Title Page
-
Name of work place
-
Date of assessment
-
Work area(s)
-
Job/Task(s)
-
Assessment conducted by
-
Location
Guidelines for complying with PPE requirements
-
Use this checklist to help you comply with the PPE requirements at your work place.
You can use the available tools in the next pages to help you accomplish the step. -
Do a work place walk-through and look for hazards (including potential hazards) in all employeesí work spaces and work place operating procedures.<br><br>Tools: <br>PPE Hazard Assessment or JHA PPE Hazard Assessment
-
Consider engineering, administrative, and/or work practice methods to control the hazards first. Identify those existing/potential hazards and tasks that require PPE.
-
Select the appropriate PPE to match the hazards and protect employees.
-
Communicate PPE selection to each at-risk employee. Provide properly fitting PPE to each employee required to use it
-
Train employees on the use of PPE and document it. <br><br>Tools: <br>PPE training certification form
-
Test employees to make sure they understand the elements of the PPE training. <br><br>Tool:<br>Sample PPE training quiz (optional)
-
Follow up to evaluate effectiveness of PPE use, training, policies,etc. against the hazards at your work place.
-
All employees have been trained
-
Employees are using their PPE properly and following PPE policies and procedures
-
Supervisors are enforcing use of required PPE (If you checked any No boxes, go back through the steps<br>and correct the deficiencies.)
-
Have things changed at your work place? (e.g.,fewer injuries/illnesses)
Conducting a Hazard Assessment
-
Select Option to be used
- Option 1: Hazard Assessment For PPE
- Option 2: Job Hazard Analysis Assessment for PPE
Option 1: Hazard Assessment for PPE
-
ON to Access Instructions
-
Hazard Assessment For PPE
Use with WAC 296-800-160 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
This tool can help you do a hazard assessment to see if your employees need to use personal protective equipment (PPE) by identifying activities that may create hazards for your employees. The activities are grouped according to what part of the body might need PPE. You can make copies, modify and customize it to fit the specific needs of your particular work place, or develop your own form that is appropriate to your work environment.
This tool can also serve as written certification that you have done a hazard assessment as required by WAC 296-800-16010 Document your hazard assessment for PPE.
Make sure that the blank fields at the beginning of the checklist (indicated by *) are filled out (see below, Instructions #4). Instructions:
1. Do a walk through survey of each work area and job/task. Read through the list of work activities in the first column, putting a check next to the activities performed in that work area or job.
2. Read through the list of hazards in the second column, putting a check next to the hazards to which employees may be exposed while performing the work activities or while present in the work area. (for e.g., work activity: chopping wood; work-related exposure: flying particles).
3. Decide how you are going to control the hazards. Try considering engineering, work place, and/or administrative controls to eliminate or reduce the hazards before resorting to using PPE. If the hazard cannot be eliminated without using PPE, indicate which type(s) of PPE will be required to protect your employee from the hazard.
4. Make sure that you complete the following fields on the form (indicated by *) to certify that a hazard assessment was done:
*Name of your work place
*Address of the work place where you are doing the hazard assessment
*Name of person certifying that a workplace hazard assessment was done
*Date the hazard assessment was done
EYES
-
Work activities, such as:
- abrasive blasting
- chopping
- cutting
- drilling
- welding
- punch press operations
- sanding
- sawing
- grinding
- hammering
- other:
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- airborne dust
- flying particles
- blood splashes
- hazardous liquid chemicals
- intense light
- other:
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
use
- Safety glasses
- Safety goggles
- Shading/Filter
- Welding shield
- Side shields
- Dust-tight goggles
- Other
-
Specify other
-
Specify Shading Filter #
FACE
-
Work activities, such as:
- cleaning
- cooking
- siphoning
- painting
- dip tank operations
- foundry work
- welding
- mixing
- pouring molten metal
- other
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- hazardous liquid chemicals
- extreme heat/cold
- potential irritants:
- other:
-
Specify other exposure
-
Specify potential irritants
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
Use
- Face shield
- Shading/Filter (# )
- Welding shield
- Other:
-
Specify Shading Filter #
-
Specify other
HEAD
-
Work activities, such as:
- building maintenance
- confined space operations
- construction
- electrical wiring
- walking/working under catwalks
- walking/working under conveyor belts
- walking/working under crane loads
- utility work
- other
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- beams
- pipes
- exposed electrical wiring or components
- falling objects
- machine parts
- other
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
Use
- Protective Helmet
- Hair net or soft cap
- Other:
-
Select applicable
- Type A (low voltage)
- Type B (high voltage)
- Type C
- Bump cap (not ANSI-approved)
-
Specify other
HANDS/ARMS
-
Work activities, such as:
- baking
- cooking
- grinding
- welding
- working with glass
- using computers
- using knives
- dental and health care services
- material handling
- sanding
- sawing
- hammering
- other:
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- blood
- irritating chemicals
- tools or materials that could scrape, bruise, or cut
- extreme heat/cold
- other
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
use
- Gloves
- Protective sleeves
- Other
-
Select Applicable
- Chemical resistance
- Liquid/leak resistance
- Temperature resistance
- Abrasion/cut resistance
- Slip resistance
-
Specify other
FEET/LEGS
-
Work activities, such as:
- building maintenance
- construction
- demolition
- food processing
- foundry work
- logging
- plumbing
- trenching
- use of highly flammable materials
- welding
- other:
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- explosive atmospheres
- explosives
- exposed electrical wiring or
- components
- heavy equipment
- slippery surfaces
- tools
- other:
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
Use
- Safety shoes or boots
- Leggings or chaps
- Foot-Leg guards
- Other:
-
Select Applicable
- Toe protection
- Electrical protection
- Puncture resistance
- Anti-slip soles
- Metatarsal protection
- Heat/cold protection
- Chemical resistance
-
Specify other
BODY/SKIN
-
Work activities such as:
- baking or frying
- battery charging
- dip tank operations
- fiberglass installation
- irritating chemicals
- sawing
- other
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
Use
- Vest, Jacket
- Coveralls, Body suit
- Raingear
- Apron
- Welding leathers
- Abrasion/cut resistance
- Other:
-
Specify Other
BODY/WHOLE 1
-
Work activities such as:
- building maintenance
- construction
- logging
- utility work
- other:
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- working from heights of 10 feet or more
- working near water
- other:
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
Use
- Fall Arrest/Restraint:
- PFD
- Other
-
Specify Other
-
Type
-
Type
-
(1) NOTE: There are other hazards requiring PPE (such as respiratory, noise, fall, etc. hazards), that are not included in this volume of the PPE
Guide but will be covered in future volumes (see WAC 296-62 for respiratory and hearing protection and WAC 296-155 for fall protection for further
assessment). However, you should consider all hazards when you conduct your hazard assessment. See a list of other WISHA rules (in ìHow to
use this guideî p. 4) for information regarding PPE for specific work places.
LUNGS/RESPIRATORY 1
-
Work activities such as:
- cleaning
- mixing
- painting
- fiberglass installation
- compressed air or gas operations
- pouring
- sawing
- other
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- irritating dust or particulate
- irritating or toxic gas/vapor
- other
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
(1) NOTE: There are other hazards requiring PPE (such as respiratory, noise, fall, etc. hazards), that are not included in this volume of the PPE
Guide but will be covered in future volumes (see WAC 296-62 for respiratory and hearing protection and WAC 296-155 for fall protection for further
assessment). However, you should consider all hazards when you conduct your hazard assessment. See a list of other WISHA rules (in ìHow to
use this guideî p. 4) for information regarding PPE for specific work places.
EARS/HEARING 1
-
Work activities such as:
- generator
- ventilation fans
- motors
- sanding
- pneumatic equipment
- punch or brake presses
- use of conveyors
- grinding
- machining
- routers
- sawing
- other:
-
Specify other activities
-
Work-related exposure to:
- loud noises
- loud work environment
- noisy machines/tools
- punch or brake presses
- other
-
Specify other exposure
-
Can hazard be eliminated without the use of PPE?
-
(1) NOTE: There are other hazards requiring PPE (such as respiratory, noise, fall, etc. hazards), that are not included in this volume of the PPE
Guide but will be covered in future volumes (see WAC 296-62 for respiratory and hearing protection and WAC 296-155 for fall protection for further
assessment). However, you should consider all hazards when you conduct your hazard assessment. See a list of other WISHA rules (in ìHow to
use this guideî p. 4) for information regarding PPE for specific work places.
Job Hazard Analysis Assessment for PPE
-
ON to Access Instructions
-
Job Hazard Analysis Assessment for PPE
Use with WAC 296-800-160 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
The Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) approach to doing a hazard assessment for PPE is a more comprehensive method and may be more useful in larger businesses with many hazards and/or complex safety issues. It also helps you assign a Risk Priority Code to the hazard to determine the course of actions you need to take to control the hazard.
Follow the instructions as you conduct your hazard assessment and fill in the hazard assessment form. You can make copies of the form or customize it to fit the needs of your work place. For more detailed explanations of the instructions and guidance on
doing the hazard assessment, including completed sample forms, see the ìAdditional Guidelines on Conducting a JHA Hazard Assessment for PPE,î pages 25-30).
This tool can also serve as written certification that you have done a hazard assessment as required by WAC 296-800-16010 Document your hazard assessment for PPE.
Make sure that the blank fields at the bottom of the form (indicated by *) are filled out.
*Name of your work place
*Address of the work place where you are doing the hazard assessment
*Name of person certifying that a workplace hazard assessment was done
*Date the hazard assessment was done -
Job Hazard Analysis Assessment for PPE:
Instructions
1. Conduct a walk through survey of your business. For each job/task step, note the presence of any of the following hazard types (see table below) their sources, and the body parts at risk. Fill out the left side of the hazard assessment form. Gather all the information you can.
• Look at all steps of a job and ask the employee if there are any variations in the job that are infrequently done and that you might have missed during your observation.
• For purposes of the assessment, assume that no PPE is being worn by the affected employees even though they may actually be wearing what they need to do the job safely.
• Note all observed hazards. This list does not cover all possible hazards that employees may face or for which personal protective equipment may be required. Noisy environments or those which may require respirators must be evaluated with appropriate test equipment to quantify the exposure level when overexposure is suspected. -
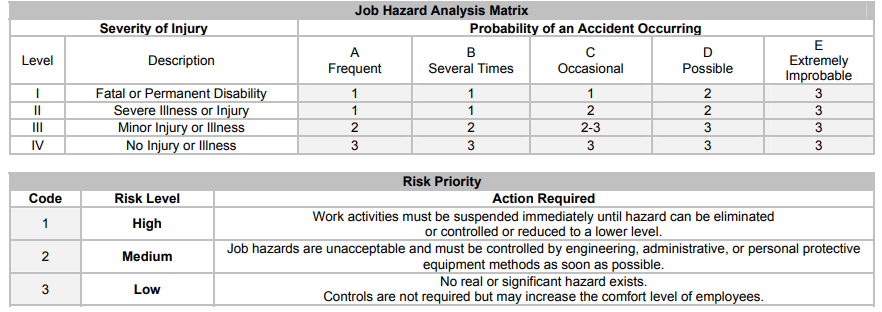
2. Analyze the hazard. For each job task with a hazard source identified, use the Job Hazard Analysis Matrix table and discuss thehazard with the affected employee and supervisor. Fill out the right side of the hazard assessment form:
• Rate the SEVERITY of injury that would reasonably be expected to result from exposure to the hazard.
• Rate the PROBABILITY of an accident actually happening.
• Assign a RISK CODE based upon the intersection of the SEVERITY and PROBABILITY ratings on the matrix. -
3. Take action on the assessment. Depending on the assigned Risk Level/Code (or Risk priority), take the corresponding action according to the table above:
• If Risk priority is LOW (3) for a task step # requires no further action.
Note: If you assign a risk code of 3, be sure that there isnít a WISHA standard that requires specific protection be provided.
For example: WAC 296-24-65003 requires personal protective equipment when using compressed air for cleaning.
• If Risk priority is MEDIUM (2) # select and implement appropriate controls.
• If Risk priority is HIGH (1) # immediately stop the task step until appropriate controls can be implemented.
***A high risk priority means that there is a reasonable to high probability that an employee will be killed or permanently disabled doing this task step and/or a high probability that the employee will suffer severe illness or injury! *** -
4. Select PPE:
• Try to reduce employee exposure to the hazard by first implementing engineering, work practice, and/or administrative controls. If PPE is supplied, it must be appropriately matched to the hazard to provide effective protection, durability, and proper fit to the worker. Note the control method to be implemented in the far right column.
5. Certify the hazard assessment:
• Certify on the hazard assessment form that you have done the hazard assessment and implemented the needed controls.
• Incorporate any new PPE requirements that you have developed into your written accident prevention program. -
-
-
Specify Job/Task step
-
Hazard Type
- Impact Person
- Penetration
- Crush or pinch
- Harmful Dust
- Chemical
- Heat
- Light (optical)
- Radiation
- Electrical Contact
- Ergonomic hazards
- Environmental hazards
-
Hazard Source
-
Body Parts At Risk
-
Severity
- I Fatal or Permanent Disability
- II Severe Illness or Injury
- III Minor Injury or Illness
- IV No Injury or Illness
-
Probability
-
Risk Code
-
Control Method Note: Engineering, work practice, and/or administrative hazard controls such as guarding must be used, if feasible, before requiring employees to use personal protective equipment.
Certification of Assessment
-
Implementation of Controls Approved By
-
Title
-
Prepared by
PPE Training Certification Form
General Information
-
Employee Name
-
Employee ID No
-
Job Title/Work area
-
Employer
-
Trainerís Name (person completing this form)
-
Date of Training
-
Types of PPE employee is being trained to use
Training Session
-
The following information and training on the personal protective equipment (PPE) listed above were covered in the training session:
-
The limitations of personal protective equipment: PPE alone cannot protect the employee from on-the-job hazards.
-
What work place hazards the employee faces, the types of personal protective equipment that the employee must use to be protected from these hazards, and how the PPE will protect the employee while doing his/her tasks.
-
When the employee must wear or use the personal protective equipment.
-
How to use the personal protective equipment properly on-the-job, including putting it on, taking it off, and wearing and adjusting it (if applicable) for a comfortable and effective fit.
-
How to properly care for and maintain the personal protective equipment: look for signs of wear, clean and disinfect, and dispose of PPE.
-
Note to employee: This form will be made a part of your personal file. Please read and understand its contents before signing.
Sign Off
-
(Employee) I understand the training I have received, and I can use PPE properly.
-
Employeeís signature
-
(Trainer must check off)
-
Employee has shown an understanding of the training.
-
Employee has shown the ability to use the PPE properly
-
Trainers signature
Personal Protective Equipment Training Quiz
-
(This is a sample quiz that you can use to make sure an employee has understood the training and can demonstrate the proper use and care of personal protective equipment. Also quiz an employee who has been retrained due to improper use of the PPE in performing his/her job tasks. You can keep this form in the employeeís file with the PPE Certification Form.)
-
1. What are the limitations of personal protective equipment?
-
2. List the types of personal protective equipment you must use when doing your work/tasks.
-
3. What are the hazards in your job for which you must use each type of PPE, and when must you use your personal protective equipment?
-
4. What are the procedures for the proper use, care, and maintenance of your PPE?
-
5. What should you look for to determine that your PPE is in good working condition?
-
6. What do you do when your PPE is no longer usable?
-
7. (Trainer/Supervisor:) Have the employee demonstrate putting on, wearing and adjusting, and taking off each PPE properly. Also have employee demonstrate how to clean and disinfect each PPE.
-
Has employee demonstrated proper use
and care of each PPE?
PPE
-
Specify PPE used
-
Compliant?
Sign Off
-
The employee has answered all the questions adequately and has demonstrated the ability to
properly use and care for the PPE needed to do his/her job. -
Trainer/Supervisor signature
-
Employee signature