cylinders, safety valves, relief valves, etc., to prevent damage?<br>
-
14.5 Are precautions taken to prevent the mixture of air or oxygen with flammable gases, except at a burner or in a standard torch?<br>
-
14.6 Are only approved apparatuses (torches, regulators, pressure reducing valves, acetylene generators, manifolds) used?<br>
-
14.7 Are cylinders kept away from sources of heat and elevators, stairs, or gangways?<br>
-
14.8 Is it prohibited to use cylinders as rollers or supports?<br>
-
14.9 Are empty cylinders appropriately marked and their valves closed?<br>
-
14.10 Are signs posted reading "DANGER, NO SMOKING, MATCHES, OR OPEN LIGHTS," or the equivalent?<br>
-
14.11 Are cylinders, cylinder valves, couplings, regulators, hoses and apparatuses kept free of oily or greasy substances?<br>
-
14.12 Is care taken not to drop or strike cylinders?<br>
-
14.13 Are regulators removed and valve-protection caps put in place before moving cylinders, unless they are secured on special trucks?<br>
-
14.14 Do cylinders without fixed wheels have keys, handles, or non-adjustable wrenches on stem valves when in service?<br>
-
14.15 Are liquefied gases stored and shipped valve-end up with valve covers in place?<br>
-
14.16 Are employees trained never to crack a fuel gas cylinder valve near sources of ignition?<br>
-
14.17 Before a regulator is removed, is the valve closed and gas released?<br>
-
14.18 Is red used to identify the acetylene (and other fuel-gas) hose, green for the oxygen hose and black for inert gas and air hoses?<br>
-
14.19 Are pressure-reducing regulators used only for the gas and pressures for which they are intended?<br>
-
14.20 Is open circuit (no-load) voltage of arc welding and cutting machines as low as possible and not in excess of the recommended limits?<br>
-
14.21 Under wet conditions, are automatic controls for reducing no-load voltage used?<br>
-
14.22 Is grounding of the machine frame and safety ground connections of portable machines checked periodically?<br>
-
14.23 Are electrodes removed from the holders when not in use?<br>
-
14.24 Is it required that electric power to the welder be shut off when no one is in attendance?<br>
-
14.25 Is suitable fire extinguishing equipment available for immediate use?<br>
-
14.26 Is the welder forbidden to coil or loop welding electrode cable around his body?<br>
-
14.27 Are wet machines thoroughly dried and tested before use?<br>
-
14.28 Are work and electrode lead cables frequently inspected for wear and damage, and replaced when needed?<br>
-
14.29 Are cable connectors adequately insulated?<br>
-
14.30 When the object to be welded cannot be moved and fire hazards cannot be removed, are shields used to confine heat, sparks and slag?<br>
-
14.31 Are fire watchers assigned when welding or cutting is performed in locations where a serious fire might develop?<br>
-
14.32 Are combustible floors kept wet, covered with damp sand, or protected by fire-resistant shields?<br>
-
14.33 Are personnel protected from possible electrical shock when floors are wet?<br>
-
14.34 Are precautions taken to protect combustibles on the other side of metal walls when welding is underway?<br>
-
14.35 Are used drums, barrels, tanks and other containers thoroughly cleaned of substances that could explode, ignite, or produce toxic vapors before hot work begins?<br>
-
14.36 Do eye protection, helmets, hand shields and goggles meet appropriate standards?<br>
-
14.37 Are employees exposed to the hazards created by welding, cutting, or brazing operations protected with PPE and clothing?<br>
-
14.38 Is a check made for adequate ventilation in and where welding or cutting is performed?<br>
-
14.39 When working in confined places, are environmental monitoring tests done and means provided for quick removal of welders in case of an emergency?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
15.0 Compressed Gas Cylinders
-
Are compressed gas cylinders going to be inspected?
-
15.1 Are cylinders legibly marked to clearly identify the type of gas?<br>
-
1910.253(b)(1)(ii) "Compressed gas cylinders shall be legibly marked, for the purpose of identifying the gas content, with either the chemical or the trade name of the gas. Such marking shall be by means of stenciling, stamping, or labeling, and shall not be readily removable. Whenever practical, the marking shall be located on the shoulder of the cylinder."
-
15.2 Are compressed gas cylinders stored in areas protected from external heat sources such as flame impingement, intense radiant heat, electric arcs, or high-temperature lines?<br>
-
1910.253(b)(2)(i) "Cylinders shall be kept away from radiators and other sources of heat."
-
15.3 Are cylinders located or stored in areas where they will not be damaged by passing or falling objects or subject to tampering by unauthorized persons?<br>
-
1910.253(b)(2)(ii) "Assigned storage spaces shall be located where cylinders will not be knocked over or damaged by passing or falling objects, or subject to tampering by unauthorized persons."
-
15.4 Are cylinders stored or transported in a manner to prevent them from creating a hazard by tipping, falling, or rolling?<br>
-
15.5 Are valve protectors always placed on cylinders when the cylinders are not in use or connected for use?<br>
-
1910.253(b)(2)(iv) "Valve protection caps, where cylinder is designed to accept a cap, shall always be in place, hand-tight, except when cylinders are in use or connected for use."
-
Additional Notes:
16.0 Hoist Equipment
-
Is hoist equipment going to be inspected?
-
16.1 Is the rated load of each hoist legibly marked and visible to the operator?<br>
-
1926.554(a)(1) "The safe working load of the overhead hoist, as determined by the manufacturer, shall be indicated on the hoist, and this safe working load shall not be exceeded."
-
16.2 Is the hoist installed according to manufacturer specifications?<br>
-
1926.554(a)(6) "All overhead hoists in use shall meet the applicable requirements for construction, design, installation, testing, inspection, maintenance, and operation, as prescribed by the manufacturer."
-
16.3 Are the controls of hoists plainly marked to indicate the direction of travel or motion?<br>
-
16.4 Is the hoist regularly inspected?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
17.0 Industrial Trucks-Forklift
-
Are forklifts to be inspected?
-
17.1 Are employees properly trained in the use of the type of industrial truck they operate?<br>
-
From OSHA: "It is a violation of Federal law for anyone UNDER 18 years of age to operate a forklift or for anyone OVER 18 years of age who is not properly trained and certified to do so."
-
17.2 Are only trained personnel allowed to operate industrial trucks?<br>
-
From OSHA: "It is a violation of Federal law for anyone UNDER 18 years of age to operate a forklift or for anyone OVER 18 years of age who is not properly trained and certified to do so."
-
17.3 Are the required lift truck operating rules posted and enforced?<br>
-
17.4 Does each industrial truck have a warning horn, whistle, gong, or other device that can be clearly heard above normal noise in the areas where it is operated?<br>
-
17.5 Are arms and legs kept inside the running lines of the truck?<br>
-
17.6 Are loads handled only within the rated capacity of the truck?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
18.0 Entering Confined Spaces
-
Are the company confined space procedures going to be inspected?
-
18.1 Have all confined spaces been identified and guarded against unauthorized entry?<br>
-
From OSHA: "Many workplaces contain areas that are considered "confined spaces" because while they are not necessarily designed for people, they are large enough for workers to enter and perform certain jobs. A confined space also has limited or restricted means for entry or exit and is not designed for continuous occupancy. Confined spaces include, but are not limited to, tanks, vessels, silos, storage bins, hoppers, vaults, pits, manholes, tunnels, equipment housings, ductwork, pipelines, etc."
-
18.2 Are all confined spaces that are identified as "permit-required" identified and guarded against unauthorized entry?<br>
-
From OSHA: "OSHA uses the term "permit-required confined space" (permit space) to describe a confined space that has one or more of the following characteristics: contains or has the potential to contain a hazardous atmosphere; contains material that has the potential to engulf an entrant; has walls that converge inward or floors that slope downward and taper into a smaller area which could trap or asphyxiate an entrant; or contains any other recognized safety or health hazard, such as unguarded machinery, exposed live wires, or heat stress.
-
18.3 Is either natural or mechanical ventilation provided prior to confined space entry?<br>
-
18.4 Are appropriate atmospheric tests performed to check for oxygen deficiency, toxic substances and explosive concentrations in the confined space before entry?<br>
-
18.5 Is adequate illumination provided for the work to be performed in the confined space?<br>
-
18.6 Is the atmosphere inside the confined space frequently tested or continuously monitored during work?<br>
-
18.7 Is there a trained and equipped standby employee positioned outside the confined space, whose sole responsibility is to watch the work in progress, sound an alarm if necessary and render assistance?<br>
-
18.8 Is the standby employee appropriately trained and equipped to handle an emergency?<br>
-
18.9 Are employees prohibited from entering the confined space without lifelines and respiratory equipment if there is any question as to the cause of an emergency?<br>
-
18.10 Is approved respiratory equipment required if the atmosphere inside the confined space cannot be made acceptable?<br>
-
18.11 Is all portable electrical equipment used inside confined spaces either grounded and insulated or equipped with ground fault protection?<br>
-
Additional Notes:
19.0 Hazard Communication
-
Is the company hazard communication going to be inspected?
-
19.1 Is there a list of hazardous substances used in your workplace and an SDS readily available for each hazardous substance used?<br>
-
1910.1200(b)(4)(ii) "Employers shall maintain copies of any safety data sheets that are received with incoming shipments of the sealed containers of hazardous chemicals, shall obtain a safety data sheet as soon as possible for sealed containers of hazardous chemicals received without a safety data sheet if an employee requests the safety data sheet, and shall ensure that the safety data sheets are readily accessible during each work shift to employees when they are in their work area(s)."
-
19.2 Is there a current written exposure control plan for occupational exposure to bloodborne pathogens and other potentially infectious materials, where applicable?<br>
-
1910.1030(c)(1)(i) "Each employer having an employee(s) with occupational exposure as defined by paragraph (b) of this section shall establish a written Exposure Control Plan designed to eliminate or minimize employee exposure."
-
19.3 Is there a written hazard communication program dealing with SDSs, labeling and employee training?<br>
-
1910.1200(e)(1) "Employers shall develop, implement, and maintain at each workplace, a written hazard communication program which at least describes how the criteria specified in paragraphs (f), (g), and (h) of this section for labels and other forms of warning, safety data sheets, and employee information and training will be met, and which also includes the following:" 1910.1200(e)(1)(i) "A list of the hazardous chemicals known to be present using a product identifier that is referenced on the appropriate safety data sheet (the list may be compiled for the workplace as a whole or for individual work areas); and," 1910.1200(e)(1)(ii) "The methods the employer will use to inform employees of the hazards of non-routine tasks (for example, the cleaning of reactor vessels), and the hazards associated with chemicals contained in unlabeled pipes in their work areas."
-
19.4 Is each container for a hazardous substance (i.e., vats, bottles, storage tanks, etc.) labeled with product identity and a hazard warning (communication of the specific health hazards and physical hazards)?<br>
-
1910.1200(b)(3)(i) "Employers shall ensure that labels on incoming containers of hazardous chemicals are not removed or defaced."
-
19.5 Is there an employee training program for hazardous substances?
-
1910.1200(h)(1) "Employers shall provide employees with effective information and training on hazardous chemicals in their work area at the time of their initial assignment, and whenever a new chemical hazard the employees have not previously been trained about is introduced into their work area. Information and training may be designed to cover categories of hazards (e.g., flammability, carcinogenicity) or specific chemicals. Chemical-specific information must always be available through labels and safety data sheets."
-
19.6 Is there an employee training for bloodborne pathogen safety?
-
1910.1030(g)(2)(i) "The employer shall train each employee with occupational exposure in accordance with the requirements of this section. Such training must be provided at no cost to the employee and during working hours. The employer shall institute a training program and ensure employee participation in the program."
-
Additional Notes:
20.0 Electrical
-
Are the company electrical hazards going to be inspected?
-
20.1 Are portable electrical tools and equipment grounded or of the double insulated type?<br>
-
1910.334(a)(3)(i) "A flexible cord used with grounding type equipment shall contain an equipment grounding conductor."
-
20.2 Are electrical appliances such as vacuum cleaners, polishers, vending machines, etc., grounded?<br>
-
1910.334(a)(3)(i) "A flexible cord used with grounding type equipment shall contain an equipment grounding conductor."
-
20.3 Do extension cords have a grounding conductor?<br>
-
1910.334(a)(3)(i) "A flexible cord used with grounding type equipment shall contain an equipment grounding conductor."
-
20.4 Are extension cords rated for the current in use?
-
NEC 240.5 “Flexible cords and cables must be protected against overcurrent, which contains the following requirements: Overcurrent devices must not be rated higher than the cord’s ampacity, as specified in Table 400.5(A) and Table 400.5(B) [240.5(A)]."
1910.304(f)(1)(i) "Conductors and equipment shall be protected from overcurrent in accordance with their ability to safely conduct current." -
20.5 Are exposed wiring and cords with frayed or deteriorated insulation repaired or replaced promptly?<br>
-
1910.334(a)(2)(ii) "If there is a defect or evidence of damage that might expose an employee to injury, the defective or damaged item shall be removed from service, and no employee may use it until repairs and tests necessary to render the equipment safe have been made." -
20.6 Are flexible cords and cables free of splices or taps?<br>
-
From OSHA: "Two provisions of the standard prohibit the repair of the jacket of a worn or frayed flexible cord with electrical tape. Section 1926.403(a) requires that the cord be approved. The original approval of the cord was based on the types of materials and construction used. As noted above, taping the cord can change the flexibility characteristics of the cord, which in turn can affect the amount of stress in the adjacent areas. This is of particular concern with respect to the grounding wire. Also, the jacket is designed both to prevent damage to the conductors and insulators inside and to further insulate the conductors. Taped repairs usually will not duplicate the cord's original characteristics; in most cases neither the jacket's strength nor flexibility characteristics will be restored. Therefore, tape repairs of the jacket may not be used to bring a worn or frayed flexible cord into compliance.
In addition, Section 1926.405(g)(2)(iii) states that "flexible cords shall be used only in continuous lengths without splice or tap. Hard service flexible cords No. 12 or larger may be repaired if spliced so that the splice retains the insulation, outer sheath properties, and usage characteristics of the cord being spliced." This standard precludes the repair of flexible cords smaller than No. 12." -
20.7 Are flexible cords used in a safe manner (not run through holes, over possible hazards, over sharp objects, used instead of permanent wiring,etc.)?<br>
-
1926.405(g)(1)(iii) "Unless necessary for a use permitted in paragraph (g)(1)(i) of this section, flexible cords and cables shall not be used:" 1926.405(g)(1)(iii)(A) "As a substitute for the fixed wiring of a structure;" 1926.405(g)(1)(iii)(B) "Where run through holes in walls, ceilings, or floors;" 1926.405(g)(1)(iii)(C) "Where run through doorways, windows, or similar openings, except as permitted in paragraph (a)(2)(ii)(1) of this section;" 1926.405(g)(1)(iii)(D) "Where attached to building surfaces; or" 1926.405(g)(1)(iii)(E) "Where concealed behind building walls, ceilings, or floors."
-
20.8 Are multiple plug adaptors rated for the current in use?<br>
-
1910.304(f)(1)(i) "Conductors and equipment shall be protected from overcurrent in accordance with their ability to safely conduct current."
-
20.9 Are ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) installed on receptacles where water may be present?<br>
-
NEC 210.8(A)(6) “Requires GFCI protection for 15A and 20A, 125V receptacles installed to serve dwelling unit kitchen counter surfaces.”
-
20.10 In wet or damp locations, are electrical tools and equipment appropriate for the use or location or otherwise protected?<br>
-
20.11 Is the use of metal ladders prohibited where the ladder or the person using the ladder could come in contact with energized parts of equipment, fixtures, or circuit conductors?<br>
-
From OSHA: " Avoid using a metal ladder near power lines or exposed energized electrical equipment."
-
20.12 Is sufficient access and working space provided and maintained around all electrical equipment to permit ready and safe operations and maintenance?<br>
-
1910.303(h)(3) “Work space about equipment. Sufficient space shall be provided and maintained about electric equipment to permit ready and safe operation and maintenance of such equipment. Where energized parts are exposed, the minimum clear work space may not be less than 1.98 m (6.5 ft) high (measured vertically from the floor or platform) or less than 914 mm (3.0 ft) wide (measured parallel to the equipment). The depth shall be as required in paragraph (h)(5)(i) of this section. In all cases, the work space shall be adequate to permit at least a 90-degree opening of doors or hinged panels.”
-
20.13 Are all unused openings (including conduit knockouts) in electrical enclosures and fittings closed with appropriate covers, plugs, or plates?<br>
-
1910.305(b)(2)(i) “All pull boxes, junction boxes, and fittings shall be provided with covers identified for the purpose. If metal covers are used, they shall be grounded. In completed installations, each outlet box shall have a cover, faceplate, or fixture canopy. Covers of outlet boxes having holes through which flexible cord pendants pass shall be provided with bushings designed for the purpose or shall have smooth, well-rounded surfaces on which the cords may bear.”
-
20.14 Are electrical enclosures such as switches, receptacles, junction boxes, etc., provided with tight-fitting covers or plates?<br>
-
1910.305(b)(2)(i) “All pull boxes, junction boxes, and fittings shall be provided with covers identified for the purpose. If metal covers are used, they shall be grounded. In completed installations, each outlet box shall have a cover, faceplate, or fixture canopy. Covers of outlet boxes having holes through which flexible cord pendants pass shall be provided with bushings designed for the purpose or shall have smooth, well-rounded surfaces on which the cords may bear.”
-
Additional Notes:
General Notes
Sign Off
-
Auditor