Title Page
-
Site conducted
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
Have you linked existing Asset
General Inspection Guidelines
-
• In addition to routine checks for each use, PPE should regularly undergo a detailed inspection by a competent person. Petzl recommends an inspection every 12 months and after any exceptional event in the life of the product.
• PPE inspection should be conducted with the manufacturer’s Instructions for Use: download the instructions at PETZL.COM.
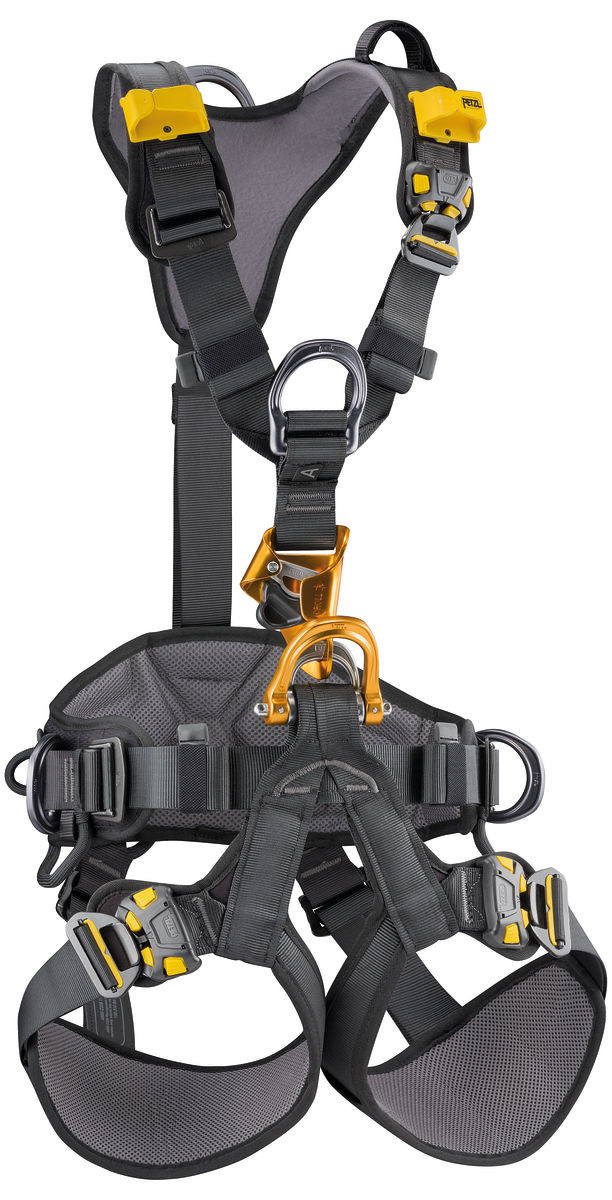
Harness Inspection
Known product history
-
Is there known history of usage conditions or exceptional event/s during use (e.g., fall or fall arrest, use or storage at extreme temperatures, contamination or modification outside manufacturer's facilities..etc)
-
Refer to the attached Harness Inspection Procedure and examples before commencing physical inspection. Refer back to this document to assist with rulings regarding particular elements/components of the harness.
1. Preliminary observations
-
Possible answer types:
Good condition (GC) = Harness is fit for continued use.
To monitor (TM) = Scheduled inspection frequency/interval must be increased/shortened.
To repair (TR) = Harness to be submitted to an approved repair agent to assessment for repairability.
Do not use/retire (R) = Harness is not fit for use it must be removed from service, destroyed & disposed of responsibly.
Not applicable (NA) = Specific question is not relevant. -
Verify the presence and legibility of the serial number
-
-
Verify that the product lifetime has not been exceeded (10 years from date of manufacture)
-
Compare with a new product to verify there are no modifications or missing parts.
2. Checking the condition of the straps (webbing)
-
-
Check for cuts, swelling, damage and wear due to use, to heat, and to contact with chemicals. Check the waistbelt straps, leg loops, leg loop/waistbelt linkage and shoulder straps, if present. Be sure to check the areas hidden by the buckles.
-
Check the condition of the safety stitching on both sides. Look for any threads that are loose, worn, or cut. The safety stitching is identified by thread of a different colour than that of the webbing.
-
Verify that hems are present on the strap ends.
3. Checking attachment points
-
Check the condition of the metal attachment points (marks, cracks, wear, deformation, corrosion...).
-
Check the condition of the textile attachment points (cuts, wear, tears...).
-
Check the condition of the plastic attachment points (cuts, wear, tears...).
-
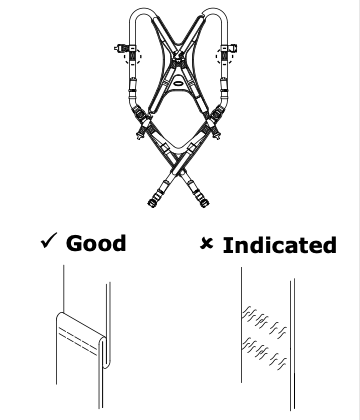
Ensure the impact indicator is not visible.
-
4. Checking the condition of the adjustment buckles
-
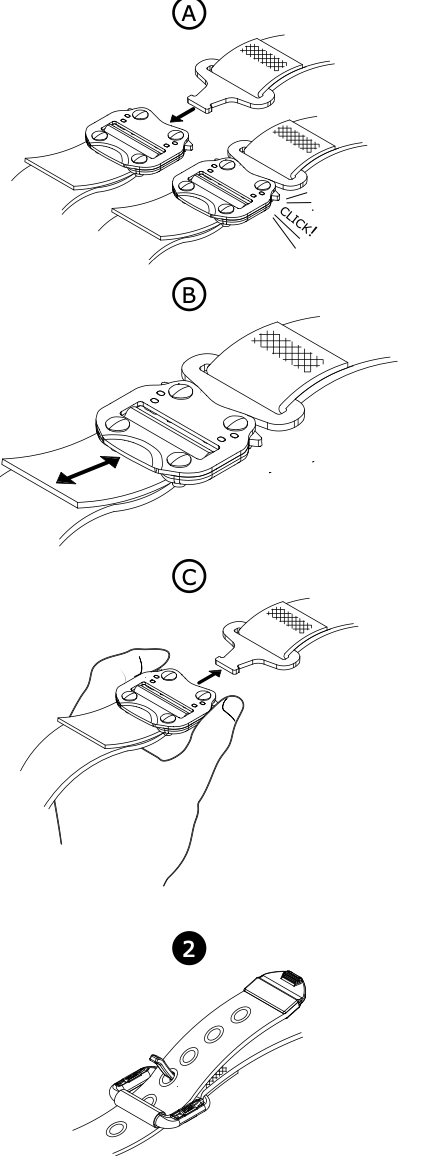
Check the condition of the DOUBLEBACK adjustment buckles (marks, cracks, wear, deformation, corrosion...).
-
-
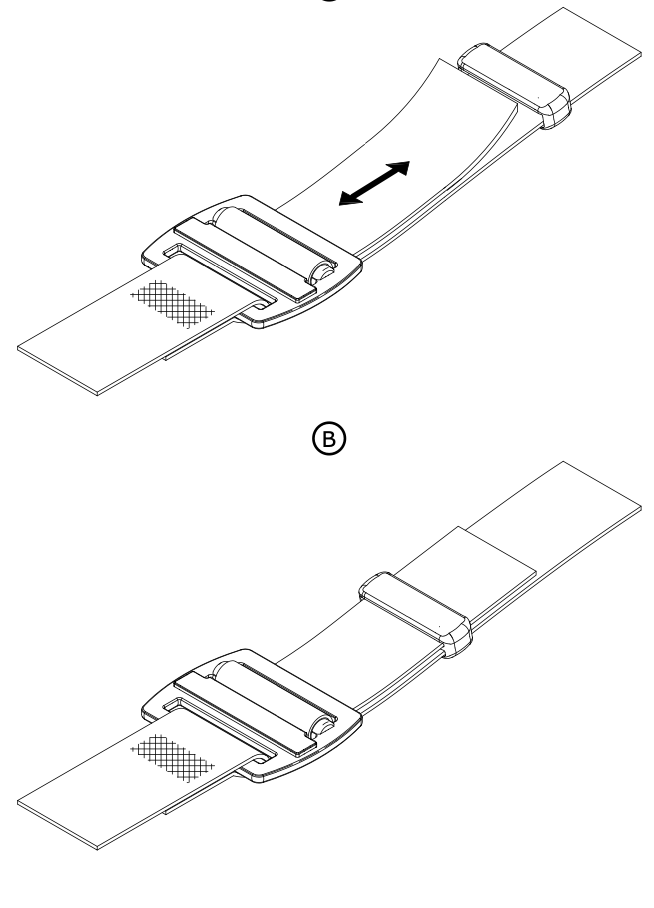
Check the condition of the FAST adjustment buckles (marks, cracks, wear, deformation, corrosion...).
-
-
Check that the straps are correctly threaded, with no twists.
-
Verify that the buckles operate properly.
5. Checking the condition of the comfort parts
-
-
Check the condition of the waist, leg and shoulder foams (cuts, wear, tears...)..
-
Check the condition of the elastic and/or plastic keepers (cuts, wear, tears...).
-
Check the condition of the leg loop elastics (cuts, wear, tears...).
-
Check the condition of the equipment loops (cuts, wear, tears...).