Information
-
Audit Title- Machine Name, Type and Asset Number - Refer to asset register
-
Document No.
-
Site
-
Has there been a previous assessment
-
What was the date of the last assessment
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Personnel Involved- List
Risk Management framework SDIS
-
The purpose of this Plant Risk Assessment is to determine if uncontrolled hazards exist to the specified equipment which could lead to death or severe, debilitating injuries.
-
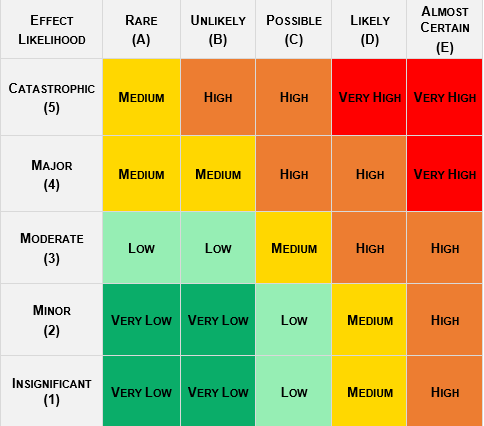
Each hazard identified will be assigned a probability and severity ranking which will subsequently be used to determine the overall risk of the hazard. Additionally, an overall risk ranking will be assigned to the machine using the rankings given to each individual hazard.
1. Mechanical Hazards
-
Mechanical Hazard is a general designation for all physical factors that can give rise to injury resulting from the mechanical action of a machine, machine parts, tools, workplaces and other objects or from projected solid or fluid materials.
1.1 Entanglement
-
Entanglement - Entanglement occurs as a result of bodily contact with one of the following: A single rotating surface, projections or gaps, counter-rotating parts, rotating and tangentially moving parts, rotating and moving parts, rotating and fixed parts and material in motion.
-
1.1 Do entanglement hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
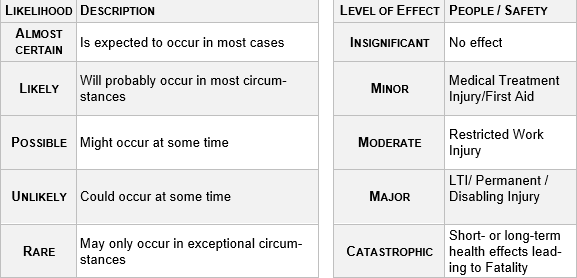
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for entanglement hazards.
1.2 Friction and Abrasion
-
Friction and Abrasion occurs as the result of bodily contact with relatively smooth parts/equipment moving at high speeds (e.g. Coil surface travelling at at excessive speeds) or abrasive hazards (e.g. abrasion wheels or belt sanders)
-
1.2 Friction and Abrasion - Do Friction and Abrasion hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from Risk Matrix for Friction & Abrasion
1.3 Cutting or Severing
-
Cutting occurs as a result of bodily contact with such items as cutting tools, saws, routers, knives, sharp strip/tube edges, moving sheet metal/coil ends and other sharp objects.
-
1.3 Cutting or Severing - Do Cutting or Severing hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Cutting or Severing hazards.
1.4 Shearing
-
Parts of the body may be sheared between two machine parts or between a a machine part and a workpiece (i.e. Coil end, bundle).
-
1.4 Shearing - Do Shearing hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk Matrix for Shearing hazards.
1.5 Stabbing or Puncturing
-
The body may be penetrated by flying objects or by rapidly moving parts and/or equipment.
-
1.5 Stabbing or Puncturing - Do stabbing or Puncturing hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Stabbing or Puncturing hazards
1.6 Impact
-
Impact occurs as a result of of bodily contact with objects acting against the inertia of the body not not penetrating it.
-
1.6 Impact - Do Impact hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Impact hazards
1.7 Crushing
-
Crushing occurs as the result of bodily contact between one part of an object moving against the other moving against another.
-
1.7 Crushing - Do Crushing hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Crushing hazards
1.8 Drawing-in or Trapping
-
Drawing-in occurs as the result of bodily contact with one of the following mechanisms: 1. In-running nips between two counter-rotating parts 2. In-running nips between a rotating surface and a tangentially moving surface.
-
1.8 Drawing-in or Trapping - Do Drawn-in or Trapping hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Draw-in or Trapping hazards
1.9 Pressurized Liquids/Gases Injection/Ejection
-
Compressed air or high-pressure fluid injection occurs as a result of skin exposure to high-pressure streams such as compressed air jets, paint sprayers or hydraulic systems.
-
1.9 Pressurized Liquids/Gases Injection/Ejection - Do pressured Liquids/Gases Injection/Ejection hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Liquids/Gases Injection/Ejection hazards
2.0 Slipping, Tripping and Falling
-
Because of their mechanical nature, hazards resulting from slipping, tripping and falling in relationship with equipment and machinery should also be considered, as well as access, egress and working surfaces (e.g. stairs, ladders and platforms)
-
2.1 Slipping, Tripping and Falling - Do slip, trip and fall hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Liklihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Slipping, Tripping and Falling hazards
3.0 Electrical Hazards
-
Electrical hazards can cause injury or death from explosion, electrical shock or burns. These can be caused by bodily contact with live parts and parts that have become live under fault conditions. Additional causes include approach of persons to live parts, insulation not adequate for conditions and electrostatic phenomena.
-
3.1 Electrical Hazards - Do electrical hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for electrical Hazards
4.0 Thermal Hazards
-
Thermal hazards can result in burns and scalds from contact with objects or materials with an extreme temperature, flames or explosions and radiation from heat sources. Additionally, health damaging effects generated by hot or cold work environments must be considered.
-
4.1 Thermal Hazards - Do Thermal hazards exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Thermal Hazards
5.0 Hazards Generated by Noise
-
Noise can result in permanent hearing loss, tinnitus, tireness and stress, other effects such as loss of balance or loss of awareness and interference with speech communication or acoustic signals.
-
5.1 Hazards Generated by Noise - Do hazards generated by noise exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
probability
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Hazards generated by noise
6.0 Hazards Generated by Vibration
-
Vibration can be transmitted to the whole body and particularly to the hands and arms. The most severe vibration may generate serious disorders, severe discomfort and vascular discorders.
-
Vibration - Do hazards generated by vibration exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Liklihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for Hazards generated by noise
7.0 Hazards Generated by Radiation
-
Hazards generated by radiation can have immediate effects or long term effects. They are produced by a variety of sources and can be generated by non-ionizing or ionizing radiation as, for example, in low frequency, radio frequency and micro waves.
-
7.1 Radiation - Do hazards generated by radiation exist which could cause or contribute to severe injuries or death?
-
Likelihood
-
Severity
-
Score from risk matrix for hazards generated by radiation
Total Machine Risk
-
Total Machine Likelihood ( Highest Likelihood selected)
-
Total Machine Severity ( Highest consequence selected )
-
Total Machine Risk ( Highest rating on risk matrix selection )
-
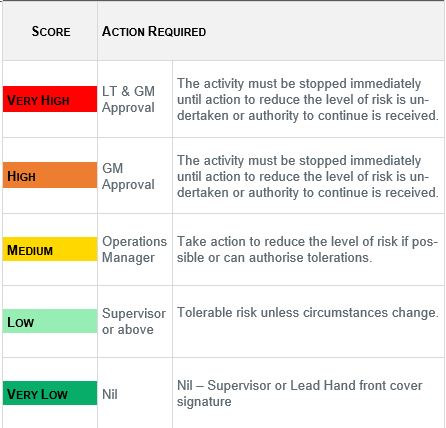
Level of Leadership Sign off based on Risk Matrix
-
Are there actions or activities that can be undertaken that can reduce the risk score
-
Have you raised these in Noggin or Raised an Maintenance Request to have them completed
Comments
-
Overall all conditions
-
Signature of person completing
-
Print this as a PDF. Present to the appropriate level of delegation of risk for sign off.