Title Page
-
Property Address:
-
Location:
-
Conducted on:
-
Inspector:
Key Criteria - 15 FAM 252.5 Safety, Health, and Environmental Requirements
-
In accordance with 15 FAM requirements, safety, health, and environmental hazards must be identified in the selection of housing to eliminate the possibility of dangerous conditions that can cause serious injuries or fatalities. This checklist is referenced under 15 FAM 252.5 and 15 FAM Exhibit 971.1 to assist POSHOs in evaluating safety, health, fire, and environmental conditions when considering leasing or purchasing a property. This checklist is not intended to be all‐inclusive. The intent is to correct serious hazards and then, through effective management, ensure that safe conditions persist for as long as the residence is occupied. Posts must verify and document that the post occupational safety and health officer (POSHO) has inspected residences under consideration for purchase or lease by the U. S. Government for safety, health, and environmental hazards, and that those hazards have been effectively controlled or eliminated. A similar inspection must be conducted and documented for living quarters allowance (LQA) residences; the resident can then negotiate with the lessor to make the required and/or recommended changes or find another suitable residence. No employee may occupy a U. S. Government-owned or U. S. Government-leased residence unless the POSHO certifies that the following requirements are met:
Other Safety Criteria - Complete Residential Checklist
-
Under 15 FAM 211.1, the objective of the Housing Abroad Program is to provide safe and secure housing. This checklist is referenced under 15 FAM 252.5 and 15 FAM Exhibit 971.1 to assist POSHOs in evaluating safety, health, fire, and environmental conditions when considering leasing or purchasing a property. This checklist is not intended to be all‐inclusive.
FUEL BURNING APPLIANCES AND EQUIPMENT - Furnaces, Boilers, Water Heaters, Kerosene Heaters, Space Heaters, Dryers, Fireplaces
-
Venting of Exhaust Gases<br>1. Outdoors away from intakes and windows<br>2. Chimney and flue constructed and installed properly (per manufacturer)<br>3. Chimney and flue inspected annually and cleaned
-
Combustion Air<br>1. Adequate combustion air ducted to unit or<br>2. Unobstructed area large enough to provide adequate combustion air<br>3. Small mechanical areas have sufficient combustion air and ventilation openings<br>4. No hazardous or flammable vapor sources near combustion equipment
-
Operation and Maintenance<br>1. Instructions available for proper operation and maintenance<br>2. Equipment operated and maintained as intended within design limits<br>3. Warning labels (English and local language) present on combustion appliances
-
Clearance to Combustibles<br>1. Clearance at least 1 m (3 ft) from exhaust flue to combustible materials<br>2. Clearance at least 1 m (3 ft) from equipment to combustible materials, boiler and furnace rooms not used for storage areas
-
Fuel Type and Storage<br>1. Fuel used is appropriate for appliance(s)<br>2. Proper type and location of fuel storage container (including tanks)<br>3. Protect fuel storage containers from damage and secure them for protection against weapons of opportunity
-
Carbon Monoxide Alarms<br>1. Carbon monoxide alarm installed, at about eye level, outside of sleeping areas (including household staff) in residences with any combustion appliance (other than cooking oven/stove) or an attached garage<br>
-
Generators<br>1. Enclosed in sound attenuated and weatherproof housing<br>2. Adequate space and, if leased, the landlord agrees to the generator placed outdoors as far away as practical and a minimum of 1.5 meters (5 feet) from any building.<br>3. Exhaust outlets greater than or equal to 1 meter (3 ft) from exterior walls and roofs, 3 meters (10 ft) from operable openings into buildings, and 3 meters (10 ft) above adjoining grade<br>4. If distance and direction of exhaust is not feasible, then extend 1 meter (3 ft) above the building. (See “Venting of Exhaust Gases”<br>section)<br>
-
Portable Kerosene Heaters (Should only be selected for use as a last resort.)<br>1. Single family home use only<br>2. Correct grade of clear kerosene (K‐1) fuel stored outside in safety cans<br>3. Refuel outdoors away from sources of ignition, and after the heater has cooled completely<br>4. Set the wick height to the manufacturer’s recommended level<br>5. Chimney is seated properly<br>6. Window opened slightly (e.g., 25mm/1 inch) in the room with the heater<br>7. Keep the heater at least 1 meter (3 ft) from combustibles<br>8. Unit is operated and maintained according to the manufacturer’s instruction and residents are i <br> informed of the instructions<br> a. Do not leave the heater unattended and turn off before going to bed<br>9. Carbon monoxide alarms must be placed in dwelling
-
Liquefied Petroleum (Propane) Gases (LPG)<br>Cylinders during use:<br>1. Must be located on the exterior of the building<br>2. Equipped with a pressure regulator having a pressure relief valve<br>3. Upright and securely anchored or chained in place<br>4. At least 7.6 meters (25 ft) from sources of ignition and 1.5 meters (5 ft) from building openings<br>Cylinder storage:<br>1. Outside within a fenced enclosure<br>2. Outlet valves closed with cap or cover<br>3. Steel posts or barriers if vehicle damage is possible<br>4. “No Smoking” signs clearly displayed around the storage enclosure with universal symbols or local language and English<br>5. Secure tanks to ensure they cannot be used as weapons of opportunity<br>6. Trained employees for LPG installation and cylinder replacement<br>7. Refilled tanks or bottles delivered, no recharging or filling of tanks or bottles at the site<br>8. Post Facility Managers or Post Occupational Safety and Health Officers (POSHO) must coordinate inspections of residences/apartment buildings, which have natural gas and ensure the local gas authority has certified lines and valves<br>
-
All Gas Service<br>1. Supply through rigid pipe (iron or steel), or tubing (steel, brass, or copper)<br> a. Exceptions for seismically active areas‐see Seismic Safety<br>2. Interior manual shut‐off valve accessible and within 1.8 meters (6ft) of appliance<br>3. Secured to ensure safe against weapons of opportunity<br>4. Leak detection using soapy water or other means must be conducted over all fittings and connections during cylinder or appliance replacement or anytime supply line work is done<br>5. Post Facility Managers or Post Occupational Safety and Health Officers (POSHO) must coordinate inspections of residences/apartment buildings, which have natural gas and ensure the local gas authority has certified lines and valves.
FIRE AND LIFE SAFETY
-
Emergency Egress<br>Adequate emergency egress can vary with the type of building. Consult the Fire Protection Guide(FPG) for guidance.
-
Maximum Travel Distance to an Exit<br>1. Without fire suppression or detection systems: 30 meters (100 ft)<br>2. With complete fire detection system and sprinkler protection in selected areas: 46 meters (150 ft)<br>3. With complete fire sprinkler system: 61 meters (200 ft)
-
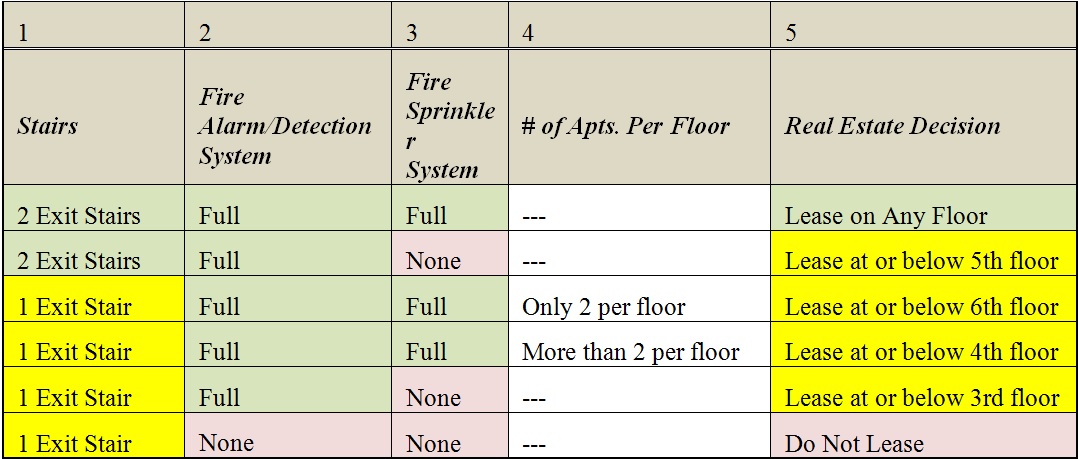
High Rise Matrix
-
Smoke Alarms<br>1. All sleeping rooms<br>2. Outside of each separate sleeping area, in the immediate vicinity of the sleeping rooms<br>3. On each level of the dwelling unit, including basements<br>4. Placement should be on the ceiling, or alternately on a wall between 10 centimeters (4 in) to 30.5 centimeters (12 in) away from the ceiling<br>5. Occupants instructed to check detectors monthly for proper operation
-
Portable Fire Extinguishers<br>1. One Department standard 10 lb. (4.45 kg) extinguisher (4‐A:40‐B:C) Wall mounted in or near each kitchen
-
Alarm Systems<br>1. Several factors influence automatic fire alarm detection and/or automatic fire suppression system requirements<br>2. Consult the Fire Protection Guide (FPG) and contact OBO/OPS/FIRE
-
Lighting<br>1. Apartment buildings or congregate residences with 10 or more occupants: public space, hallway, stairway, or other means of egress must have illumination of 1 foot candle power at floor level<br>by emergency lighting<br>2. If emergency generator is not available to provide emergency lighting, provide battery‐powered emergency lights in public spaces, hallway, stair way or other means of egress installed and maintained correctly<br>3. All emergency light fixtures shall have 90 minutes battery backup regardless of generator power availability.
-
Exit Signs<br>1. Exit doors in public corridors on floors with sleeping accommodations:<br>2. Illuminated exit signs<br>3. Directional signs if path is not straight or the exit is less than obvious
-
Window Grilles<br>1. Operable from the inside<br>a. Minimum opening: 5.7 ft2 (0.529 m2)<br>b. Minimum dimension: 20” (51 cm) x 41.1” (104.4 cm) OR 34.2” (86.9 cm) x 24” (61 cm) and not be more than 44’’ from the floor<br>c. Bars or grilles must have inside release mechanism
WATER HEATER PROTECTION
-
Temperature and Pressure Relief Valves<br>1. Separate temperature and pressure relief valves (PRV and TRV) or combination temperature and pressure relief valves installed.<br>2. TPRV drain piping installed to direct discharge to floor<br>3. TPRV drain piping is not reduced, threaded at the end, and has no uphill runs<br>4. TPRV drain piping has no other valve downstream of TPRV<br>5. Water temperature is not above 120 degrees F (49 degrees C) at the point of use
PLATE GLASS SAFETY
-
Tempered/Safety Glass Locations<br>1. Locations listed below need to ensure that glass is tempered, mylar coated, a non‐breakable replacement material or protected by a barrier. Decals or markings should be used where the presence of glass is not easily seen.<br>2. Entry and exit doors, storm doors, glass sliding doors<br>3. Windows located within 46 centimeters (18 in) of the floor<br>4. Doors and enclosures for bathtubs, showers, sauna<br>5. Stairway enclosures and handrail panels
GARAGE DOOR SAFETY
-
Safety Features <br>1. Inherent reversal system. This system can be a photo eye, a door edge sensor, or any other device that provides equivalent protection. If an electric eye is used, it should be installed at a height of 4 to 6 inches above the floor.
-
Design <br>1. Door is properly balanced. A properly balanced garage door will stay in place when stopped in any partially open position.<br>2. Install the push button wall control as high as practical on the garage door’s wall to restrict children's access to it. Ensure remotes are out of reach of children and that children are educated about the potential dangers with these mechanisms and the garage doors they operate.
-
Maintenance 1. Ensure garage doors are inspected annually and preventative maintenance is conducted routinely.<br> a. Manually check door springs, hinges, cables, rollers and/or bearings, and ensure that reversal <br> system sensors are clear and free of obstruction.<br> b. Check door insulation for pest harborage and ensure insulation is intact.<br> c. Door should go up and down easily when operated manually.<br> d. Door opener should be attached with a reinforcement bracket.
ELECTRICAL
-
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters 1. Installed for wet locations (indoors or outdoors) and all kitchen countertop outlets at the outlet or the circuit breaker:<br> a. 110‐volt systems, installed GFCIs trip at 4 to 6 mA<br> b. 220‐volt systems, installed GFCIs trip at 10 mA<br>2. Do not install outlets where local code prohibits them in certain wet locations
-
Appliance Cords <br> 1. In good condition, insulated, and provided with a plug.
-
Grounding 1. A grounding electrode connected to panel at the service entrance and bonded to the neutral (grounded) conductor. Impedance of the ground path for any made electrodes may not exceed 25<br>ohms, as measured using appropriate stake or stakeless ground resistance testing equipment. Verify and, if missing, contact the FIR/FAC Help Desk via e‐mail (obo@cesengineers.com) or call 866949‐6751 for assistance with grounding system installation.
-
Electric Service Supply & Panels<br>1. Missing knock‐outs and twist‐outs in breaker panel(s) must have fill plates<br>2. Breaker panel front working clearance of 30" (76cm) wide x 36" (92cm) deep<br>3. Breakers labeled as to function/area served<br>4. Outdoor outlets are GFCI and have weatherproof boxes
-
Circuit Capacity<br>1. Review usage and capacity and avoid excessive electrical loads. <br> a. Verify that the following most commonly used branch circuit connectors in residences are protected <br> by fuses or circuit breakers having trip elements not larger than:<br><br> Wires (Comparable U.S. Wire Size) Trip Setting<br> 1.5 mm2 (smaller than #14 AWG, 15A) 10A<br> 2.5 mm2 (smaller than #12 AWG, 20A) 16A <br> 4 mm2 (smaller than #10 AWG, 30A) 25A <br> 6 mm2 (smaller than # 8 AWG, 50A) 40A<br> 10 mm2 (smaller than # 6 AWG, 65A) 50A<br> 16 mm2 (smaller than # 4 AWG, 85A) 60A
FALL PROTECTION
-
Railings 1. Installed on all porches, balconies and raised floor surfaces more than 76 centimeters (30 in) above the floor or grade below<br>2. Sturdy supports (balusters) with no openings larger than 10 centimeters (4 in) and bottom of railing assembly no more than 10 centimeters from the floor and can withstand the force of 91 kilograms (200 lbs) in any direction.<br>3. Guardrails at a minimum height of 91 centimeters (36 in) (107cm/42 in is recommended) for balconies, decks, elevated patios, and other similar structures for single family and duplex housing<br>units.<br>4. Guardrail installation at apartments and representational areas open to the public must be 107 centimeters (42 in) high
-
Stairs and Handrails<br>1. For open stairways, supports (balusters) no more than 10 centimeters (4 in) apart. Triangle formed by <br> riser, tread and bottom guardrail element does not allow passage of sphere 152 millimeters (6 in) in <br> diameter<br>2. Handrails installed for stairways at 86‐97 centimeters (34‐38 in)<br>3. Stair riser height maximum 196 millimeters (7.75 in), treads minimum depth 254 millimeters (10 in)<br>4. Stairways are not to be less than 91 centimeters (36 in) in clear width at all points above the handrail <br> height<br>5. Spiral stairway treads must have a minimum tread width of 66 centimeters (26 in). Treads shall have a <br> minimum tread depth of 190 millimeters (7.5 in) measured at a point 305 millimeters (12 in) from the <br> side where the treads are narrower.<br>6. Handrails and the top rails of stair rail systems are capable of withstanding, without failure, a force of <br> at least 91 kilograms (200lbs) applied within 5 centimeters (2 in) of the top edge, in any downward or <br> outward direction, at any point along the top edge.
-
Homes with Small Children<br>1. Latching device on windows that allows opening no more than 10‐13 centimeters (4‐5 in), but window <br> remains operable<br>2. Furniture away from windows and railings
SWIMMING POOLS
-
Barrier and Other Safety Features <br>1. Barrier: A permanent, 4‐sided, non‐climbable barrier (fence, wall, etc.) ≥ 122 centimeters (4 ft) height that prevents direct access from living areas and excludes ancillary activities (e.g., barbecues, bars, ping‐pong tables).<br> a. Self‐closing, self‐latching, lockable hardware on all access points (gates/doors) with latch release ≥ <br> 137 centimeters (54in) . Alternatively, the latch release can be on the pool side of the gate if ≥ 7.6 centimeters (3 in) below the top with no opening > 1.3 centimeters (0.5 in) within 4.5 centimeters (18<br>in) of the release.<br> b. Gates/doors must open away from the pool.<br> c. Barrier distance from pool must be between 1.5m and 5.2m (5 – 17 ft) to allow for emergency <br> response and to exclude ancillary activities.<br>2. Other:<br> a. No entrapment hazards<br> b. Rescue equipment available (shepherd’s crook, pole, ring buoy) and in plain view<br> c. Depth markings and no diving indicated. Safety rules posted at community use pools and residential <br> use pools that are used as community use pools, i.e., CMR, MSGR<br>d. First aid kits and emergency communication means for community use pools and residential use <br> pools that are used as community use pools<br>e. Outlets equipped with Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) and covers<br>f. Pool chemicals stored separate from other materials in a cool, dry, ventilated area with restricted <br> access<br>g. Drain covers are being replaced every 5 years
ELEVATORS
-
Elevator Lobby & Car<br>1. All elevator cars have functional doors independent of shaft doors<br>2. Elevator doors (car & shaft) reverse direction when an object is either contacted by the leading edge of the door or detected by an electronic door protection device<br>3. All external car operating features, lobby controls and hardware are intact and function properly<br>4. Car operating buttons, including the emergency alarm button, function properly.<br>5. Car lights are on, and bulbs or tubes are secure.<br>6. Car service panel is locked<br>7. Car emergency phone is connected to a 24‐hour operator and car’s audible signals are operating<br>8. All door mechanisms are enclosed to avoid pinch/shear points
-
Machine Room & Maintenance<br>1. Machine room access door is locked, and keys stored securely<br>2. Good housekeeping, no trash, not being used as a storage area, no excessive oil leaks, control cabinet(s) intact<br>3. Illumination is adequate to perform inspection<br>4. ABC fire extinguisher located in machine room<br>5. Temperature is not above 49 degrees C (120 degrees F)<br>6. Elevator is under a service contract and service logbook is utilized and up to date<br>7. Elevator has a current safety certificate
ENVIRONMENTAL
-
Air Pollution (For Level 1 or higher air pollution posts)<br>1. At least 150 meters away from major roadway (recommended)<br>2. No other nearby air pollution sources [e.g., drycleaner or large fueling station (14M l/year) within 100m]<br>3. Property barrier and vegetation (recommended)<br>4. Centralized air filtration (otherwise room air cleaners may be needed)
-
Asbestos<br>1. Acquisitions: asbestos inspection conducted, and risk of asbestos determined<br>2. Asbestos materials identified and maintained in good condition<br>3. Maintenance and minor renovations avoid disturbance of asbestos materials<br>4. If asbestos material is to be disturbed, it is removed
-
Leaded Paint<br>1. Only lead‐free paint is applied (e.g., < 90 ppm in dried paint film)<br>2. Painted surfaces in good condition with minimal damage<br>3. Paint sampled prior to renovation or major maintenance work<br>4. Leaded paint removed prior to start of work or minimize disturbance
-
Pesticides<br>1. Building conditions or location not inviting to common local pests<br>2. No history of chronic pest problems or extensive pesticide use<br>3. Willing and capable to implement Integrated Pest Management(IPM) program in USG occupied space<br>4. Habitats and attractants to common pests avoided<br>5. Self‐help measures, to include self-help education, are available to control pests (if control measures are not effective)<br>6. Professional pesticides, used outdoors only, are a last resort and limited to Department‐authorized products
-
Water Quality<br>1. Tap water is potable (microbiologically safe and within acceptable contaminant levels listed in the <br> Department’s drinking water standards)<br> a. If there are multiple zones, they are noted on the QC program<br>2. If tap water is not potable, then supplemental means [e.g., pointof‐ use (POU) device such as a <br> distiller or bottled drinking water] are used to render the water potable and quality control <br> monitoring is done<br>3. Water used for bathing water and other contact uses meets recreational water criteria<br>4. If supplemental treatment is employed, O&M and QC programs are in place<br>5. Unless a lead‐removing POU is employed, water from the main taps is confirmed by testing to have <br> lead levels below 15 ppb
SEISMIC ISSUES (FOR POSTS IN SEISMIC ZONES 2B, 3 OR 4)
-
Seismic Safety<br>1. Seek seismically best available structures in accordance with expectations outlined in 19 STATE 74458 and in collaboration with OBO's Climate Security & Resilience Program<br>2. Generators should be securely anchored (ground or slab) at all anchorage points of the frame, and generator connections should be flexible (earthquake resistant).<br>3. Propane tanks, kerosene heaters: use flexible connections to the tank and anchor storage tanks to the ground, fence, or wall to prevent tipping.<br>4. Water heaters, propane (LPG) gas cylinders and natural gas:<br> a. Use flexible, metallic connections for water and gas lines<br> b. Use metal straps which are bolted using expansion bolts to a masonry/concrete wall, or lag bolts to <br> a wood stud wall, at the top and bottom of the water heater and propane cylinders<br> c. Block in space between water heater and wall to prevent rocking<br>5. Heavy and tall furniture such as bookcases should be secured to prevent sliding or tipping, using L‐brackets or other device and remove casters or wheels to prevent rolling<br>6. Check for weaknesses in chimneys such as damage or missing bricks. If roof is not composed of concrete, verify that the max height above the roof line is no more than 2 times the least side<br>dimension (or chimney is braced)<br>7. Ensure cabinet latches are strong enough, especially in the kitchen, to prevent contents from falling out; install safety latches for added security<br>8. Brace and bolt storage racks and shelves to the floor and walls and secure contents so they can’t slide off<br>9. Mini‐split HVAC Units: To prevent tipping, confirm secure anchorage/attachments to all anchorage points for the unit
Local Considerations
-
List any additional local considerations
Footnotes and Legend
-
Key Citations
15 FAM 250 Housing Program Management including Safety, Health and Environmental requirements including requirements for properties under consideration for purchase or lease and prior to occupancy
a.k.a. "POSHO certification” requirement for properties under consideration for purchase or lease and prior to occupancy
15 FAM 800 Scope, policy, and authorities of the Fire Protection Program for overseas posts
15 FAM 840 Procedures and guidelines for fire protection equipment
15 FAM 900 Scope, policy and authorities of the Safety, Health and Environmental Management Program Abroad
15 FAM 950 Standards including the swimming pool safety, carbon monoxide, integrated pest management, and drinking water safety standards under 15 FAM 900.
15 FAM 970 Safety, Health, and Environmental Requirements for Real Property -
References Air Quality Hub Air Quality Hub
ASHRAE ASHRAE Handbook ‐ Fundamentals
FPG OBO/OPS/FIR's Fire Protection Guide
Earthquake Preparedness Earthquake Preparedness at US Foreign Service Posts
IBC International Building Code
IFGC International Fuel Gas Code
IMC International Mechanical Code
IRC International Residential Code
NEC National Electrical Code
NFPA 101 National Fire Protection Association
SHEM Resource Guide OBO/OPS/SHEM's Safety/Occupational Health and Environmental Management Resource Guide -
OBO Program Offices
CFSM/FAC Facilities Management
OPS/FIRE Office of Fire Protection
OPS/SHEM Safety, Health, and Environmental Management
PDCS/DE Office of Design and Engineering
PDCS/DE/CSE Office of Design and Engineering Civil/Structural Engineering Division
PDCS/DE/CSE (CS&R) OBO’s Climate Security & Resilience Program (situated within PDCS/DE/CSE)
PDCS/DE/EE Office of Design and Engineering Electrical Engineering Division
PDCS/DE/ME Office of Design and Engineering Mechanical Engineering Division -
I certify that all the information listed in the above report are correct and true.
-
POSHO
-
POSHO Assistant