Title Page
-
Inspection
-
Regulatory Requirements
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Client Name
-
Additional time for off-site report writing
-
During this visit, we will audit the scaffolding activities and documentation available on-site at the time of inspection. Our inspection will measure the compliance of scaffolds with the Work at Height Regulations 2005 (WAHR), various National Access and Scaffolding Confederation (NASC) guidance documents, including TG20 (NASC Guidance on the application of BS EN 12811) & SG4 (Preventing Falls in Scaffolding), System Scaffold Manufacturer's Instructions, and any available design information.
The Working at Height Regulations, Schedule 3, Part 2 states that scaffolds should have strength and stability calculations carried out unless a note of the calculations, covering the structural arrangements contemplated, is available, or it is assembled in conformity with a generally recognised standard configuration. This means that scaffolds have two options:
1. They can be designed by calculation by a competent design engineer, or
2. They can be constructed in accordance with a known standard (TG20 for tube and fitting scaffolds, Manufacturer's instructions for system or aluminium scaffolds).
Scaffolds erected in accordance with the appropriate standard will be legally compliant. TG20 compliant scaffolds can be inspected against a TG20 Compliance sheet that can be generated within the TG20 eGuide.
Duties of Persons Using Scaffold
-
The Client is responsible for ensuring the scaffold is only used as defined in the client brief and the loading and limitations stated in the handover certificate are not exceeded. The client should inform ESS Contracts Managment of any damage caused to the scaffold and any movement or distress so these matters may be corrected.
-
The Client is responsible for ensuring fall prevention measures are checked before the scaffold is used in accordance with regulation 13 of the Work at Height Regulation 2005.
-
If the client fails to inform the ESS contracts Manager of any damage, misuse or the failure to inspect, then the ESS responsibility for the scaffold will be reduced by the extent of that damage, misuse or failure to impact.
-
During any work on the building or structure that may result in materials being displaced or removed, where there could be risk of significant items falling onto persons below, the client should assess the need for adequate containment. The client should then inform ESS contract management if the containment already on the scaffold requires upgrading.
-
Unauthorised Scaffold Modifications - It is the client responsibility that any individuals using the scaffolding structure must not make any alternations to it under any circumstances. The unautorised modification of scaffolding by unqualified operatives can result in fatalities or serious injuries to site personnel or the general public, can result in property damage, may invalidate insurance cover and could be an offence against the individual under section 7 of the Health and Safety at Work Act. Scaffolding may only be modified by competent scaffolders who have been autorised to do so by ESS contracts managment
1. Site Conditions
-
1.1 Adequate welfare facilities, clean, tidy and maintained?
- Safe
- Fair
- Poor- Improvement required
- At Risk - Accumulation of waste materials and all surplus to be cleared and removed from the site by the relevant contractor.
- Yes
- No
- Other
- N/A
-
1.2 Adequate safety signage in place , and fixed where required ?
- Safe
- Fair
- Poor- Improvement required
- At Risk - Accumulation of waste materials and all surplus to be cleared and removed from the site by the relevant contractor.
- Yes
- No
- Other
- N/A
-
Site Safety Signage
-
1.3 Location and description of workplace (Including any plant, equipment or materials) inspected:
- Independent Tied Access Scaffold
- Loading Bay
- Access Staircase
- Protection Gantry
- Birdcage Scaffold
- Gin Wheel and Rope
- Harness and Lanyard
- Edge Protection Guard Rail
- HAKI Access Staircase
- Other Specify
2. Scaffold Surroundings
-
2.2 Has public protection been provided?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
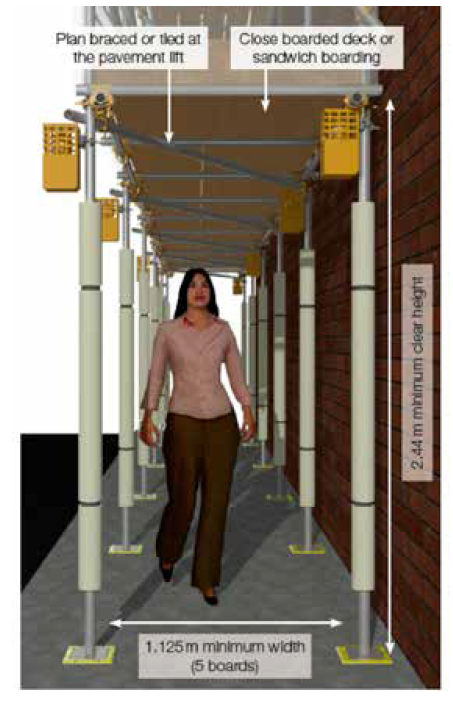
A pavement lift allows members of the public – after erection – to walk under the first lift of scaffolding on a public pavement. Free passage is achieved by omitting the ledger bracing below the first lift and by increasing the first lift height to provide sufficient headroom, with additional ties or plan braces fitted to stabilise the scaffold.
The pavement lift may be supplanted with safety features such as lighting, protective boarding or foam padding
around the uprights etc). -
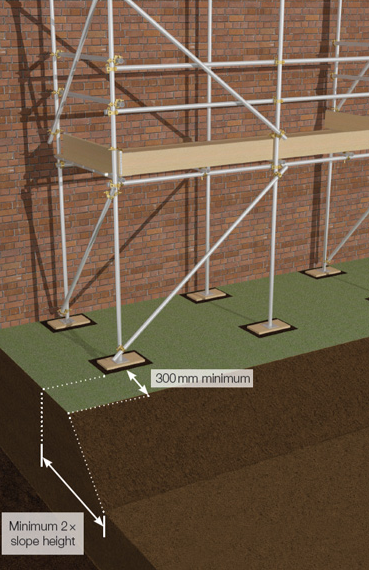
2.3 Are scaffolds erected a safe distance away from trenches or excavations?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
If based on the sloping ground- Client should be consult with engineer to check the adequacy of sloping foundations
-
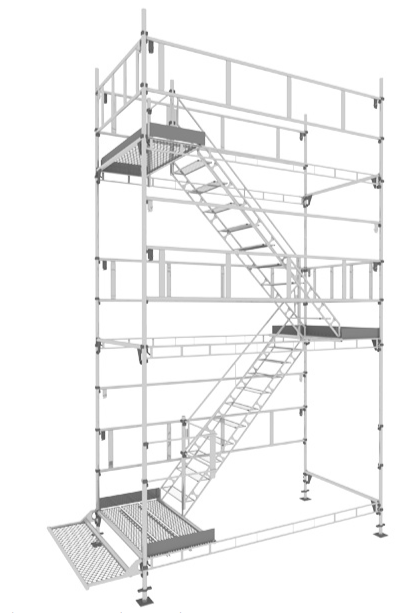
2.4 Is there safe access and egress to every scaffold platform?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
Staircase Towers -If a proprietary staircase is used, the manufacturer's instructions for the erection, alteration and dismantling of the equipment must be followed. The staircase tower should be physically tied or stabilised to the permanent structure or scaffolding structure, following the guidance of the manufacturer.
-
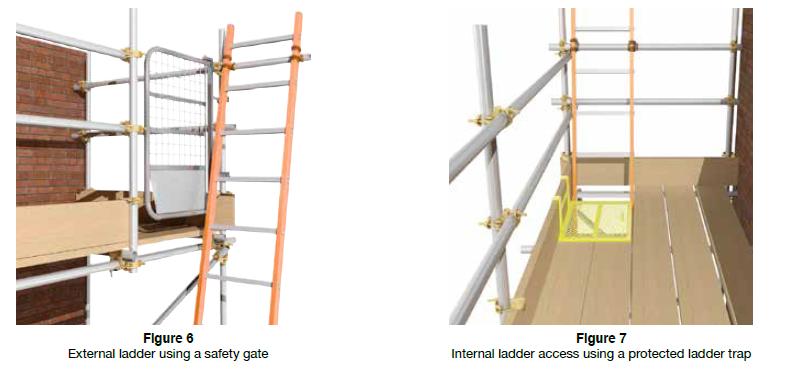
Where the client specification does not clearly specify the type of ladder access required, the scaffolding contractor should always consider providing the safest means of access possible.
-
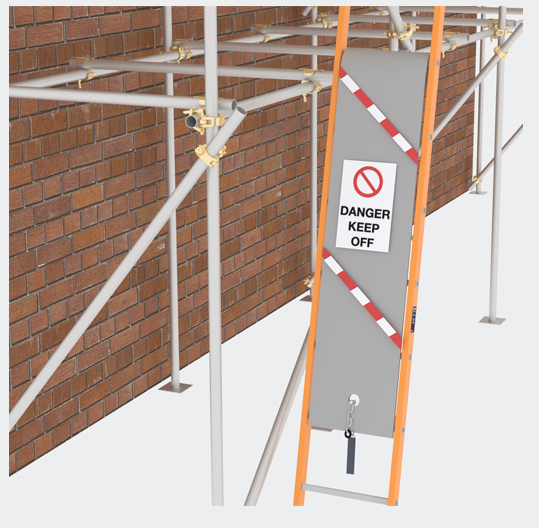
Preventing unauthorised access. It is the client's responsibility to prevent unauthorised access to scaffolding at all times. On sites where othervice secured it is recommended that ladders for the first lift are removed and kept in a secure storage area when not in use, if possible, or protected with a ladder guard. If a ladder guard is used, it must cover six rungs, making five rungs unusable. Access to stair towers should also be prevented by fencing and securing them.
3. Scaffolding Structure
-
3.0 Location and description of the workplace (Including any plant, equipment or materials) inspected:
-
Location and description of the workplace (Including any plant, equipment or materials) inspected:
-
Location and description of the workplace (Including any plant, equipment or materials) inspected:
-
Location and description of the workplace (Including any plant, equipment or materials) inspected:
-
Location and description of the workplace (Including any plant, equipment or materials) inspected:
-
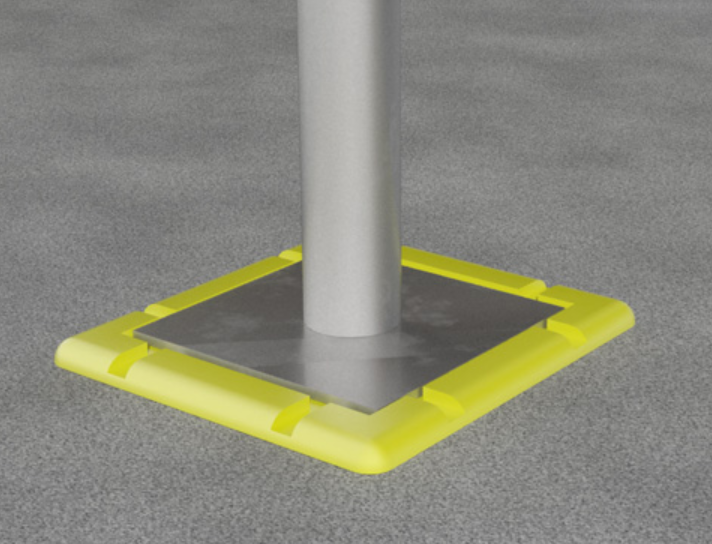
3.1 Are all baseplates and sole boards present and compliant ?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
The scaffold standards should each be founded on a base plate 150 x150mm on plan. Please note : Base plates may be omitted if the scaffold is founded on the hard surface, such as steel or structural concrete that is even, level and of adequate thickness to prevent the preparation the scaffold tubes. However best practice it is recommended that base plates are used routinely.
-
Sole Boards- Sole boards must be provided if the scaffold is directly supported by soilor subgrade. They must be provided for scaffolds on non-structural pavements such as brick and block paving, small concrete slabs, tarmac or asphalt
-
3.2 Scaffold square, straight, and plumb in all directions?
- Safe fit for purpose
- Scaffold Pass with observations
- Scaffold not to be used
- Unauthorised Scaffold Modifications by Third Parties
- Other
- Scaffold Erect in Progress- Incomplete Scaffold not to be used by other trades!
- Scaffold Dismantle in Progress- Incomplete Scaffold not to be used by other trades!
- Yes
- No
- N/A
-
3.3 Scaffold has been clad with monarflex ,debris-netting or brick guards?
- Safe fit for purpose
- Scaffold Pass with observations
- Scaffold not to be used
- Unauthorised Scaffold Modifications by Third Parties
- Other
- Scaffold Erect in Progress- Incomplete Scaffold not to be used by other trades!
- Scaffold Dismantle in Progress- Incomplete Scaffold not to be used by other trades!
- Yes
- No
- N/A
-
3.4 Are scaff-tags fitted at all access/egress points?
- Pass
- Fail
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Yes
- No
-
Information - Tagging a scaffold as safe to use is not a legal requirement, but is regarded as
being good practice and is therefore strongly recommended. However, tagging a scaffold that is
unsafe, incomplete, or under-adaption is a legal requirement and should be undertaken in all
circumstances until such time as the scaffold is confirmed as being safe to use and fit for
purpose. The Work At Height Regulations 2005 state that "While a scaffold is not available for use, including during its assembly, dismantling or alteration, it shall be marked with general warning signs in accordance with the Health and Safety (Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 and be suitably delineated by physical means preventing access to the danger zone"Tagging a scaffold as safe to use is not legally required, but it is considered good practice and is strongly recommended. On the other hand, if a scaffold is deemed unsafe, incomplete, or being adopted, it must be tagged as such by law. This should be done until the scaffold is confirmed as being safe to use and fit for purpose. Additionally, the Work at Height Regulations 2005 stipulates that a scaffold must be marked with general warning signs and physically cordoned off to prevent access to the danger zone while it is not being used, including during assembly, dismantling, or alteration. -
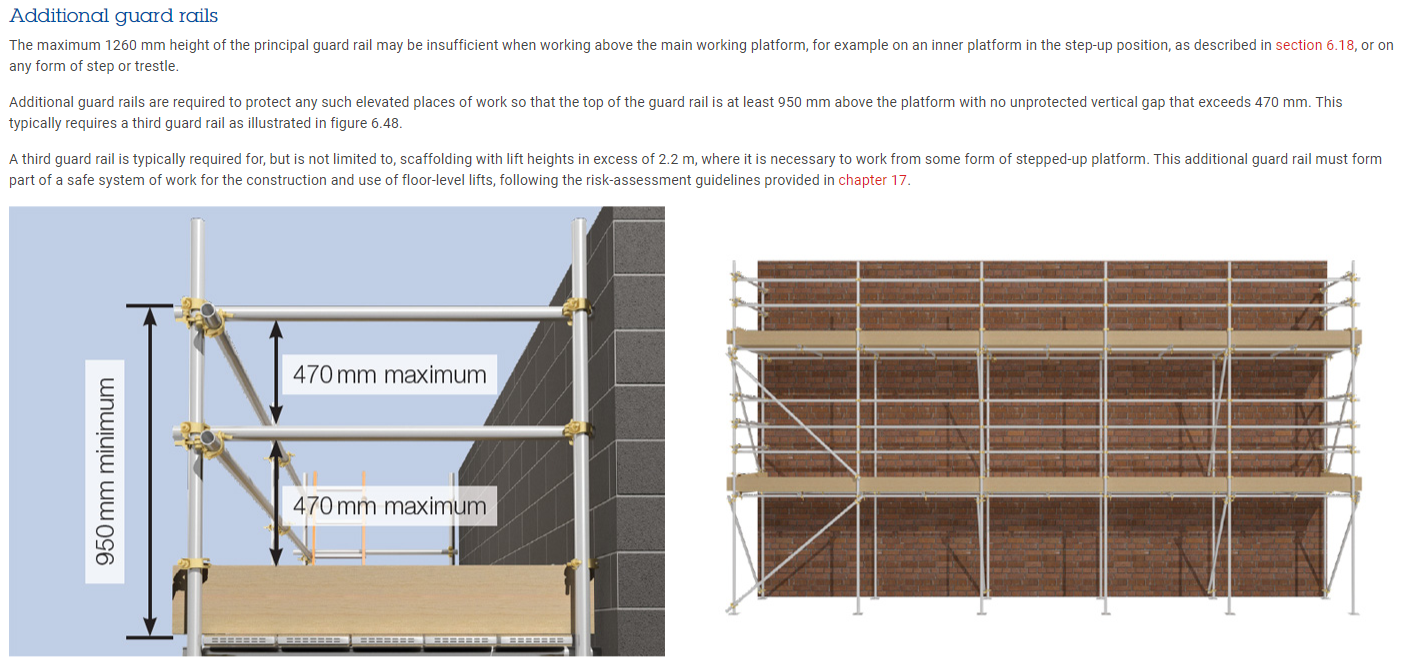
3.5 Are Handrail and toe boards fitted where there is a risk of persons or materials falling?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
Guard Rails -Temporary edge-protection systems for scaffolding structures are generally provided by horizontal tubes known as guard rails. All scaffolding lifts, other than foot lifts, require guard rails to prevent falls.
-
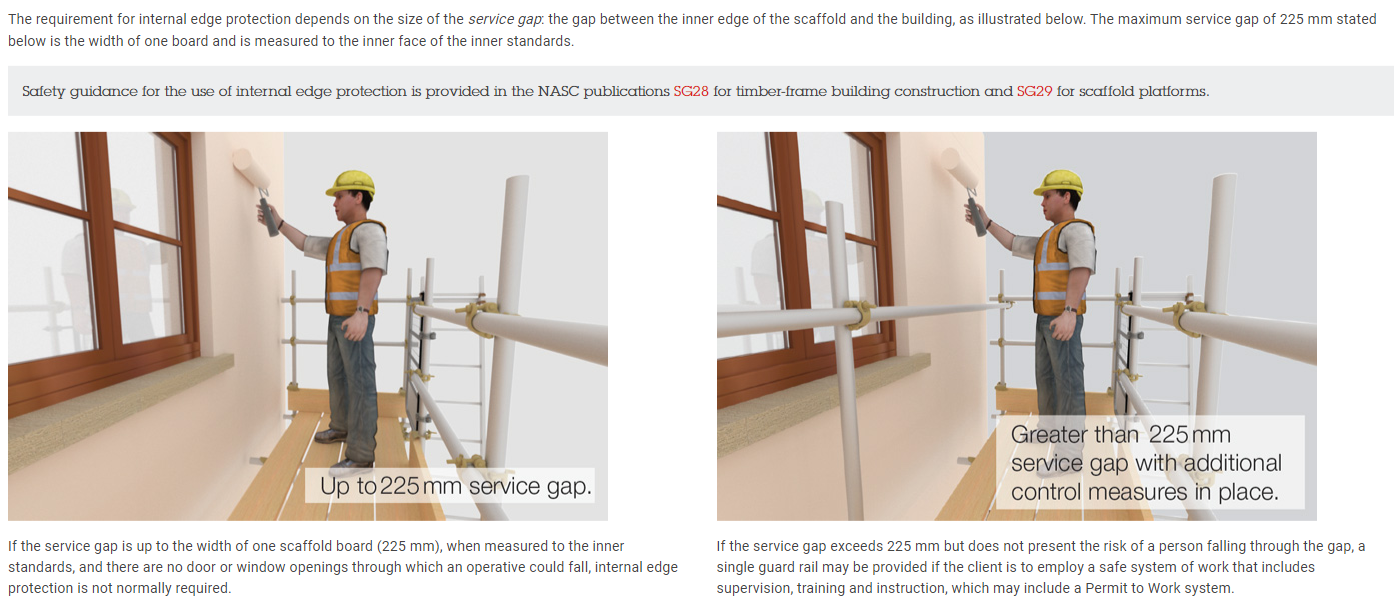
3.6 Do any areas of scaffold exceed the maximum clearance of 225 mm from exterior of building under construction?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
Internal edge protection up to 225mm and greater than225mm service gap
-
Internal edge protection greater than 225mm service gap and working from an inner platform with a risk of injury.
-
3.7 Are working platforms suitable for the trades?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
Inside board loading - The inside board platforms should only be loaded to a maximum of 0.75kN/m2 (75kg m2) This allows for personnel to work on the platforms, with tools and light materials, but it does not allow materials to be stored on the boards.
-
3.8 Are all inside boards secured to prevent movement?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
3.9 Are scaffold boards free from defects?
- Safe
- At Risk
- Some boards are showing signs of warping and splitting to be monitored
- Unautorised Scaffold Modification- At Risk Urgent Corrective Action Required
- Other
- Improvement Needed
- Yes
- No
- Safe access and egress obstructed
-
3.10 Are the scaffold ties correctly positioned fixed and tested as per the design drawings/TG20 compliance sheet?
- Pass
- Fail
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Yes
- No
-
Anchor proof testing -Tie(s) test requirements
-
3.11 Are plan /ledger/sway(façade) bracing in place and correct fitting used ?
- Pass
- Fail
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Yes
- No
-
4.0 Scaffold build as per TG20 /Design
- NASC TG20 Compliance Scaffold- TG20 compliance sheets provide a written record that scaffolding is compliant and exempt from the need for additional design. Compliant scaffolds are standard configurations of scaffolding that have been designed by structural calculation in accordance with BS EN 12811therefore does not need a special design.
- Bespoke Scaffold Design-
- Engineer Input Required
- Other
Raising and Lowering Materials
-
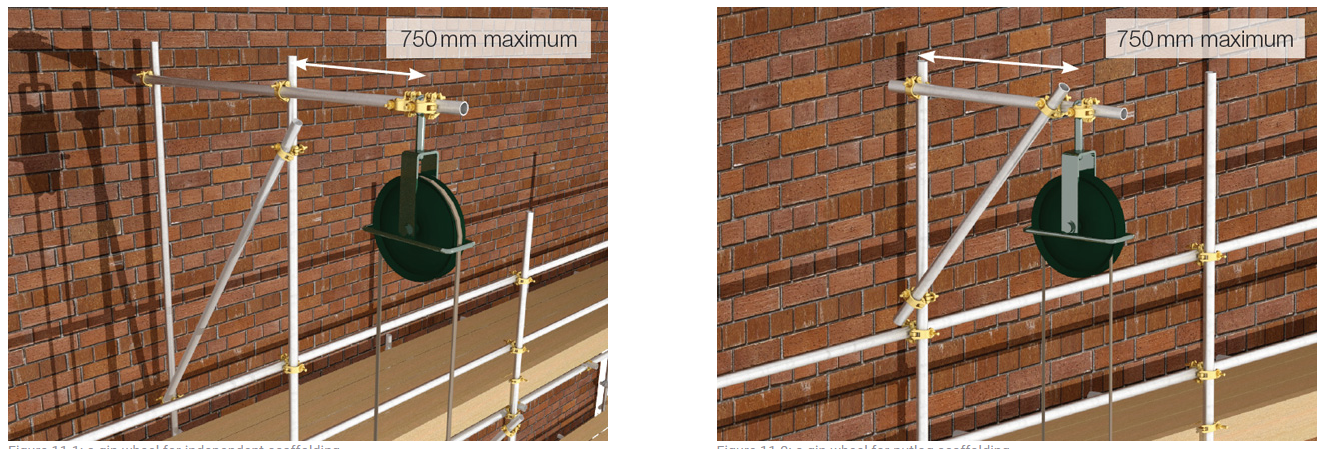
Gin Wheels and Rope is fixed to the structure ?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
It is the gin and wheel and rope are fit for purpose and fixed properly ?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
Gin and Wheel serial number
-
Gin wheel and rope Thorough examination certificate available on site ?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
If the client requests that the equipment is left in place, the ESS contracts manager will inform the client of their statutory duties in writing. This written record should specify whether accessories such as the rope are to be provided. The gin wheel and rope should be removed from the scaffold before handover and not left on site, where they may be used without authorization.
4. Housekeeping
-
4.1 Are working areas free of trip hazards?
- Safe
- Fair
- Poor- Improvement required
- At Risk - Accumulation of waste materials and all surplus to be cleared and removed from the site by the relevant contractor.
- Yes
- No
- Other
- N/A
-
4.2 Are all the spare materials in a neat and tidy condition?
- Safe
- Fair
- Poor- Improvement required
- At Risk - Accumulation of waste materials and all surplus to be cleared and removed from the site by the relevant contractor.
- Yes
- No
- Other
- N/A
-
Waste materials stored in designated bins or skips provided?
- Safe
- Fair
- Poor- Improvement required
- At Risk - Accumulation of waste materials and all surplus to be cleared and removed from the site by the relevant contractor.
- Yes
- No
- Other
- N/A
5. Documentation
-
5.1 Are the task-specific risk assessment and method statement present on-site?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
5.2 Is there a hand over certificate in place?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
Scaffold Handover to the Client
-
5.3 Anchor Proof testing certification (Scaffold ties test) available on site ?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
-
5.3 Has the previous audit report been closed out?
- Yes
- No
- Improvement Needed
- N/A
- Other
- No
- Yes
6. Sign Off
-
6.1 Name of person completing this report.
-
6.2 Name of the site person receiving this report.
-
Scaffolding Structure
- Safe fit for purpose
- Scaffold Pass with observations
- Scaffold not to be used
- Unauthorised Scaffold Modifications by Third Parties
- Other
- Scaffold Erect in Progress- Incomplete Scaffold not to be used by other trades!
- Scaffold Dismantle in Progress- Incomplete Scaffold not to be used by other trades!
- Yes
- No
- N/A
I confirm the contents of this report have been discussed with myself and I am aware of any issues highlighted in the body of this report.
7. Closure
-
7.1 I confirm all actions highlight in this report have been actioned on:
Name of the person closing this report.
-
Add signature