Title Page
-
Client Details
-
Directorate
-
Location
-
Prepared by
-
Conducted on
-
Personnel involved
-
No. of employees at this location
-
Document No.
Description of the Premise and Work Activities
-
Description of the business at this location, it's activities or general undertaking
-
Description of the premise (floors, freehold or leasehold, responsibility for the maintenance, rooms, W/C's, parking arrangements etc.)
-
Information about workers (number of employees, agency workers, volunteers, fully time/part time etc.)
-
Photo(s) of the Location
Health & Safety Management
Evidence of Statutory and Organisational Mandatory Safety Documentation
-
Policy<br><br>Does the client know where the company's health and safety General Policy statement and other policies are located; is the policy signed and up-to-date; is the person being interviewed aware of policy content and it's application?
-
Management Structure<br><br>Is the person being interviewed aware of the health and safety management structure; is the management structure illustrated in a organisational chart identifying individuals with key health and safety management responsibilities and is it effectively communicated to workers so that any required issues and change will be identified and promptly made?
-
Monitoring<br><br>Is periodic monitoring, self checks or inspections being completed by the company or service being inspected; are they being completed at the recommended intervals; are they being completed correctly, circulated or forwarded to the appropriate person(s); are actions being identified being completed in suitable timescales?
-
Hazard Reporting<br><br>Is there an effective hazard reporting system in place that can be evidenced such as maintenance or fault logs, daily diary and hand over discussions between workers; if hazard reporting is through an 'open door' policy, does the person receiving safety concerns make a documented record of issues brought to their attention; does hazard reporting feed into a procedure to implement positive change such as a regular meeting agenda?
-
Employee Safety Handbooks (ESH)<br><br>Are all workers provided with an ESH either in hard copy or made available to them electronically; are signed receipts retained to show that workers have been provided with an ESH, have read and understand the rules and guidance set out by the organisation that they are expected to abide?
-
Electrical Safety (portable appliances)<br><br>Are portable electrical appliances subjected to informal/formal inspection and testing by a competent person; is there an asset register containing appliances identifiable by unique referencing and indicating pass/fail results?
-
Safety Records<br><br>Is there evidence to demonstrate that safety records are being completed to show that where there is delegated health and safety responsibility that it is being completed to a satisfactory standard? Evidence of the Managers Compliance Checklist is being completed every 12 months.
-
Health & Safety Law Poster or individual cards<br><br>Is the HSE's Health & Safety Law poster the current version, suitably completed and displayed in a location that all employees can we it; alternatively are Health & Safety Law cards provided to workers individually?
Accident Reporting & Investigation, Contractors and Employee Consultation
-
Accident Reporting and Investigation System<br><br>Is the accident reporting being completed effectively in the way directed by the organisation; is the appropriate information being collected at the time of recording; is there a means to ensure the correct information is collected by persons unaware or uneducated in the requirements of the First Aid at Work regulations such as first aid book or accident record form to be used by remote or field based workers; is collected information kept secure and confidential?<br><br>Is accident/incident investigation being undertaken effectively regardless of severity; is risk assessment being reviewed during the investigative process; are learning outcomes and changes recorded and cascaded to those exposed to hazards?
-
Employee's Liability Insurance (where applicable, public bodies exempt) - (CRITICAL FAIL QUESTION)<br><br>Is there a valid certificate of Employee's Liability Insurance Certificate held either in hard copy or electronically?
-
Contractors (selection, monitoring and documentation)<br><br>Are contractors suitably vetted for competence and safety compliance; do they all go through the organisation's vetting and procurement process; do contractors provide risk assessments and method statements (RAMS) for the work they are expected to undertake; is the work contractors do monitored both during their work and after to ensure it is undertaken safety and completed to the expect level and quality?
-
Enforcing Authority Reports<br><br>If an enforcing authority (such as HSE, CQC, Fire Authority, Ofsted etc.) has visited and made recommendations or requirements relating to the improvement of health and safety within the organisation or department, has the enforcing authorities requirements now been meet?
-
Consultation with Employees<br><br>Is there evidence to demonstrate that employees have been consulted on matters relating to their health, safety and welfare such consultation in regards to the development of risk assessment, policy and procedure?
Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment & Business Continuity Plan - Review of the Practical Application
-
Where required to be documented; have risk assessments been completed and communicated to those likely to be exposed?<br>It is a legal requirement that all companies employing five or more employees document risk assessment. The client should be able to demonstrate that research has been performed to understand the common risks in the industry.
-
Have documented risk assessments been completed on the the organisations approved template? If not do they follow the 'five steps' approach to risk assessment endorsed by the enforcing authorities?
-
Where possible to determine, have existing controls (i.e. controls currently in practice) been identified for hazards during the risk assessment process?
-
Has the perceived effectiveness of controls been assessed or risk assessment reviewed by a person who understands hazard and control? There should be evidence to suggest risk assessment has been completed in consultation with others.
-
Where applicable; does written risk assessment identify a person responsible for implementing additional controls or change with a target date to complete the action?<br>A client should be able to produce an Action Plan where risk assessment shows additional control(s) have been identified and where completed they should be signed off.
-
Is there a service or business continuity plan in place for critical organisational functions/processes?<br>(Dated, indicating regular review)
-
General Comments (if any):
Facilities Management
Facilities Management
-
Does the person or department being audited have facilities management responsibilities?<br>(Response to this specific question has no weighting)
Electrical Safety (mains installation)
-
Electrical Safety (Hard wired)<br><br>Is there evidence that the electrical fixed installation has been tested by a qualified electrician within the recommended interval; is the test certificate compliant with a professional body such as NICEIC; does the certificate indicate that the electrical system to be satisfactory; has any recommendations or requirements been actioned; is there accompanying remedial works certificates and electrical condition reports; if a new build are there commissioning certificates?
Gas Safety (Mains)
-
Gas Safety (mains)<br><br>Is there evidence to demonstrate that the mains gas supply and mains gas appliances has been inspected/tested within the last 12 months by a competent engineer registered to the Gas Safe Register?
Water Management
-
Water Management (Legionella)<br><br>Where required, has a Water Management Survey/Legionella Assessment been documented; does the documentation identify potential areas where Legionella bacterium may proliferate; does the survey contain a plan or schematic of the hot and cold water system; does the assessment make recommendations to comply with L8 the Control of Legionella and if so, is there evidence to demonstrate that the identified actions and controls have been completed, planned or otherwise managed?<br><br>Is the water tested monthly; does water testing indicate any concerning results; do risk assessments show a schedule of thorough cleaning of water outlets (routine cleaning and periodic dismantling and rescaling)?
Asbestos Management
-
Asbestos Survey & Management of Asbestos Containing Materials (ACM)<br><br>Has a survey been produced for the premise, evidence of a documented survey and where ACM's are found, a management plan? The client should be able to demonstrate a good understanding of the hazards associated with Asbestos; evidence to suggest that ACM's are monitored for deterioration and action taken to eliminate or control potential exposure.<br>Visitors/contractors to the premise should be made aware of ACM's and there locations before becoming exposed, evidence should be able to demonstrate how finding of the Asbestos Survey is communicated to other persons.
-
Removal of Asbestos Containing Materials<br><br>Where ACMs have been removed the client should be able to demonstrate that they have been removed by a competent person and disposed of responsibility, therefore evidence should be available for the appropriate selection of contractor which can be licensed or non-licensed dependent upon the work undertaken. The client should be able to demonstrate within their safety records (where criteria has been met) that notification to the enforcing authority of licensed and non licensed work has been completed. Where applicable the client should retain records of any disposal documentation and air quality sampling.
Building (other)
-
Lift Equipment (passenger and goods lifts, slings and hoists, lift trucks etc.)<br><br>Is there evidence to demonstrate that lifting equipment is serviced periodically and certified safe to use (Certificate of Thorough Examination within the specified timeframe for the purpose of the lifting equipment); for lifting equipment not requiring a Certificate of Thorough Examination (such as Pump/Pallet Trucks) - is there evidence to demonstrate that this equipment is subjected to safety inspection by users or other nominated persons?<br><br>Do Certificates of Thorough Examinations indicate that recommendations to improve safety is being completed?
-
Anchor points (buildings, lifts etc.)<br><br>All anchor points would be subjected to 6 monthly testing and certificated as such for review. Do anchor points show a collar indication last testing and do any collars from those seen indicate 'unsafe' to use?
-
Building Maintenance<br><br>Where responsibility rests with the client being audited, does the premise appear to be in good repair? <br>Does the client have sight of contractor Risk Assessment and Method Statement (RAMS)?<br>The client should be able to demonstrate through discussion and risk assessment consideration to:<br> Falls from height - Maintenance work often involves using access equipment to reach roofs, gutters, building services, and raised sections of plant and machinery. It can be all too easy to fall from these positions, or to drop things onto people beneath.<br> Isolation and permits to work - Isolation and lock off arrangements, and in some cases permits to work, are essential to enable maintenance work to be conducted safely.<br><br><br>
Workplace Transport
-
Workplace Transport (external such as estate management, car parking)<br><br>Workplace transport is any activity involving vehicles used in a workplace. Vehicles driven on public roads are excluded, except where the vehicle is being loaded or unloaded on a public road adjacent to a workplace. <br><br>A clear consideration to the following three points should be evident:-<br>Safe site (design and activity) - segregation, traffic routes, visibility, speed, signs/signals/marking, lighting, reversing, parking, coupling/uncoupling, loading/unloading, tipping, overturning, sheeting, housekeeping (clean routes and unobstructed);<br>Safe vehicle - appropriate selection, maintenance;<br>Safe driver - considering new recruits and existing employees, training, fitness to operate.<br><br>Other considerations - shared premise, visitors, public, contractors and monitoring of all of the above.
Waste Management
-
General and Special Waste Collection<br><br>To be able to demonstrate that waste (general or controlled waste) is being disposed of responsibility by a licensed waste collector. Waste collection notes will be retained together with waste collection agreements.
Training & Competence
Evidence of both Organisational Compulsory Training & Specific Training Requirements
-
Induction for all Workers<br><br>Is there evidence to demonstrate Induction Training has been completed (this may include both corporate/standard induction and localised induction not the team/service/department?
-
General Safety Awareness (including refresher)<br><br>Has the organisation or section of identified a basic level of general safety awareness training for it's workers; where the organisation has identified a basic framework of mandatory training and refresher training for all workers, does the person(s) in the position of responsibility ensure this training requirement is being completed by all (this includes computer based or e-learning)?
-
Health & Safety - Representative/Supervisor/Responsible Person Training<br><br>Is the Responsible Person able to demonstrate through training to the appropriate level in order to fulfill their duties? Training/refresher training such as CIEH Level 2 in Health and Safety, IOSH or the British Safety Council (BSC) Managing Safely are examples of the acceptable training courses along with risk assessment training.
-
Job Specific Training Requirements<br><br>Is the organisation or department able to demonstrate where job specific or specialist training is required or where skills gaps exist? A completion of a training/skills matrix is an expectation to demonstrate that worker competence is under ongoing scrutiny.
-
Workplace Transport (Vehicle Safety) and Driver/Operator Competence<br><br>Is there clear evidence to demonstrate that vehicles are being maintained with regular planned preventative maintenance, regular user/driver daily checks (recorded) and that vehicle faults and mechanical failures are repaired with vehicles removed from use where necessary?<br><br>Are DVLA license checks performed regularly and are drivers or mobile plant operators suitably licensed or competent with an adequate level of refresher training provided where required?
Fire & Emergency Arrangements
-
Does the person or department being audited have responsibilities in regards to fire safety arrangements?<br>(Response to this specific question has no weighting)
Review of Fire Safety Documentation & Emergency/Contingency Planning Arrangements
Premise Fire Risk Assessment and Planning
-
Premise Fire Risk Assessment<br><br>Has the Premise Fire Risk Assessment been satisfactorily completed; has it been completed or reviewed within the last 12 months; has an action pan been developed as a result of completing the assessment; does the action plan clearly detail what improvements are required/recommended and allocate responsibility of completing to an individual?<br>Does a floor by floor plan accompany the assessment; does the plan show locations of gas and electricity isolation, fire call points, fire extinguisher type and location, emergency lights, established refuge areas, equipment to aid escape by those with limited mobility?
-
Fire Action Plan/Evacuation Plan<br><br>Based upon the findings of the Premise Fire Risk Assessment, has a Fire Evacuation Plan been documented; is the plan been reviewed periodically?
Fire Alarm, Early Detection, Emergency Lighting and Escape
-
Fire Alarm<br><br>Is there an adequate means of raising the alarm without putting person(s) exposed to unnecessary risk; where fire alarms are fitted, is it a commercial system; has the installed system been serviced in the last year; does servicing include the testing/inspection of smoke or heat rise detectors; do early detection heads (from those seen) appear to be appropriately located and uncovered?
-
Fire Escape<br><br>Are fire escape routes/exits (internal and external) clear, unobstructed and good floor condition; are fire doors self close or able to self-close in the event of a fire emergency?
-
Fire Signage <br><br>This will include, during a tour of the premise, a review of the escape route directional signs, fire action notices to ensure they are completed and displayed an in appropriate number, extinguisher identification and usage appropriately located and correct, blue circular advisory signs and labels, refuge area signs and instructions for any communication systems, lift instructions during a fire emergency.
-
Emergency Lighting<br><br>Has emergency lighting been installed within the premise - if not, why and is there an alternative such as glow sticks, torches? <br>Has emergency lighting been subjected to annual inspection/servicing (wired system), is emergency lighting subjected to monthly testing by a nominated person (includes torches and are glow sticks within date)?<br>Are wired emergency lights subjected to regular discharging and recharging to add longevity to the battery units?<br>Does emergency lighting aid suitable and safe escape to the outside of the building, particularly over external stairs and escape route junctions?
-
Flammable sand Combustibles<br><br>Are flammable sand combustibles removed or kept to a minimum in the premise; consideration to better housekeeping, appropriate storage locations and proximity to ignition sources such as floor heaters, coiled and/or overloaded extension leads?
Fire Evacuation Drills & Assembly Point(s)
-
Fire Drills/Emergency Evacuations<br><br>Has a fire drill or false alarm prompting an evacuation taken place within the last six months (recorded)?<br>Do records show who participated within the fire drill, length of time to evacuate and any noted issues? It is recommended where multiple final exit points exist that during planned evacuation drills that different exit routes/exits are blocked to replicate a fire in that area to raise awareness of alternative routes.
-
Assembly Point<br><br>Has an appropriate assembly point been identified; is the assembly point away from neighbouring hazardous areas or activities; is it suitable for controlling the occupants from the evacuated premise; has crossing the road been avoided where possible; is the assembly point away from fire hydrants or areas likely to be used by the emergency services?
Other Fire Safety Records
-
Fire Safety Records<br><br>Are records available and up to date for premise and vehicle extinguishers, call point testing, extraction system servicing or cleaning, Fire Warden and Marshall training, fire suppression and early detection systems, fire roller shutters, battery fed door guards etc. and periodic fire safety checks lists to be completed by the nominated person?
Premise & Workplace Environment
Review of the working environment, further premise specific documentation and observations of the current working practices amongst employees
Lighting, Workspace, Temperature & Ventilation
-
Lighting<br><br>Is the workplace lighting adequate for the workplace activities (consider activities, testing lux levels and reviewing against current guidance)? <br>Is lighting selected and maintained to reduce developing health problems such as eyestrain, headaches or errors in working activities? Is lighting protected where impact is likely such as changing rooms at sports fields or halls, warehouse environments where high level storage an access is required, food preparation environments where diffusers or double walled fluorescent lighting strips is strongly advised?
-
Workspace<br><br>Is Workspace suitable for the number or workers and activities; is the activities requiring the need for ample space around the operator; is there excessive clutter under desks, along traffic routes, in stairwells; is storage being exceeded by requirements?
-
Workspace temperature<br><br>Means to monitor and control workplace temperature; is minimum temperature being met for indoor and outdoor environments (considering physical activities); has higher temperatures been considered in general risk assessments? Has adequate controls been considered for working in both high and low workplace temperatures?
-
Workplace Ventilation<br><br>The adequate supply of ventilation either by natural or mechanical means; where air conditioning is installed evidence is maintained to demonstrate that systems are subjected to periodic servicing and maintenance. W/C's will be fitted with extract ventilation where natural ventilation is not possible and will have an overrun to ensure odours are dispelled.
Flooring, Glazing and Welfare Facilities
-
Flooring<br><br>Has the flooring type been suitably selected for the type of location and expected activity of the premise/room(s); does it display good slip resistance potential?<br>Is the flooring in suitable condition; flat, even, contrasting colours where changes of levels are unavoidable?
-
Glazing<br><br>Is glazing for the premise in good repair (consider areas such as glazed balustrades, wets areas (including mirrors), glazing facing playgrounds/sports fields/swimming pools, vision panels, display cabinets, Crittal Windows (old metal windows)); is safety or protective film been fitted where necessary or other protection against impact?<br>Has areas of glass manifestations been risk assessed; do glass manifestations use awareness stickers to reduce the likelihood of injury by a person walking into glazing panels?<br>Is safety or toughened glass fitted where required; can it be identified by markings?
-
Welfare Facilities<br><br>Is there an adequate number of W/C's for the number of employees using the premise?<br>Are sanitary facilities clean and in good working order; is there soap and means of drying hands?<br>Is there adequate ventilation either by natural or mechanical means?<br>Is there any signs of abuse of the facilities?<br>Are emergency pulls fitted to disable toilets where determined to be beneficial?
-
Welfare at Work (a brief guide) - INDG293
Storage, Access & Egress, Building and Workplace Transport
-
Storage Racking and Mezzanines<br><br>The client will be able to demonstrate that they have sufficient storage space for their requirements without hindering safety by poor housekeeping standards. Consider racking and shelving; has is been installed and certified safe by an expert inspector (SEMA inspection) within the previous 12 months? Is there a responsible person nominated for the racking and are they able to demonstrate weekly formal (recorded) inspections of the racking systems?<br>Safe Working Loads (SWL) should be clearly displayed on the racking and also indicating how to load the racking. Racking (on light inspection) appear to be in good condition, anchored to the floor, shelf locking pins in place showing no faults or other damage to the framework? Where determined necessary the racking system will be protected against impact for workplace vehicles. <br>Safe Working Loads should also be available for Mezzanines.
-
Access and Egress<br><br>Does the premise meet expectations in regards to access and egress?<br>The Health and Safety at Work Act places a duty on both the employer and the employee to maintain safe access to the place of work at all times. Similarly safe egress must be ensured. That is, the normal entry and exit routes to the workplace must remain unobstructed and clear of hazards. Moreover, emergency exits must always be kept clear of obstructions and available for immediate use in an emergency. The law applies to all places of work. Offices, harbours, construction sites, swimming pools and other leisure facilities are examples of sites subject to this law. Risk assessments must be carried out and recorded to ensure access and egress to all workplaces, whether permanent or temporary, remain safe.
-
Workplace Transport (internal such as warehouse)<br><br>Workplace transport is any activity involving vehicles used in a workplace. Vehicles driven on public roads are excluded, except where the vehicle is being loaded or unloaded on a public road adjacent to a workplace. <br><br>A clear consideration to the following three points should be evident:-<br>Safe site (design and activity) - segregation, traffic routes, visibility, speed, signs/signals/marking, lighting, reversing, parking, coupling/uncoupling, loading/unloading, tipping, overturning, sheeting, housekeeping (clean routes and unobstructed);<br>Safe vehicle - appropriate selection, maintenance;<br>Safe driver - considering new recruits and existing employees, training, fitness to operate.<br><br>Other considerations - shared premise, visitors, public, contractors and monitoring of all of the above.
-
Workplace Transport (a brief guide) - INDG199
-
Workplace Transport Safety - HSG136
-
Segregation (people, plant, processes)<br><br>Where applicable does the workplace demonstrate adequate segregation between people and hazards? Review to be made of how the client has applied the hierarchy of control to workplace hazards and demonstrates understanding of control options.
Equality Act 2010
-
Equality Act 2010<br><br>Has disability been considered within risk assessment; has issues been identified and plans made to resolve?<br>Equality law recognises that bringing about equality for disabled people may mean changing the way employment is structured, the removal of physical barriers and/or providing extra support for a disabled worker. This is the duty to make reasonable adjustments. <br>The aim of the duty is to make sure that, as far as is reasonable, a disabled worker has the same access to everything that is involved in doing and keeping a job as a non-disabled person. <br><br>Public sector equality duty<br>The public sector equality duty (section 149 of the Equality Act) applies to public bodies and those carrying out public functions. It supports good decision-making by ensuring public bodies consider how different people will be affected by their activities. Does the client to which section 149 applies have due regard? Having due regard means consciously thinking about the three aims of the equality duty as part of the process of decision making, including the provision of a robust health and safety management system.
-
Disability in the Workplace (easy read version)
-
Disability in the Workplace (large print version)
Work Equipment and Machinery
Review of work equipment (inc. machinery) to include statutory inspections, pre-use safety checks, planned preventative maintenance (PPM) and adherence to established safe working practices
Lifts and Lifting Equipment
-
Lifting Equipment<br>(slings, hoists, fork lift trucks including attachments, electrically operated pallet trucks and manually operated pallet pump trucks etc.)<br><br>It should be demonstrated that all lifting equipment has been appropriately selected for the task intended and is subjected to periodic inspections, both formal and pre-use user checks. For equipment identified under the Lift Operations and Lifting Equipment Regulations (LOLER) regular servicing and periodic inspections should be available for review including a valid Certificate of Thorough Examination produced independently from the engineer tasked with routine maintenance.<br><br>Risk assessment should be reviewed to ensure hazards associated with lifting equipment has been acknowledged.<br>Does lifting equipment appear to be in good order and stored correctly?<br>Is lifting equipment secured from unauthorised use and/or tampering?
-
Lifts used by people at work<br>(Passenger and goods lifts including stair lifts but exclude escalators and travelators/moving walkways)<br><br>Passenger lifts and combined goods / passenger lifts in workplaces which are primarily used by people at work, are subject to periodic thorough examination (either 6 or 12 monthly) and inspection, as required by LOLER and PUWER. Is evidence of services and Certificate of Thorough Examination available to review?<br><br>
-
LOLER - L113
-
Thorough Examination of Lifting Equipment - INDG422
-
Fork Lift Trucks (including repairs to fork arms)<br><br>Where repair is needed; the client is able to produce evidence that repairs have been carried out by the manufacturer or someone of equal competence as directed by BS ISO Standard 5057.<br>There evidence of training (including familiarisation training) for operators). Good control of keys and operator daily safety checks and planned preventative maintenance. Certificates of Thorough Examinations will be available completed at the appropriate intervals.<br>Can the type of lift truck be used safety in the expected locations (in or outside warehouse, terrain or gradients, road use etc.)? <br><br>
Other equipment (where applicable)
Gas (Portable)
-
Gas Safety (Cylinders)<br><br>Are portable gas appliances subjected to periodic inspection/testing with evidence to demonstrate; are gas cylinders appropriately stored and secured (suitable ventilation, secure from tampering and not kept in excessive quantity; are details/written gas supplier agreements available to review?
-
British Gas Association - Cylinder ID, coding and labelling - TIS6
-
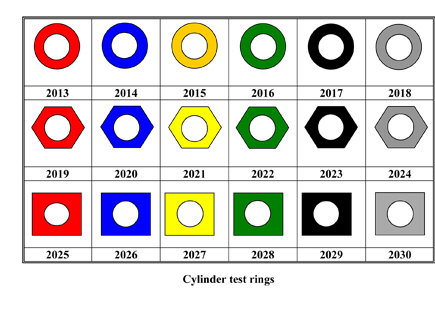
Cylinder Test Rings
Pressure Systems & Pressure Vessels
-
Pressure Systems and Pressure Vessels<br><br>Is there evidence to demonstrate that pressure vessels and pressure systems subjected are tested and inspected in accordance with the manufacturers 'Written Scheme of Examination' (review of the Written Scheme of Examination is required)?
-
Pressure Systems (a brief guide) - ING261
-
Pressure Systems ACOP L122
-
Guarding<br><br>Where guarding is required and/or fitted, it will be functional as intended and used by operatives. Guarding will not be missing or damaged (such as cracked or obscuring vision) without the equipment showing it has been taken out of use.
-
Equipment (general)<br><br>Other equipment found and used for work purposes will have been suitability risk assessed, with evidence of appropriate levels of training, safety inspections/exams, emergency stops fitted In a suitable location where required - functional and unobstructed?
Work at Height
-
Ladders, Platforms, Harness and Fall Arrest<br><br>Ladders and platforms will be of the suitable type for the purpose which there are intended for, wooden ladders disposed of in preference to alloy unless strong justification is provided. Ladders and platforms shall be uniquely identifiable in a register and subjected to monthly safety checks as well as pre use checks.<br><br>Harnesses and fall arrest equipment would have suitably and sufficiently risk assessment to justify their requirement; this equipment will be subjected to pre use checks, periodic formal safety inspections by competent persons.
-
Work At Height (a brief guide) - INDG401
-
Safe Use of Ladders & Stepladders (a brief guide) - INDG455
Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV) and Commercial Extraction Systems
-
Local Exhaust Ventilation (LEV)<br><br>LEV would have been implemented where it has been risk assessed that this additional control is necessary to carry away airborne contaminates. There isn't a specific legal requirement to have airflow indicators or similar fitted to an extraction, but by law have to make sure your LEV system keeps working properly. Best practice would be the use of airflow indicators at the hood and this will provide you reassurance that the flow-rate is maintained, that the protection for employees is there and that you're not wasting money. There are other ways of checking airflow such as using anemometer, or a dust-lamp or smoke tracer (with the work process running). However, an airflow indicator is currently the only method that will show the operator or supervisor immediately if there's a problem. LEV hoods as best practice should be labelled tested and pass/fail after a Thorough Examination and Test (TExT) by a competent person this includes 'on-tool' extraction systems.<br><br>Observations would be ideally made to verify that extraction systems are being used by workers.
-
A Guide to LEV - HSG258
Environmental & Other Issues
Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) inc. Dust, Fumes, Vapours and Health Surveillance
-
COSHH - Reducing the Risk<br><br>The responsible person would show an understanding of COSHH requirements and evaluated the workplace to determine what involves hazardous substances, what substances can cause harm, what tasks lead to exposure and determined if the risk of harm can be reduced perhaps by avoiding the hazardous substance entirely or use of a safer process, using a milder substance or use of a safer form (such as a solid rather than a liquid). Review the accident records to see if there are any obvious concerns.
-
COSHH - Inventory of Hazardous Substances and Safety Data Sheets (SDS)<br><br>The responsible person will have completed an inventory listing all substances considered hazardous that are used or stored in the workplace. This will be complemented by collecting the Safety Data Sheets for each substance, as good practice the SDS will be dated with the review date. The responsible person will show a basic understanding of Workplace Exposure Limits (WELs) and may have crossed referenced SDS against Substances listed EH40 workplace exposure limits.
-
COSHH - COSHH Assessment<br><br>From information collected from Safety Data Sheets the responsible person would have made their own assessments applying the SDS information to their own tasks. This may have been achieved using the Health and Safety Executives COSHH Essentials online assessment tool.
-
COSHH - Implementation of Control<br><br>On successful completion of COSHH Risk Assessment, controls identified through the assessment will be demonstrable. This is achievable through the use of:-<br>Control equipment (general ventilation, LEV, enclosures, or where the air cannot be cleaned - refuges and respiratory protective equipment (RPE), spillage capture, decontamination, clean-up procedures, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) etc.).<br>Ways of working - operating procedures, supervision and training but also includes decontamination procedures, emergency procedures, 'permits to work'<br>Worker behaviour - wearing any PPE required, using control equipment, following hygiene procedures, warning supervisors if anything appears wrong.<br>
-
The HSE COSHH ACOP - L5
Noise at Work
-
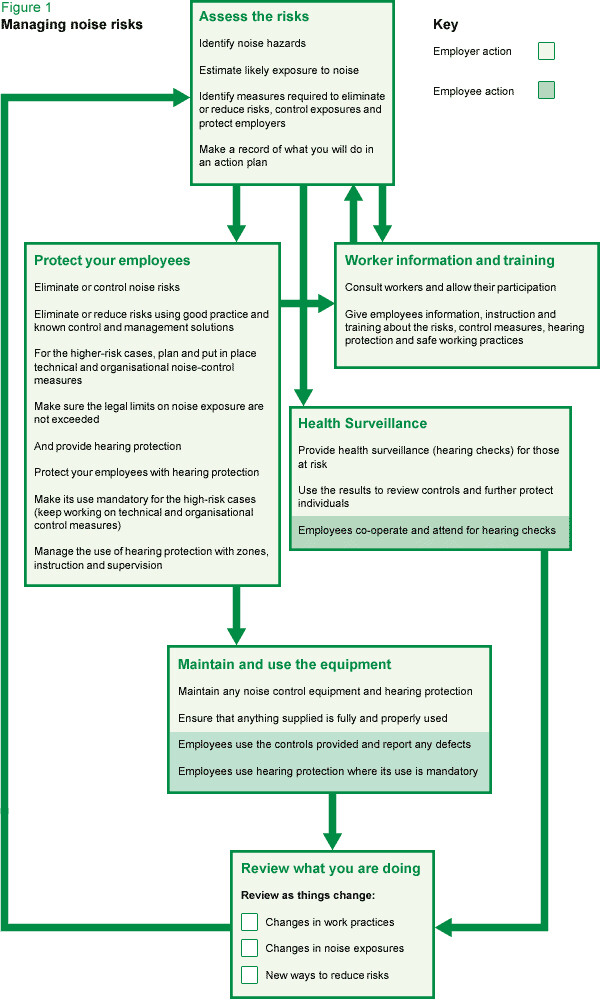
Noise - Meeting the Employers' Legal Responsibilities<br><br>The Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005 (Noise Regulations 2005) <br>Where applicable the client will be able to demonstrate that they are preventing or reducing risks to health and safety from exposure to noise at work. The client will be able to demonstrate that they:-<br><br>Assess the risks to their workers from noise at work;<br>Take action to reduce the noise exposure that produces those risks;<br>Provide workers with hearing protection if they cannot reduce the noise exposure enough by using other methods;<br>Make sure the legal limits on noise exposure are not exceeded;<br>Provide their workers with information, instruction and training;<br>Carry out health surveillance where there is a risk to health.<br><br>
-
INSPECTOR NOTE:
What are the action levels and limit values?
The Noise Regulations require you to take specific action at certain action values. These relate to:
the levels of exposure to noise of your employees averaged over a working day or week; and
the maximum noise (peak sound pressure) to which employees are exposed in a working day.
The values are:
lower exposure action values:
daily or weekly exposure of 80 dB;
peak sound pressure of 135 dB;
upper exposure action values:
daily or weekly exposure of 85 dB;
peak sound pressure of 137 dB.
There are also levels of noise exposure which must not be exceeded. These are called exposure limit values:
daily or weekly exposure of 87 dB;
peak sound pressure of 140 dB. -
Flow Chart for Noise at Work (INSPECTOR ONLY)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) - General
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)<br><br>It will be demonstrated that PPE has been carefully selected only as a last resort after implementing other controls and provided to employees free of charge. PPE will be CE marked and selected to suit the user (considering size, fit and weight). If different PPE is worn together consideration would have been given to if they work together i.e. cause a piece if PPE to not function properly. Receipts for PPE provided individually or available would have been collected and available to review. Never allowing exemptions from wearing PPE for those jobs that 'only take a few minutes'.
-
Personal Protective Equipment - Maintenance and Storage<br><br>Evidence that PPE is being looked after and stored corrected when not in use. Appropriate selection of the replacement parts where applicable and that replacement PPE is kept in suitable quantities; being able to demonstrate who is responsible for maintenance and how it is to be done.
-
Personal Protective Equipment - Monitoring, Review and Planning for Emergencies<br><br>Evidence that regular checking that PPE is being used; display of safety signs to remind workers to use PPE.<br><br>Emergency equipment<br>Careful selection, maintenance and regular and realistic operator training is needed for equipment for use in emergencies, like compressed-air escape breathing apparatus, respirators and safety ropes or harnesses.
-
PPE at Work - L25
Vibration
-
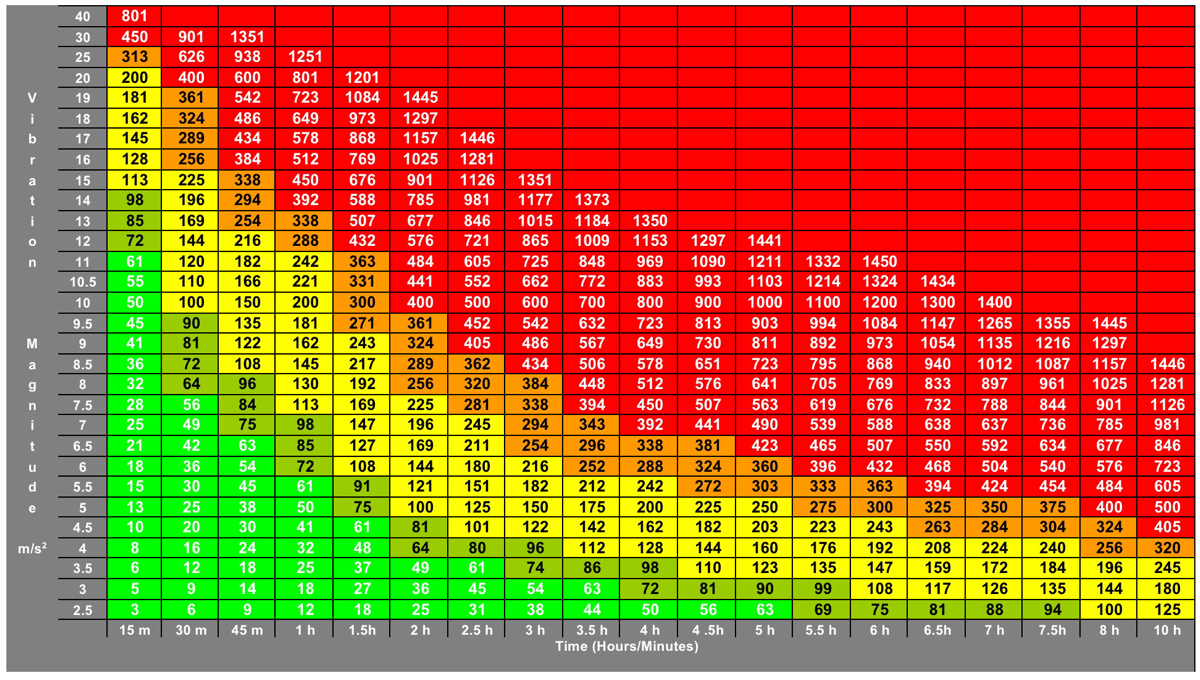
Hand-arm Vibration<br><br>Evidence to demonstrate that you have assessed and identified measures to eliminate or reduce risks from exposure to hand-arm vibration so that you can protect your employees from risks to their health.<br><br>Where the risks are low, the actions you take may be simple and inexpensive, but where the risks are high, you should manage them using a prioritised action plan to control exposure to hand-arm vibration.<br><br>Where required, you would have ensured that:<br>Control measures to reduce vibration are properly applied; and<br>You provide information, training and health surveillance.<br>Reviewing what you are doing if anything changes that may affect exposures to vibration where you work.
-
Hand-arm Vibration ACOP - L140
-
HAV Ready Reckoner
-
Instructions
-
Whole Body Vibration<br><br>Able to demonstrate the control of whole body vibration through assessment and controlling exposure. It will be demonstrated that: You assess the vibration risk to your employees; You decide if they are likely to be exposed above the daily exposure action value (EAV) and if they are: - introduce a programme of controls to eliminate or reduce their daily exposure so far as is reasonably practicable; You decide if they are likely to be exposed above the daily exposure limit value (ELV) and if they are: - take immediate action to reduce their exposure below the limit value; You provide information and training on health risks and controls to employees at risk; You consult your trade union safety representative or employee representative about the risks and what you plan to do; You keep a record of your risk assessment and control actions; I review and update your risk assessment regularly.
-
INDG Booklet on Whole Body Vibration from the HSE
Employee Assistance Programme (EAP)
-
Summary of Service
Employee Assistance Programmes (EAP) are employee benefit programmes offered by many employers. EAP are intended to help employees deal with personal problems that might adversely impact their work performance, health and well-being. EAP generally include assessment, short-term counselling and referral services for employees and their immediate family. -
Is the client aware of the Employee Assistance Programme?<br>Be able to demonstrate what the service aims to provide and where to find further information.
Supplementary Safety Checks (if applied)
-
Does the auditor/inspector want to open an additional safety checklists:-
-
Do you want to open the Fire Safety Checklist?
Fire Safety
-
Comments:
-
Do you want to open the Workplace Transport Checklist?
Workplace Transport
-
Comments:
Sign off
Sign off
-
Add signature
-
Add signature