Information
-
Incident Investigation Title
-
Document No.
-
Client / Site
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Personnel
-
Date and time of incident:
Incident summary from report
-
Provide a summary of the incident:
-
Add media
Task being conducted:
-
Enter details of task being conducted:
Persons involved / Witnesses
-
Name: Position: Location at time of incident:
Reference documentation:
-
SOP used?
-
Documents used?
-
Work activity briefing?
Immediate Actions:
-
List immediate actions taken as a result of the incident:
Supplementary Actions:
-
List supplementary actions taken:
Time line / Sequence of events:
-
Enter the sequence of events from initial report and interviews:
-
Add photos as required
-
Add drawing
STEP 1: Determine type of Incident
Accident:
-
Collision
-
Explosion
-
Fire
-
Hazardous substance release
-
Occupational
-
Other:
Crime:
-
Fraud
-
Hijacking
-
Industrial espionage
-
Sabotage / Vandalism
-
Theft
-
Violent crime
-
Crime
-
Other:
Environmental impact:
-
Impact
-
Pollution
-
Spillage
-
Erosion
-
Emission
-
Other:
Equipment Failure:
-
Component
-
Structural
-
Other:
Human Resources Occurrence:
-
Disputes
-
Go slow / Work to rules
-
Social demands
-
Strikes
-
Other:
Industry specific Incident:
-
Please specify:
Natural Event:
-
Earthquakes
-
Flooding
-
Hurricane / tornado
-
Lighting
-
Wind
-
Other:
Non-conformances:
-
Legal
-
Quality
-
Environmental
-
Health and safety
-
Financial
-
Other:
Product Interruption
-
Raw material
-
Supplier failure
-
Utility failure
-
Other:
Resources Wastage
-
Logistical
-
Other:
STEP 2: Identify all consequences / losses resulting from the incident / event (What were the consequences?)
Losses
-
Damage
-
Illness
-
Injury
-
Death
-
Production Losses
-
Asset losses
-
Civil liability
-
Criminal liability
-
Vicarious liability
-
Financial loss
-
Image / reputation loss
-
Sub-standard quality / product. / service
-
Customer / market share loss
-
Loss of employees / staff. - resignation
-
Other:
STEP 3: For each loss that was due to exposure to / contact with a source of energy or with a substance, identify the way in which the contact occurred as well as the agency ( primary item / substance inflicting the injury, damage, etc.)
Type of contact:
-
Caught between or under (crushed / amputated)
-
Caught in (pinch / nip points)
-
Contact on (snagged, hung)
-
Contact with (electricity / heat / cold / radiation / chemical / noise)
-
Drowning (inundation)
-
Fall from elevation to lower level
-
Fall on same level (slip / and fall, trip over)
-
Handling (lifting / pushing / pulling)
-
Over stress (overexetion / overload / overexposure / ergonomic )
-
Struck against (running / bumping into)
-
Struck by (hit by moving object)
-
Other:
General agency
-
Aircraft
-
Animals / insects / people
-
Building / structure
-
Compressed air
-
Container
-
Expired product
-
Equipment
-
Electricity
-
Explosive device
-
Fall of ground
-
Fire
-
Fixed walkway
-
Hand tools
-
Installation
-
Locomotive
-
Ladder / stairs
-
Lifting equipment
-
Material goods
-
Machinery
-
Metal - cold
-
Metal - hot
-
Motor vehicles
-
Natural phenomenon
-
Obstruction
-
Sharp edge
-
Surface
-
Transport
-
Trucking / tramming
-
Trackless machines
-
Vessels
-
Other:
Occupational hygiene agency
-
Biological
-
Chemical
-
Cold
-
Dust
-
Ergonomically
-
Fumes
-
Gases
-
Heat
-
Illumination
-
Noise
-
Psychological
-
Radiation
-
Smoke
-
Vapors
-
Vibration
-
Other:
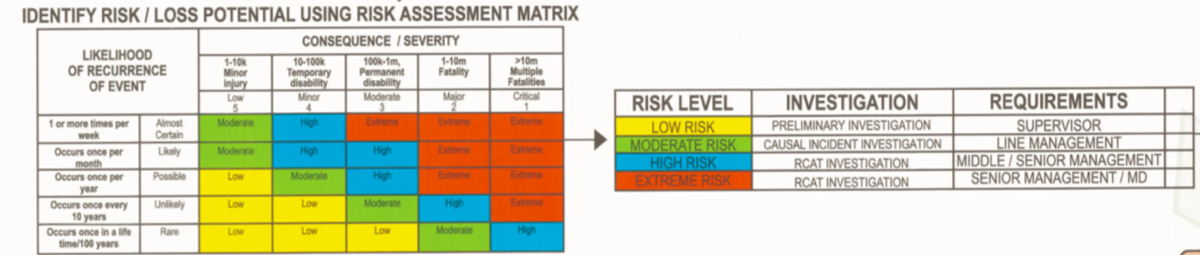
STEP 4: Determine the risk for this incident, considering the likely recurrence of the event and potential worst-case consequences of the event, should it occur again, in order to determine the level of investigation and management involvement and then gather evidence
-
Identify RISK / LOSS potential using Risk Assessment matrix
Risk level / Investigation / Requirements
-
LOW RISK - Preliminary Investigation - Supervisor
-
MODERATE RISK - Causal incident investigation - Line / Site Manaagment + Safety Officer
-
HIGH RISK - RCAT investigation - MIDDLE / SENIOR Management + SHEQ Corodinator / Group SHEQ Management
-
EXTREME RISK - RCAT Investigation - Divisional Manager / Group SHEQ Manager
Gather incident information / evidence (facts) - DO NOT DISTURB SCENE WITHOUT APPROVAL FROM CLEINT + GROUP SHEQ MANAGER
-
“WHO” - People evidence Important pointers: - witnesses are not limited to eyewitnesses - witnesses may be fearful / ill - do not lead the witnesses or force answers - do not argue with / refute the witness
-
List of people interviewed and titles (ask people to write written statements as well / record if need be)
-
“WHERE” - Position Evidence Important pointers: - accuracy of information is critical - Record locations of all principal elements - use drawing / mapping / photography - video if needed - keep accurate photo logs
-
Photos of scene / equipment / people / injury / building / surroundings / weather / landmarks
-
Add drawing if required
-
What “PARTS” Evidence Important pointers: - some overlap with position evidence - chain of custody consideration - can be liquids /gases / not just solids - must be protected - undamaged parts may tell as much as damaged parts - some physical evidence will require scientific interpretation
-
List of possible parts evidence:
-
“WRITTEN” Paper evidence Important pointers: - potentially the most durable evidence - can directly reveal underlying causes
-
List all paper evidence:
-
“HOW” - process evidence Important pointers: - identify process (production / project) conditions - identify where normal parameters where not met - identify abnormalities - identify the physical environment and especially sudden changes to that environment, is factors that need to be identified. The situation at the time of the accident is what is important, not what the usual conditions were
-
Comments:
-
“REENACTMENT / RECONSTRUCTION” of incident
STEP 5: Identify the immediate causes
SUB-STANDARD ACTS / AT-RISK BEHAVIOR. Identify the possible individual or team actions that contributed to the incident
1. Following procedures / practices / rules / standards
-
Deviation by individual
-
Deviation by group
-
Deviation by Supervisor
-
Operation of equipment without authority
-
Improper position or posture for the task
-
Overexertion of physical capability
-
Work or motion at improper speed
-
Improper lifting
-
Improper loading
-
Short-cuts
-
Other:
Use of tools or equipment
-
Improper use of equipment
-
Improper use of tools
-
Use of defective equipment (aware)
-
Use of defective tools (aware)
-
Improper placement of tools / equipment / or materials
-
Operation of equipment at improper speed
-
Servicing of equipment in operation
-
Other:
Use of protective methods
-
Lack of knowledge of hazards present
-
PPE not used
-
Improper use of PPE
-
Servicing of energized equipment
-
Equipment / materials not secured
-
Disabled guards / warning systems / safety devices
-
Removal of guards / warning systems / safety devices
-
PPE not available
-
Other:
In attention / lack of awareness
-
Improper decision making or lack of judgement
-
Distracted by other activities
-
Inattention to footing and surroundings
-
Horseplay
-
Acts of violence
-
Failure to warn / make safe
-
Use of drugs and alcohol
-
Routine activity without thought
-
Other:
SUB-STANDARD CONDITIONS / “AT RISK” CONDITIONS: Identify the possible conditions that contributed to the incident
Protective systems
-
Inadequate guards or protective devices
-
Defective guards or protective devices
-
Inadequate PPE
-
Defective PPE
-
Inadequate warning systems
-
Defective warning systems
-
Inadequate isolation of process or equipment
-
Inadequate safety devices
-
Defective safety devices
-
Other:
Transportation equipment and tools
-
Defective vehicles / vessels / aircraft / and rolling stocks
-
Inadequate vehicles / vessels / aircraft / and rolling stocks
-
Improperly prepared vehicles / vessels / aircraft / and rolling stocks
-
Defective equipment
-
Inadequate equipment for the purpose
-
Improperly prepared equipment
-
Defective tools
-
Inadequate tools
-
Improperly prepared tools
-
Other:
Work exposure to
-
Fire / explosion
-
Noise
-
Energized electrical systems
-
Energized systems other than electrical
-
Radiation
-
Temperatures extremes
-
Hazardous chemicals
-
Mechanical hazards
-
Clutter of debris
-
Storms / acts of nature
-
Slippery floors / walkways
-
Other:
Work place environment / layout
-
Congestion / restricted motion
-
Inadequate / excessive illumination
-
Inadequate ventilation
-
Unprotected height
-
Inadequate workplace layout: - demarcation inadequate - controls inadequate - displays inadequate - labels inadequate - locations out of reach or sight - conflicting information is prescribed
-
Other:
STEP 6: Identify the root (basic) causes
HUMAN FACTORS - Identify the possible human factors that contribute to the immediate causes
Inadequate physical capability
-
Vision deficiency
-
Hearing deficiencies
-
Other sensory deficiencies
-
Reduced respiratory deficiency
-
Other permanent physical disabilities
-
Temporary disabilities
-
Inability to sustain body positions
-
Restricted range of body movements
-
Substance sensitivities or allergies
-
Inadequate size / strength
-
Diminished capacity due to medication
-
Diminished capacity due to inadequate intake of substance
-
Other:
Inadequate physical condition
-
Previous injury or illness
-
Fatigue: - due to workload - due to lack of rest - due to sensory overload
-
Diminished performance: - due to temperature extremes - due to oxygen deficiency - due to atmospheric pressure variation
-
Blood sugar insufficiency
-
Impairment due to drug / alcohol use
-
Other:
Inadequate mental state
-
Poor judgement
-
Memory failure
-
Poor coordination or reaction time
-
Emotional disturbance
-
Fears / phobias
-
Low mechanical aptitude
-
Low learning aptitude
-
Influenced by medication
-
Other:
Mental stress
-
Preoccupation with problems
-
Frustration
-
Confusing directions / demands
-
Conflicting directions / demands
-
Meaningless / degrading activities
-
Emotional overload
-
Extreme judgement / decision demands
-
Extreme concentration / perception demands
-
Extreme boredom
-
Other:
Behavior
-
Improper performance is rewarded: - saves time / effort - avoids discomfort - gains attention
-
Improper supervisory example
-
Inadequate identification of critical safe behaviors
-
Inadequate reinforcement of critical safe behaviors: - proper performance is critiqued - inappropriate peer pressure - inadequate performance feedback - inadequate disciplinary process
-
Inappropriate aggression
-
Inappropriate use of production incentives
-
Supervisor implied haste
-
Employee perceived haste
-
Habit / personal preference
-
Vandalism
-
Other:
Inadequate skill level
-
Inadequate assessment of required skills
-
Inadequate practice of skill
-
Inadequate performance of skills
-
Lack of coaching on skill
-
Insufficient review of instruction to establish skill
-
Other:
WORKPLACE FACTORS - Identify the workplace factors that contributed to the immediate cause
Inadequate training / knowledge transfer
-
Inadequate knowledge transfer: - inability to comprehend - inadequate instructor qualifications - inadequate training equipment - misunderstood instructions
-
Inadequate recall of training material: - training not reinforced on the job - inadequate refresher training frequency
-
Inadequate training effort: - inadequate training programme design - inadequate training goals and objectives - inadequate new employee orientation - inadequate initial training - inadequate means to determine if qualified for job
-
No training provided: - need for training not identified - training records incorrect or out of date - new work methods introduced without training - decision made not train
-
Other:
Inadequate management / supervision / employee leadership
-
Conflicting roles / responsibilities: - unclear reporting relationships - conflicting reporting relationships - unclear assignment of responsibility - conflicting assignment of responsibility - improper or insufficient delegation of authority
-
Inadequate leadership: - standards of performance missing or not enforced - inadequate accountability - inadequate / incorrect performance feedback - inadequate work site walkthrough - inadequate safety promotion
-
Inadequate correction of prior hazards / incident
-
Inadequate identification of worksite / job hazards
-
Inadequate management of change system
-
Inadequate incident reporting / investigation system
-
Inadequate or lack of safety meetings
-
Inadequate performance measurement and assessment
-
Other:
Inadequate contractor selection & oversight
-
Lack of contractor pre-qualifications
-
Inadequate contractor pre-qualifications
-
Inadequate contractor selection
-
Use of non-approved contractor
-
Lack of job oversight
-
Inadequate oversight / supervision
-
Other:
Inadequate engineering / design
-
Inadequate technical design: - design input obsolete - design input not correct - design input not available - design output inadequate - design input not feasibly - design output not clear - design output not correct - design output not consistent - no independent design review
-
No / inadeqaute risk assessment
-
Inadequate standards / specifications / and / design criteria
-
Inadequate assessment of potential failure
-
Inadequate ergonomic design
-
Inadequate monitoring of construction
-
Inadequate assessment of operational readiness
-
Inadequate monitoring of initial operation
-
Inadequate evaluation and / documentation of change
-
Other:
Inadequate purchasing / material control and material handling
-
Incorrect item received: - inadequate specifications to vendor - inadequate specifications on requisition - inadequate control on changes to orders - unauthorized substitution - inadequate product acceptance requirements - no acceptance verification performed
-
Inadequate research on materials / equipment
-
Inadequate mode or route of shipment
-
Improper handling of materials
-
Improper storage of materials / spare parts
-
Inadequate material packaging
-
Material shelf life exceeded
-
Improper identification of hazardous material
-
Improper salvage and / waste disposal
-
Inadequate use of safety & health data
-
Other:
Inadequate tools / equipment
-
Inadequate assessment of needs and risks
-
Inadequate human factors / ergonomic considerations
-
Inadequate standards
-
Inadequate availability
-
Inadequate adjustment / repair / maintenance
-
Inadequate salvage and reclamation
-
Inadequate removal / replacement of unsuitable items
-
No equipment record history
-
Inadequate equipment record history
-
Other:
Inadequate work rules / polices / standards / procedures
-
Lack of PSP for the task: - lack of defined responsibilities for PSP - lack of critical task / job safety analysis
-
Inadequate development of PSP: - inadequate coordination with process / equipment design - inadequate employee involvement in the development - inadequate definition of corrective actions - inadequate format for easy use
-
Inadequate implementation of PSP due to deficiencies: - contradictory requirements - confusing format - more than one action per step - no check-off spaces provided - inadequate sequence of steps - confusing instructions - technical error / missing steps - excessive references - potential situations not covered
-
Inadequate enforcement of PSP: - inadequate monitoring of work - inadequate supervisory knowledge - inadequate reinforcement - non-compliance not corrected
-
Inadequate communication of PSP: - incomplete distribution to work groups - inadequate translation to appropriate languages - incomplete integration with training - out of date revisions still in use
-
Inadequate task observation of PSP
-
Other:
Inadequate communication
-
Inadequate horizontal communication between peers
-
Inadequate vertical communication between supervisor and person
-
Inadequate communication between different organizations
-
Inadequate communication between work groups
-
Inadequate communication between shifts
-
Inadequate communication methods
-
No communication method available
-
Incorrect instructions
-
Inadequate communication due to job turnover
-
Inadequate communication of safety and health data / regulations / guidelines
-
Standard terminology not used
-
Verification / repeat back techniques not used
-
Messages to long
-
Speech interference
-
Cultural / ethnic communication barriers
-
Other:
STEP 7: Identify the systems deficiencies that contributed to the existence of the root cause
-
Review status of current / system control activities:
S: Are there systems standards for this activity: YES / NO. If NO check and begin by developing system standards
STD: Are existing standards adequate? YES / NO. If NO check and develop adequate standards
C: Is there full compliance with standards? YES / NO. If NO check and develop means to ensure compliance
Planning and leadership
-
Planning and implementing
-
Resourcing
-
Management commitment
-
Document and data control
-
Committees and employee involvement
-
External regulations and standards
-
External relations
-
Management reviews
Competency / training / and communication
-
Employee orientations / awareness
-
Competency & training needs identified
-
Training program content and delivery
-
Training program effectiveness
-
One on one communication
-
Group SHEQ Meetings
-
Program promotions
Management of operational risk and change
-
Identification of operational risk
-
Operational analysis
-
Significant task identification and analysis
-
Management of change
-
Task and operation controls
Operational management and design
-
Planning for product realization
-
Processes related to interested parties
-
Design and development
-
Production and service function
Purchasing systems
-
Equipment / materials and suppliers
-
Contractors
Work processes and operating permits
-
Organization permits and high risk work controls
-
Externally required permits
-
Organization SHEQ rule program
Inspections
-
Planned general inspections
-
Specialized SHEQ equipment inspections
-
Mobile and material handling equipment
-
Engineering maintenance systems
-
Statutory compliance
-
House keeping inspections
Occupational health systems
-
Occupational health administration
-
Hazard recognition and evaluation
-
Hazard controls
-
Occupational hygiene monitoring
-
Occupational medicine
-
Records
PPE
-
PPE requirements
-
PPE availability
-
PPE Compliance
Incident / NCR / investigation and analysis
-
Incident / NCR investigation process
-
Middle and senior management participation
-
Incident / NC analysis
-
Record keeping
Emergency preparedness
-
Emergency preparedness administration
-
Emergency response plans
-
Emergency response teams
-
Emergency equipment
-
Mutual aid
Measurement / monitoring and audits
-
Routine process measurements
-
System audits
Corrective and preventative action systems
-
Corrective and preventative action process
-
Corrective and preventative action communication
-
Control of NC product
-
Other:
Conclusions:
-
Enter investigation conclusions:
Recommendations:
-
Enter recommendations for corrective action:
-
Target date:
-
Signature of investigating officer:
-
Suggestions/ recommendations from safety committee
-
Signature of Section 16.2 manager:
-
Signature of Section 16.1 manager: