Information
-
Organization Assessed:
- ARW Headquarters
- Medical Group
- Mission Support Group
- Maintenance Group
- Operations Group
- Other
- 220th EIS
- 164 WF
-
Area:
-
Unit:
-
Unit:
-
Organization Commander:
-
Date of Assessment:
-
Assessment Conducted by:
-
Mishap Prevention Program Conformance Grade:
- Met and Effective
- Met But Needs Minor Improvements
- Met but Needs Significant Improvements
- Not Effective
MHE MISHAP PREVENTION EFFECTIVENESS
12 Month Mishap Summary - MHE
-
Reported MHE mishaps within the last 12 months within this unit.
-
Total Mishaps:
-
Lost Workdays:
-
Days on Restricted Duty:
-
On-Duty Mishaps:
-
Off-Duty Mishaps:
-
Management and Supervisory Support
-
What was found unsatisfactory for the unit's mishap prevention program?
-
Experience and Trends:
-
Remarks:
Outstanding Performers
-
Outstanding performers identified within the unit?
-
Comments:
MHE PROGRAM COMPLIANCE
Material Handling Equipment (MHE) IAW DAFMAN 91-203, Chapter 12
-
Unit/Shop:
-
12.2.1. Identify authorized DAF, MAJCOM/FLDCOM, Locally devised forms, or Automated systems for documenting and tracking inspections, maintenance, training and other MHE activities.
-
12.2.2. Unit's frequency of using MHE. (Cranes, hoists and derricks)
-
Equipment idle for at least one month, but less than six months, inspected prior to placing in service. (Documentation)
-
Equipment idle for six months or more given a complete inspection prior to placing in service. (Documentation)
-
Standby cranes and derricks inspected at least semiannually. (Documentation)
-
12.2.3. Unit uses Gasoline or Diesel-Powered MHE in general purpose warehouse?
-
12.2.3. MHE approved by the Group CC and coordination with FES, BE, and SEG. (Documetation)
-
12.2.3. Equipment parked so it does not block fire aisles, fire-fighting equipment, fire alarm boxes, stairways, elevators or fire exits.
-
12.2.3. Warehouse supervisor conduct daily inspections to ensure parked in designated locations, equipment does not contain excessive grease and lint, and gasoline lines, tanks, oil seals and so forth are not leaking.
-
12.2.3. Minimum of 10-foot clearance between parked MHE and combustible materials.
-
12.2.3.1. Liquid petroleum (LP)-fueled industrial and lift trucks parked near sources of heat, open flames or similar sources of ignition.
-
12.4. Does the unit have/use Hoists, Slings, Cranes, Derricks, Powered Industrial Trucks and associated components?
-
12.4. Inspections. Inspect for damage or wear at intervals specified (frequent and/or periodic), including observations during operation.
- Compliant
- Non-Compliant
- Complies w/ Comments
-
12.4. Were deficiencies identified and determined hazardous with the last year?
-
12.4. Did the operator or shop/facility supervisor communicate with SEG?
-
12.4.1. Prior-To-Use Inspection. A visual/prior to use inspection (pre-operational) inspection performed by the operator or designated person prior to each shift.
-
12.4.2. Frequent Inspection. A visual inspection will be performed by the operator or designated person at certain intervals: normal use – monthly; heavy use – weekly; severe use – daily.
-
12.4.3. Periodic Inspection. A complete inspection performed by qualified person at intervals between 1 and 12 months. Usage Intervals: normal service – annual; heavy service – semiannual; severe service – quarterly.
-
12.4.4. (Monthly/Annual) Inspections documented for each item (Show separate documentation w/ date, time, inspector signature, equipment identifier, and condition).
-
12.4.4. Inspection criteria IAW 91-203 and applicable ANSI standards or manufacturer instructions.
-
12.4.8. Hoist, Sling and Hook Certification. Certification documentation by the manufacturer when purchased or repaired are maintained for the life of the equipment (or until the hooks are replaced).
-
12.4.10. Inspections shall be documented IAW paragraph 12.2.1.
-
Does the unit have Nuclear Certified Equipment (NCE)?
-
12.5. Supervisor or designated representative perform periodic inspection semiannually.
-
12.6. Qualification and Training. Designated qualified personnel identified as unit training instructors.
-
12.6.1. Supervisor and VCO keep list of approved instructors, with their background and experience on the type(s) of equipment the instructor is providing training.
-
Do materials handling and lifting equipment operators conduct daily or prior-to-use inspections and document them on AF Form 1800 per requirements of AFI 91-203, para.35.1.1. Ref: AFI 91-203, para. 35.3.3.6.
-
12.6.2. Lesson plans for each vehicle or equipment type, accomplished by the unit IAW AFMAN 24-306.
-
12.6.2. Lesson plans include formal instruction, hands-on demonstrations, practical exercises performed by the trainee and performance evaluation.
-
12.6.3. Do instructors evaluate each operator at least once every three (3) years and provide refresher training in as applicable? Does the instructor provide written certification of training completion to the OR&L?
-
12.7. All hoists, slings, and overhead cranes been inspected and load tested IAW AFI 91-203 Chapter 12? Is the record of each inspection and testing maintained on file?
-
If the forklift is equipped with a portable fire extinguisher, has all inspections been conducted and documented (monthly, annual, etc.) Ref: AFI 91-203, para. 35.3.3.4.6.
-
12.8.2.4 Are electric or battery powered used indoors and if internally combustion engines are operated inside is an exhaust or other ventilation approved by BE installed?
Findings
- Finding
-
Discrepancy or Observation:
-
-
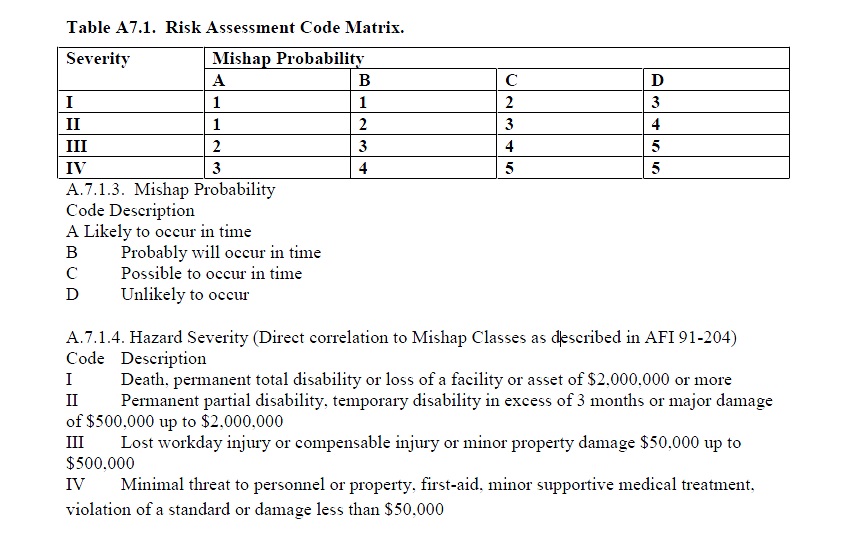
Probability:
-
Severity:
-
Risk Assessment Code:
-
Reference:
-
Cause:
- Training
- Equipment
- Technical Data
- Human Error
- Misconduct
- Process Inadequate or Faulty
- Leadership/Supervision
- Other
-
Describe:
-
Recommended Action:
-
Functional Area or Shop Inspected:
-
Supervisor or POC:
-
Phone Number:
-
Date and Time:
-
Bld:
- 2006 (Main Gate)
- 2000
- 917
- 911
- 909
- 903
- 888
- 887
- 885
- 883
- 876
- 875
- 872
- 849
- 846
- 820
- 220
- Unlisted
-
Describe:
-
Room(s):
-
Follow-Up Date:
Out Brief
Formal Outbrief
-
Was the commander available for a formal out brief within 3 days?
-
CC Rank, Name, Title:
-
Out brief conducted on:
-
Signature:
-
Supervisor or POC Rank, Name, Title:
-
Out brief conducted on:
-
Signature:
-
Why was the CC not briefed?
Formal Report
-
Formal report sent to the commander on:
-
Safety office representative rank and name:
-
Signature:
Explanation of Causes and RACs
-
TR- TRAINING: Inadequate training in: guidance/policy/procedure, training oversight, initial qualification training, hands-on training , controls/metrics of training process/progress, training evaluation, training documentation, individual(s) not qualified, not experienced enough to perform task.
EQ- EQUIPMENT: Correct tools/equipment not available, unserviceable or not used, incorrect tool selection. Equipment defect or design flaw, inadequate equipment maintenance.
TD- TECHNICAL DATA: Tech data, operating instruction, or checklist incorrect, conflicting, misleading, unavailable, overly complex , outdated. (If tech data is incorrect/conflicting, misleading or too complex, individual must generate AFTO 22 and submit copy to MXS supervision)
HE- HUMAN ERROR: Used as last resort. When all equipment, technical data, training, and other factors are adequate. When another qualified technician would not have made the same error.
MC- MISCONDUCT: When all equipment, technical data, training, and other factors are adequate. The technician is fully aware of all requirements, demonstrates task competency, and the process is correct as written. Another qualified technician would not have made the same error and there is clear evidence the technician consciously disregarded technical data and/or regulations.
PI- PROCESS INADEQUATE OR FAULTY: Used when root cause analysis indicates all other root cause codes are not applicable. Established shop process for accomplishing the task is faulty and will be changed as a result of the root cause analysis.
LS- LEADERSHIP/SUPERVISION: Ineffective communication, decision making process ineffective, involvement insufficient, physical work environment issue, failure to adequately program resources.
OT- OTHER: Enter specific issues that cannot be linked to ROOT CAUSES above. -