Information
-
Project description
-
Contract No. GW
-
Contractor
-
Subcontractors on site
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Contractor's representative
-
This audit sheet must be read in conjunction with the industry standard for Electrical Installations on construction sites – Edition No. 2 – COR/14/21592
1.0 Temporary Switchboard Construction
-
1.1 Does the switchboard have a tie bar or other device to prevent strain of cables and flexible cords, and protection against mechanical damage?
-
1.2 Is the switchboard securely attached to a pole, post, wall or other stable, free-standing structure?
-
1.3 Is the degree of protection appropriate for the environment in which it is installed (minimum protection IP23)?
-
1.4 Are all main switches and isolating switches accessible at all times, clearly marked and capable of being locked in an open (off) position?
-
1.5 Does the switchboard have markings at least 6mm high identifying all main/isolating switches?
-
1.6 Does the switchboard incorporate insulated stands for supporting cables and flexible extension cords or have a stand fixed near the switchboard?
-
1.7 Does the switchboard have a lockable door for isolation and security purposes that will not damage the cables when closed?
-
1.8 If there are more than one final sub-circuit, does the switchboard have a lockable cover, lock-dog or other security device to prevent unauthorised access to circuit breakers and RCDs?
-
1.9 If supply is needed for equipment such as welders and floor sanders, is there at least one 15A single phase socket outlet?
-
1.10 Ensure the switchboards are:
-
1.10.1 Readily accessible.
-
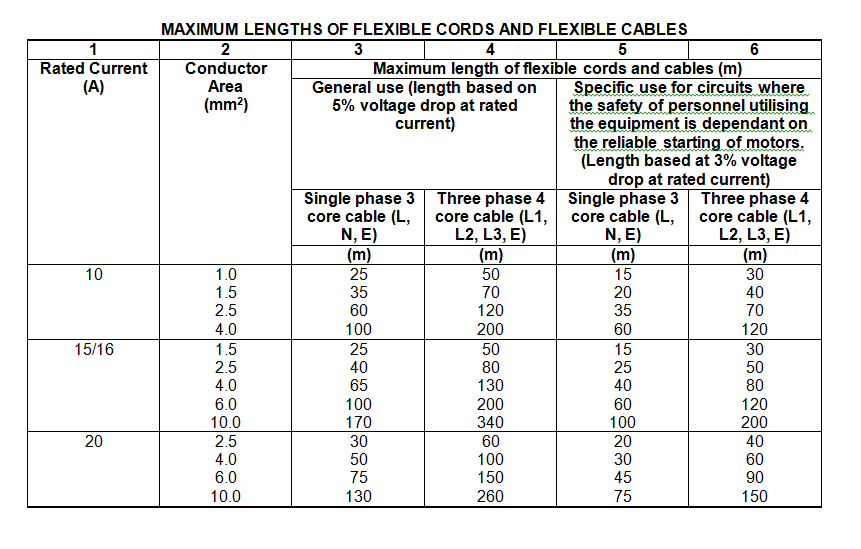
1.10.2 Located to suit the maximum flexible extension cord lengths as set out in table 1 (references).
-
1.10.3 Located so that there is a minimum clearance of 600mm with the door fully open.<br>
-
1.11 The switchboard door must have:
-
1.11.1 A sign on the door – ‘KEEP CLOSED – RUN LEADS THROUGH BOTTOM’.
-
1.11.2 An opening at the bottom to allow flexible cords to pass through without damage.
2.0 Electrical Circuits
-
2.1 Ensure that every final sub-circuit (including lighting & socket outlets) is protected by a circuit breaker, except final sub-circuits exceeding 50A, which may be protected with high rupturing capacity (HRC) fuses.
-
2.2 Ensure that every final sub-circuit (including lighting and socket outlets) is protected by an RCD with a rated tripping current of 30mA.
-
2.3 Has a Certificate of Electrical Safety been issued?
3.0 Identification of wiring
-
3.1 Is the construction (temporary) wiring segregated and distinguishable from the permanent wiring? Green, Yellow or Green/Yellow wiring shall not be used as construction wiring.
-
3.2 Is the wiring clearly labelled?
4.0 Protection of wiring
-
4.1 Is the existing permanent wiring protected from mechanical damage?
-
4.2 Check that leads are not lying in mud or water or in areas where they can be damaged or become tripping hazards.
-
4.3 Use stable, insulated lead stands to keep them above head-height. Do not allow leads to be wrapped around scaffolds or falsework – use S-shaped insulated hooks instead.
-
4.4 Where extension leads are joined outdoors or where water may be present, the plugs are to be protected with a waterproof cover.
5.0 Flexible extension cords
-
Ensure that:
-
5.1 Flexible extension cords have heavy duty sheathing.
-
5.2 The sheathing is not coloured green.
-
5.3 The maximum length complies with table 1 (references)
-
5.4 Where cords cannot be raised, ensure that there are other means of providing mechanical protection.
6.0 Portable socket outlet assemblies (PSOA)
-
Ensure that the PSOA:
-
6.1 Incorporates over-current and RCD protection.
-
6.2 Is of robust construction.
-
6.3 Has extended sides or covers over the outlets.
-
6.4 Incorporates a heavy duty flexible cord no more than two metres long.
7.0 Unused electrical wiring
-
7.1 Is there any unused electrical wiring?<br><br>Any unused permanent and construction wiring must be appropriately terminated by a licensed electrician or removed.
8.0 Aerial conductors
-
8.1 Are the aerial conductors insulated?
-
8.2 Are the aerial conductors clearly identified and marked?
-
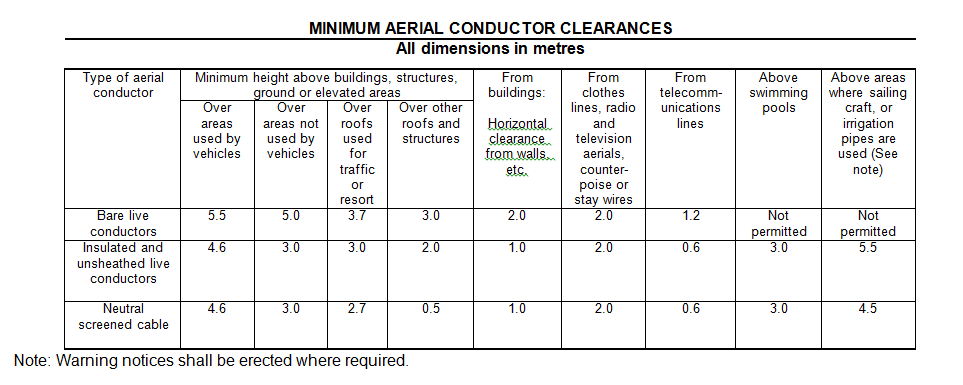
8.3 Is there sufficient height clearance, as per table 2 (references)?
9.0 Inspection and testing
-
9.1 Have certificates of electrical safety been issued for all tools and construction wiring, including switchboards? This includes any alterations, additions, modifications and repairs that have been carried out.
-
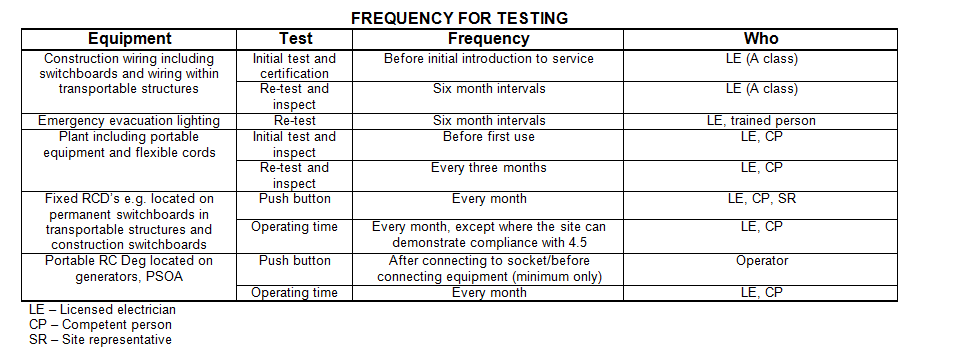
9.2 Has all new equipment been inspected and tested, and records kept? Results of inspection and testing should include details of visual inspection, continuity of earthing system, insulation resistance value, polarity, correct circuit connections and RCD trip times.
-
9.3 Are records kept of inspection and re-testing, including testing of repaired units and hire equipment?
-
9.4 Is the portable equipment tagged as tested and safe?
-
9.5 Are all fixed RCD’s tested every month?
-
9.6 Are the test results recorded and kept on site or made available when requested? Electronic records are acceptable
10.0 Generators
-
10.1 Hard wired generator used?
-
10.1.1 Has the generator been installed and certified by a licensed electrician and a certificate of electrical safety issued?
-
10.1.2 Was it inspected by a licensed electrical inspector before it was used for the first time, and after any alteration to the location or the installation of the generator?
-
10.2 Free standing generator used?
-
10.2.1 Does it have a label indicating if the unit is a bonded generator or an isolated winding generator?
-
10.2.2 Is the generator protected by a RCD not exceeding 30mA?
11.0 Lighting
-
11.1 Is the lighting protected from mechanical damage?
-
11.2 Are the lights fitted with devices such as wire cages or manufactured from impact resistant material such as polycarbonate?
-
11.3 If emergency lighting is installed in areas where there is insufficient natural lighting, is it sufficient to allow safe egress from site?
-
11.4 If exit lights are installed, are they located no more than 1m above an exit, or 2m directly in front of an exit?
12.0 Transportable structures
-
12.1 Is the transportable structure’s supply from a flexible cord? Supply must not be from another transportable structure, or to an inlet on the same structure.
-
12.2 Are there socket outlets on the structure? Socket outlets on the outside of the structure must only be used to supply electrical equipment and lighting close to the structure.
13.0 Construction wiring installed on fences
-
13.1 Is the wiring mechanically protected, even if unlikely to be damaged during construction work?
-
13.2 Is the wiring run along the top (or top rail), securely fixed and clearly identified?
-
13.3 If works has been completed, has the wiring been removed?
14.0 Power lines
-
14.1 Make sure there is always a safe distance between live powerlines and cranes, earth moving equipment, elevated work platforms, hoists, scaffolds, falsework and portable ladders by observing “no go zone” safe clearances.
-
14.2 Work in “No go zones” require the following:
• Written permission from the power authority.
• For work between 3m and 6.4m under or beside and power line, a dedicated safety observer.
• No work is permitted above, or within 3m under or beside any live power line.
• For scaffolds, the no go zone clearances are 5m above or below, and 4.6m beside any power line on poles. Clearances are from the top of any guard rail or part of the scaffolding.
15.0 Equipment and PPE
-
Are appropriate items of equipment and protective clothing in use for electrical work, such as the following:
-
15.1 Insulated ladders for live electrical work.
-
15.2 Insulated tools for all electrical work.
-
15.3 Appropriate safety clothing worn.
16.0 Safe Working
-
16.1 Ensure contractor ensures all electrical work is being preformed/controlled by suitably licensed electricians.
-
16.2 Is each new cable being installed individually identified?
-
16.3 Does the contractor have a suitable system to ensure electrical isolations from existing systems are safely controlled or tagged to protect those working on plant and equipment?
-
16.4 Does the contractor have a system to control how new plant and equipment is made live during commissioning so all on site can observe the new/changed status?
-
16.5 Does the contractor have the appropriate licenses/certificates of competency to complete the works?
References
-
Table 1
-
Table 2
-
Table 3
Additional information
-
Add any additional information
Action required
-
Contractor is to review the comments, and consider the recommended actions within this audit. The contractor needs to demonstrate they are complying with their obligations as an employer, what specific remedial action they propose for this site, and if any overall modifications are required to their Health and Safety Plan / safety procedures / supervision. Prompt corrective action is required to eliminate any agreed deficiencies, and any areas of disagreement need to be further explored in writing. All “failed responses” need to be addressed/resolved.
Signatures
-
Gippsland Water responsible officer
-
Auditor
-
Contractor's representative