Information
-
Organization Assessed:
- ARW Headquarters
- Medical Group
- Mission Support Group
- Maintenance Group
- Operations Group
- Other
- 220th EIS
- 164 WF
-
Organization Commander:
-
Date of Assessment:
-
Assessment Conducted by:
-
Fall Protection Program Conformance Grade:
- Met and Effective
- Met But Needs Minor Improvements
- Met but Needs Significant Improvements
- Not Effective
MISHAP FALL PREVENTION EFFECTIVENESS
12 Month Mishap Summary - Fall From Working Surfaces
-
Reported fall mishaps within the last 12 months within this unit?
-
Total Mishaps:
-
Lost Workdays:
-
Days on Restricted Duty:
-
On-Duty Mishaps:
-
Off-Duty Mishaps:
-
Management and Supervisory Support
-
What was found unsatisfactory for the unit's mishap prevention program?
-
Experience and Trends:
-
Remarks:
Outstanding Performers
-
Outstanding performers identified within the unit.
-
Comments:
FALL PROTECTION PROGRAM COMPLIANCE
Fall Protection Program IAW DAFMAN 91-203, Chapter 13
-
13.3.1. Unit Fall Protection Policy Statement developed and implemented.
-
Policy provides general goals and guidance for the fall protection program. (e.g. ANSI/ASSP Z359.2)
-
13.3.2. Responsibilities. (Unit CC) Fall Protection Program developed and implemented promoting a safe and healthful workplace.
-
13.3.2.2. Unit Fall Protection Program Administration. The unit fall protection program will be administered and managed by a competent person
-
The competent person will be identified in writing by the unit commander and meet the requirements of ANSI/ASSP Z359.0 and ANSI/ASSP Z359.2.
-
-
13.3.2. Responsibilities. (Unit CC) designated Qualified, Competent, and Authorized persons.
- Qualified
- Competent
- Authorized
- Out-Sourced
- Non-Compliant
-
13.3.2.3. Qualified Persons identified in writing.
-
13.3.2.3.1. Trained and meets responsibilities IAW ANSI/ASSP Z359.2 and 29 CFR § 1910.21(b).
-
13.7.5. Recurring training performed at least annually.
-
13.3.2.4. Competent Persons identified in writing.
-
13.3.2.4. Competent Persons trained and meet the responsibilities IAW ANSI/ASSP Z359.2 and 29 CFR § 1910.104(b).
-
13.3.2.4. Competent Persons document the administration, development, implementation, evaluation, and review of the Fall Pro Program?
-
13.3.2.4. Competent Persons document providing and evaluating Fall Pro Training?
-
13.3.2.5. Authorized Persons identified in training records.
-
13.7.2. Authorized personnel trained by competent or qualified person trainer IAW ANSI/ASSP Z359.2.
Responsibilities of Occupational Safety IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.3.2.6.
-
13.3.2.6. Installation Occupational Safety. SEG provides advice and guidance to the Unit Fall Protection Program Administrator in the management of the unit fall protection program.
-
13.3.2.6.1. Installation Occupational Safety. Assist with fall hazard surveys and development of written fall protection and rescue procedures to ensure rescue procedures, equipment and training meet fall protection requirements.
-
13.3.2.6.2. Installation Occupational Safety. Identify unabated fall hazards and providing a risk assessment code (RAC) and tracked in accordance with AFI 91-202.
-
13.3.2.6.3. Conduct thorough annual review of fall protection program elements and documents annually in safety inspection/assessment reports.
Responsibilities of Fire & Emergency Services (FES) IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.3.2.7.
-
13.3.2.7. F&ES. Assist with the fall hazard surveys and development of written fall protection and rescue procedures.
-
13.3.2.7. F&ES. Ensure equipment and training meet fall protection requirements in paragraph 13.4 and paragraph 13.5.
-
13.3.2.7. F&ES. Does FE&S act as the competent rescuer when they meet the requirements?
-
13.3.2.7. F&ES. Perform rescues at height and included in the organizational rescue plan and agreed to by the installation fire chief.
Responsibilities of Rescuers IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.3.2.8.
-
13.3.2.8. Authorized Rescuers. Authorized rescuers will meet the definition outlined in ANSI/ASSP Z359.0 and meet all applicable responsibilities in ANSI/ASSP Z359.2.
Responsibilities of Supervisors IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.3.2.9.
-
13.3.2.9.1. Supervisor. Ensure authorized, qualified and competent persons using a fall protection/fall arrest system are trained and evaluated on proper use, application and inspection of fall protection/fall arrest systems.
-
13.3.2.9.2. Supervisor. Be familiar with the shop’s typical work assignments and fall protection/fall arrest systems required.
-
13.3.2.9.3. Supervisor. Responsible for the procurement of fall protection/fall arrest systems required by the organization or shop as directed by qualified person.
-
13.3.2.9.4. Supervisor. Provide recommendations for qualified and competent personnel in the organization to the unit commander.
-
13.3.2.9.5. Be designated in writing by the unit commander.
Responsibilities of Trainers IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.3.2.10.
-
13.3.2.10. Trainers. Trainers designated in writing by the unit commander.
-
Outside Org Trainer. Documentation of the service agreement kept on file.
Fall Protection Assessment IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.3.3.
-
13.3.3.1. Unit Fall Protection Program Administrator assess compliance of the fall protection program requirements, with assistance of the competent/qualified person, as needed.
-
Are Findings documented and corrected.
-
13.3.3.1.1. Final report routed to the unit commander for review and signature within 10 days of assessment completion.
-
13.3.3.1.2. Unit Fall Protection Program Administrator maintain a minimum of three (3) years of completed assessments.
-
13.3.3.2. Occupational Safety Office complete an annual assessment of fall protection program requirements and document results
Fall Hazard Survey IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.4.
-
13.4.1. Survey team led by the unit competent/qualified person(s).
-
13.4.1. Survey team comprised of the work center supervisors, authorized persons, installation occupational safety office and F&ES.
-
13.4. Fall Hazard Survey Conducted
-
13.4.2.1. Survey Includes: Identification of fall hazards and details of each
-
13.4.2.1.1. Survey Details: Means of access to the fall hazards.
-
13.4.2.1.2. Survey Details: Locations of the fall hazards.
-
13.4.2.1.3. Survey Details: Tasks that create exposure to fall hazards.
-
13.4.2.1.4. Survey Details: Hidden fall hazards that are not always readily apparent.
-
13.4.2.2. Survey Includes: Pertinent information about the fall hazards to include showing its basic configuration. (Use of graphics, drawings and/or photographs)
-
13.4.2.3. Survey Includes: Identification of environmental factors that will affect any of the fall protection system.
-
13.4.2.4. Survey Includes: A risk assessment to determine the level of risk for each fall hazard identified.
-
Fall Hazards Identified and RAC's Assigned
-
13.4.2.5. Appropriate abatement actions determined, as required by AFI 91-202.
-
13.4.2.6. Fall protection method(s) selected for each identified hazard.
-
13.4.3. Competent or qualified person prepare the fall hazard survey report
-
13.4.3. Fall hazard survey report submitted to the unit fall protection program administrator, F&ES and Occupational Safety Office.
-
13.4.4. Fall hazard surveys updated or re-accomplished when changes occur in the work center.
-
13.4.4. Completed fall hazard surveys maintained by the unit fall protection program administrator and be available to qualified, competent and authorized workers for reference.
Written Fall Protection & Rescue Procedures IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.5.
-
13.5.1. Fall protection and rescue procedures and tasks documented specifically for each workplace.
-
13.5.1. Procedures prepared and modified by a qualified or competent person.
-
13.5.1. Fall protection and rescue procedures reviewed every two years for currency and accuracy.
-
13.5.2. Written Procedures Identified
-
13.5.2.1. Purpose of the fall protection procedure.
-
13.5.2.2. Location and photographs/diagrams of the fall hazard(s) and fall protection system setup.
-
13.5.2.3. Appropriate standards, regulations or requirements for the task(s) conducted.
-
13.5.2.4. Training requirements for the fall protection procedure based on the fall protection equipment required.
-
13.5.2.5. Fall protection system design parameters. (Include fall calculations based on equipment and equipment design parameters, which include a detailed list of PPE and who developed the procedure, when it was developed, system certifications and inspection logs.)
-
13.5.2.6. Equipment requirements.
-
13.5.2.7. Procedures documenting how to safely erect, use, and dismantle the fall protection equipment.
-
13.5.2.8. Preparatory actions to be conducted by the supervisor to ensure authorized persons know the fall protection and rescue procedures.
-
13.5.2.9. Steps to take when work is completed, e.g., clean up, storage.
-
13.5.2.10. A detailed rescue plan, which includes:
-
13.5.2.10.1. Coordination with outside rescue agencies (installation F&ES Flight, contracted rescue unit, etc.)
-
13.5.2.10.2. Procedures to contact the rescue agency.
-
13.5.2.10.3. Training on actions an authorized person can take to attempt self-rescue, when possible.
-
13.5.2.10.4. Actions to be taken by the organization to rescue fallen authorized personnel, when possible.
-
13.5.2.10.5. Location of rescue anchorage.
-
13.5.2.10.6. Equipment needed.
-
13.5.2.10.7. Location of attachment to fallen employee’s harness.
-
13.5.2.10.8. Specific actions to achieve successful rescue.
-
13.5.2.10.9. Required training for rescuers.
Fall Protection Training IAW DAFMAN 91-203, para 13.6.
-
13.7.4. Retraining. Supervisors ensure authorized persons are retrained in accordance with 29 CFR § 1910.30(c).
-
13.7.5. Reoccurring Training. Performed at least annually, when work conditions change or new fall protection/fall arrest systems are procured?
-
13.7.5. Recurring Training. Training establishes employee proficiency, in-depth review of current/previous procedures, and introduce a new/revised control methods and procedures, as necessary.
-
13.7.5.1. Competent & Authorized persons are retrained at least every two years.
-
13.7.5.1. Annual refresher training conducted the year following attendance in the initial course.
-
13.7.5.2. Competent and Authorized Rescuers meet training requirements as identified in ANSI/ASSP Z359.2.
-
13.7.6. Training Documentation. All training, e.g., familiarization, initial, retraining and recurring, are documented IAW AFI 91-202, with the required information detailed in OSHA Publication 2254, Training Requirements in OSHA Standards.
-
13.8. Equipment Inspections and Maintenance.
-
13.8.2. Authorized person(s) shall inspect PFAS prior to use.
-
13.8.3. Supervisors shall ensure all PFAS components receive a thorough inspection at least quarterly.
-
This inspection shall be documented and maintained for at least one year.
-
13.8.4. Supervisors shall maintain manufacturer’s instructions and performance testing information for PFAS used by their employees.
FINDINGS
- Finding
-
Discrepancy or Observation:
-
-
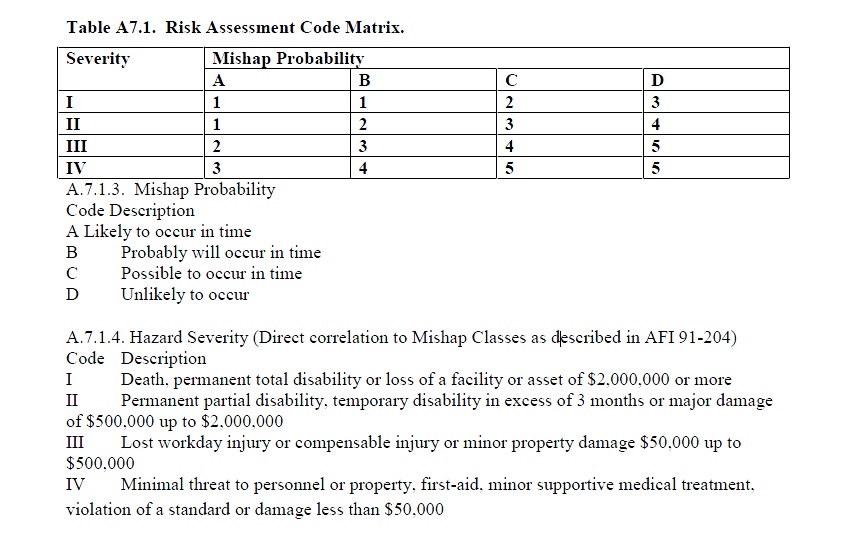
Probability:
-
Severity:
-
Risk Assessment Code:
-
Reference:
-
Cause:
- Training
- Equipment
- Technical Data
- Human Error
- Misconduct
- Process Inadequate or Faulty
- Leadership/Supervision
- Other
-
Describe:
-
Recommended Action:
-
Functional Area or Shop Inspected:
-
Supervisor or POC:
-
Phone Number:
-
Date and Time:
-
Bld:
- 2006 (Main Gate)
- 2000
- 917
- 911
- 909
- 903
- 888
- 887
- 885
- 883
- 876
- 875
- 872
- 849
- 846
- 820
- 220
- Unlisted
-
Describe:
-
Room(s):
-
Follow-Up Date:
OUT-BRIEF
Formal Outbrief
-
Was the commander available for a formal out brief within 3 days?
-
CC Rank, Name, Title:
-
Out brief conducted on:
-
Signature:
-
Supervisor or POC Rank, Name, Title:
-
Out brief conducted on:
-
Signature:
-
Why was the CC not briefed?
Formal Report
-
Formal report sent to the commander on:
-
Safety office representative rank and name:
-
Signature:
EXPLANATION OF CAUSES & RACs
-
TR- TRAINING: Inadequate training in: guidance/policy/procedure, training oversight, initial qualification training, hands-on training , controls/metrics of training process/progress, training evaluation, training documentation, individual(s) not qualified, not experienced enough to perform task.
EQ- EQUIPMENT: Correct tools/equipment not available, unserviceable or not used, incorrect tool selection. Equipment defect or design flaw, inadequate equipment maintenance.
TD- TECHNICAL DATA: Tech data, operating instruction, or checklist incorrect, conflicting, misleading, unavailable, overly complex , outdated. (If tech data is incorrect/conflicting, misleading or too complex, individual must generate AFTO 22 and submit copy to MXS supervision)
HE- HUMAN ERROR: Used as last resort. When all equipment, technical data, training, and other factors are adequate. When another qualified technician would not have made the same error.
MC- MISCONDUCT: When all equipment, technical data, training, and other factors are adequate. The technician is fully aware of all requirements, demonstrates task competency, and the process is correct as written. Another qualified technician would not have made the same error and there is clear evidence the technician consciously disregarded technical data and/or regulations.
PI- PROCESS INADEQUATE OR FAULTY: Used when root cause analysis indicates all other root cause codes are not applicable. Established shop process for accomplishing the task is faulty and will be changed as a result of the root cause analysis.
LS- LEADERSHIP/SUPERVISION: Ineffective communication, decision making process ineffective, involvement insufficient, physical work environment issue, failure to adequately program resources.
OT- OTHER: Enter specific issues that cannot be linked to ROOT CAUSES above. -