Information
-
Audit Title:
-
Area/Location/Complex/Cell Inspected:
-
Area Supervisor:
-
Inspected By:
-
Conducted on:
Safety Theme Inspection
-
Select this month's Safety Theme
- Fit For Work
- Driving
- Ground Stability
- Lifting, Rigging and Hoisting
- Energy Isolation
- Working at Heights
- Hazardous Substance
- Permit to Work
- Protective Devices
- PPE
-
Golden Guide: Permit to Work
-
Is the crew doing work that requires a permit?
-
What Permits are need?
-
What are the limits or restrictions of the permit? Give an explanation.
-
Does the crew understand the permit?
-
What conditions might affect the crew's work today that may need to be consider in my permit?
- Risks can change
- Weather
- Low visibility
- Other work in area
- Personnel changes
-
Is the worker being diligent in their Employee Lead Engagements to keep people who are not involved in their work area aware of the risks?
-
BE PREPARED! does the crew have what they needed to meet the requirements of the permit?
-
MAKE SURE EVERYONE IS ON THE SAME PAGE! Does the crew know what each person's role is?
-
Golden Guide: Protective Devices
-
Did the worker stop work when adequate guards were not in place on the machines being worked around?
-
Did the worker avoid reaching around, over or under guarding?
-
Did the worker inspect the guarding regularly and report, repair or replace anything with a doubting condition?
-
Does the worker understand what to do if any of the following alarms are activated in their area:
-
Start-Up Alarm - warn that equipment will start to move, get out of the way
-
Personal Detection Alarm - warn that the air they are breathing is unacceptable and further action is necessary, follow site's procedures
-
Warning Alarm - may be audible, visible, or both and signal an upset condition in the area, specific action needed, usually means evacuate
-
Did the worker read signs near alarm (if activated) to view instructions on what to do?
-
Did the worker refrain from entering an area with an activated alarm until knowing it was safe to do so?
-
What type of fire protection does the worker have?
- Extinguishers
- Suppresion System
- Hoses
-
Is the worker able to reach any fire protective equipment without difficulty?
-
Has all of the worker's fire equipment been inspected?
-
Did the worker report all uninspected equipment or out-of-date inspections?
-
Does the worker have an escape plan?
-
In an emergency it is hard to keep calm and make good decisions. The worker should plan ahead, look around, and make sure they know how they will leave the area in an emergency.
-
Does the worker's job require a respirator?
-
Does the worker know to change cartridges for different gases, chemicals and dust around them?<br>ie.<br>- Pink/purple for dust and exhaust<br>- Yellow for organic vapor/solvents<br>- Green for ammonia
-
Did the worker inspect and perform a fit check before use?
-
Did the worker participate in the annual fit-test program?
-
Did the worker clean the respirator after finishing and store it in a clean, dry area that is protected from damage and others?
-
Golden Guide: PPE
-
Is the worker following both the site's PPE requirements and the PPE required for this job?
Does the worker have the following PPE:
-
Hard hat
-
Safety glasses
-
Hearing protection
-
Steel-toed boots
-
Reflective vests
-
Golden guide
-
Flashing blue light
-
Is the worker's PPE in good shape?
-
Make sure the PPE fits.
Don't use poor PPE. Replace PPE that is torn, cracked, damaged, has holes, or is expired.
Never use PPE that belongs to others. -
Golden Guide: Fit For Work
-
How is the worker feeling today? If they are finding it hard to focus they might be at risk. Explain.
-
Is the worker at risk from something that might stop them from focusing on what they're doing?
-
Speak up! Report to the supervisor if they feel any of the following.
- Sleepiness
- Weakness
- Distraction
- Illness
- Dehydration
- Anxiety
- Lack of Concentration
-
-
Is the worker managing their energy levels throughout the day?
-
Choose the action taken in response to the hazard.
- Adjusted work plan for the day.
- Getting help with a difficult task.
- Communicated any changes during shift.
- Took a planned task rest break.
- STOPED work until it was safe to continue.
-
Is the worker in control?
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: Never work if impaired or intoxicated!!
Watch out for each other, report signs of co-worker's impairment for their own safety. -
Has the worker taken any drugs or alcohol? Explain.
-
Is the worker taking medication that may affect their ability to work safely?
-
Spot the signs
- Drowsy
- Agressive
- Nervous
- Excitable
- Disoriented
- Irrational
- Neglect in Personal Hygiene
- Smell of Alcohol
- Indirect Evidence (empty bottles, wrappers...)
-
Are any of the other workers around showing signs of impairment?
-
Spot the signs...
- Drowsy
- Agressive
- Nervous
- Excitable
- Disoriented
- Irrational
- Neglect in Personal Hygiene
- Smell of Alcohol
- Indirect Evidence (empty bottles, wrappers...)
-
What is the worker doing to manage their overall health?
-
How new is this job to the worker?
-
Only do jobs that the worker is trained for and feels competent doing.
-
Has there been changes in the work environment that might make the worker's assigned tasks new to them?
-
Only do the jobs when the worker is confident that they can do it safely. It's ok to ask questions if they are not sure of the tasks they're about to perform.
-
Explain how they are managing these changes.
-
Golden Guide: Driving
-
Is the worker qualified, competent, and authorized to operate this vehicle?
-
Never operate a vehicle for which the worker is not trained and authorized. They should refuse to operate a vehicle that they have not been trained to operate.
-
Only operate vehicles for which the worker has received specific training and are confident and competent to operate.
-
Is the worker feeling or doing something that could make their driving unsafe?
-
The worker needs to be fit to drive, pick the selection that best describes their current state.
- Feeling Tired
- Taking Medication
- Drowsy
- Strong Emotions
-
Check the worker's vehicle, follow all required inspection procedures before turning it on. At a minimum, walk around the vehicle and check:
- Tires
- Fluids
- Whipers
- Emergency Brakes
- Lights
- Seat Belts
-
What seat belts are available for every passenger and are they ready for use?
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: you are responsible for everyone in the vehicle. Do not drive if your passengers are not buckled up.
-
What will the worker do to avoid distractions while driving?
- Get Comfortable (adjust mirrors, lights, steering wheel, heater/AC)
- Wear my prescription eye glasses and or protective eye wear
- Secure all cargo to prevent movement
- Do not use handheld devices while driving
-
What conditions could affect the worker's safety or the safety of others?
- Prepare and follow a plan for longer trips.
- Let someone know you have arrived safe.
- change course if conditions change, change your course.
- Scan for and report changing weather or conditions.
- Slow down or stop if conditions change too much.
- Keep your eyes on the road.
- Ask for help in tricky areas.
-
What does the worker need to do to operate safely around other people or equipment?
- Know where people are.
- Check and recheck their location.
- Never assume others' intentions.
- Make clear contact with pedestrians near your vehicle.
-
Can others see the worker's vehicle?
-
Does the worker have a buggy whip or light beacon on the vehicle?
-
Make clear contact with pedestrians.
- Make eye contact
- Wave
- Flash lights/headlamps
- Use of horns
-
Which procedure references to the driving job the worker is doing?
- Vehicles operating in close proximity
- Starting or backing up your vehicle
- Passing another vehicle
-
What does the worker need to do when they leave the vehicle?
- Turn off the ignition.
- Set the brakes.
- Turn the wheels into a bank or berm.
- Follow individual site procedures for leaving on warning lights.
-
What does the worker need to do when driving on poor quality/unpaved roads?
-
Golden Guide: Ground Stability
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: Never enter an area of unsupported ground.
-
Did the worker know the risks of unstable ground wherever they were going?<br>- Slope angles and wall heights<br>- Areas with loose rock<br>- Stockpiled materials<br>- Barricaded areas<br>- Proximity to high walls
-
Was the worker aware of the work that may affect the ground stability around them?<br>ie. drill and blast activity, heavy equipment operation above, excavation work.
-
Did the worker look and listen for signs of unstable ground before starting work and while working?
-
Did the worker barricade or block areas where unsafe conditions exist until the hazard was addressed?
-
Did the worker report recent rock falls and full catch berms immediately?
-
Was the worker aware that constant road traffic in an open pit can affect the stability of adjacent slopes?
-
Did the worker monitor the ground on the roads?
-
Did the worker safely remove water from areas where it accumulated?
-
Did the worker leave the area when in doubt about ground stability?
-
Which of the following signs of unstable ground did the worker manage and/or report?
-
Loose or overhanging material
-
Visible cracks in a high wall or bench
-
Water seepage or ponding
-
Undercuts
-
Full catch benches
-
Pit wall failures
-
Stockpile failure
-
Heavy rain or freeze/thaw cycles
-
Unusual sounds
-
Unstable slopes for possible falling rocks
-
Recent rock falls
-
Golden Guide: Lifting, Rigging and Hoisting
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: Never position yourself under a suspended load.
-
Was this a routine lift?
-
Did the worker double check how it should be done by following the site's procedure?
-
Did the worker plan the lift and do a pre-lift risk assessment?
-
Did the worker verify the weight of the load and make sure the rigging can support it?
-
Did the worker plan a safe path for the lift by thinking about what might be in the way or underneath?
-
Did the worker work only with qualified/trained people for lifting operations, rigging, and signaling?
-
Did the worker ensure they had enough people to perform the lift safely?
-
Did the worker get up to date on weather conditions for the time of the lift?
Did the worker do a formal lift plan including:
-
Clearences
-
Load vs. crane limits
-
Load orientation
-
Specialized rigging (engineered)
-
Site conditions
-
Personnel responsibilities
-
Did the worker continuously check and update the plan as conditions changed?
-
Did the worker control the access to all areas within the swing radius of the boom and load at all times to secure the drop zone?
-
Did the worker keep communicating to ensure the lift operator and the signaler maintain uninterrupted contact?
-
Did the worker use proper hand signals?
-
Were the meaning of the hand signals clarified with everyone before the lift?
-
Did the worker continuously look for new hazards that could affect the lift?
-
Did the worker lift according to conditions?
-
Was the lift adjusted when changes occurred?
-
Was the worker in the drop zone?
-
How did the worker position themselves to avoid getting caught between loads and other objects?
- Stop, start, and move loads slowly
- Keep the load as low as possible
- Use Tag-lines to control the load better
- Adjust body position throughout the lift to stay out of harm's way
-
Golden Guide: Energy Isolation
-
How will the worker control the potential energy sources identified?
- By following the site's procedures for energy isolation
- By asking someone about unsure work
- By physically isolating all energy sources
-
Before you start work:
-
Use redundant blocking mechanisms where possible.
-
First disconnect, then lock and tag electrical equipment.
-
Secure all valves around you.
-
Put a block or pin on all hydraulics, including suspended attachments, before locking out pumps.
-
Bleed (ensure pipelines are empty) and block pressurized systems (install blank).
-
De-energize conveyor belts and other mechanical equipment and block them against motion.
-
Use engineered (secure) support to prevent raised equipment from falling.
-
How does the worker know that the energy has been isolated?
- By never assuming equipment is de-energized
- Triple checking - talk to people, checking locks, and testing equipment out safely
- By starting equipment from the main energy source after isolation to ensure it does not work
- By returning the equipment to "off" or a neutral position after testing
-
Is there more than one person working on the system?
-
Who are the workers? Does each worker have their own lock?
-
Did the worker return the equipment to a safe operating condition when the work was completed?
-
Is the system fully re-assembled?
-
Did the crew replace everything that was removed, like guards and covers?
-
Were all of the isolating devices removed?
-
Each lock was removed by the owner.
-
All locks and tags were removed.
-
Only an authorized person can remove someone else's lock - never do it yourself.
-
Was the system/equipment restored to operational condition when turned back on?
-
What electrical hazards are in the work area?
- Live Power
- Exposed Conductors
- Worn or broken insulation or connectors on power or welding cables
- Wires pulled loose from cable connectors
- Open electrical panels
- Bypassed electrical interlocks on equipment
- Material close to or blocking electrical equipment
- Unidentified terminations
- Unlabled electrical equipment
- No electrical hazards present
-
What will the worker do to make sure no one is exposed to electrical hazards in the work area?
- Yes
- No
- N/A
-
How does the worker know the electrical equipment isn't live?
-
How did the worker ensure nothing in the area would become dangerous when it came into contact with the electrical equipment?
- Special electrical equipment was used outdoors or near water
- Dust and mud was cleaned off of electrical equipment when safe to do so
- Kept a safe space - moved all material away from electrical equipment
- Hung things out of the way
- Used insulated hooks to hang all electrical wires and cables away from water/people passing
-
Is the worker competent to do this work?
-
Is the worker confident that he knows how to be safe around the electrical energy around other workers?
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: You should only work on live electrical equipment if you have all of the following: the right qualifications, the appropriate procedures, the right equipment, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE, appropriate to flash potential, such as voltage gloves, fire retardant suits, face shields, etc.), and authorization.
-
What energy sources will the crew be exposed to?
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Hydraulic
- Pressurized
- Pneumatic
- Chemical
- Gravity
-
Golden Guide: Working at Heights
-
What are the fall hazards in the work area?
- Near open holes
- Near slopes and edges
- At heights above 6 feet
- Near water/tanks
- No fall hazards present
-
What is the worker's rescue plan if they do happen to fall?
-
If the worker has to work at heights or from an elevated surface, how do they plan to do it safely?
- Check that any ladders, platforms, railings, grating and floors that will be stood on are in good condition
- Avoid slipping and sliding by checking/cleaning any grease, mud, ice, snow, oil, etc.
- Maintain three points of contact at all times while climbing
- In a secure and comfortable position once up
- Position body and load to maintain balance
-
What tools/objects could fall and injure some below the work area?
- Secure all tools, equipment and other handheld devices
- Barricade the area
-
How does the worker safely access at height locations that have not been designed for routine access and work?
- Use a lift (if trained and authorized)
- Erect a temporary work platform (if trained)
- Install life lines and engineered anchor points with trained and competent people
- PPE
- Make special arrangements for a rescue if necessary
-
Is the worker working at a height above 6 feet?
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: Never work without approved fall protection when working at heights above 1.8 metres (6 feet).
-
Golden Guide: Hazardous Substance
-
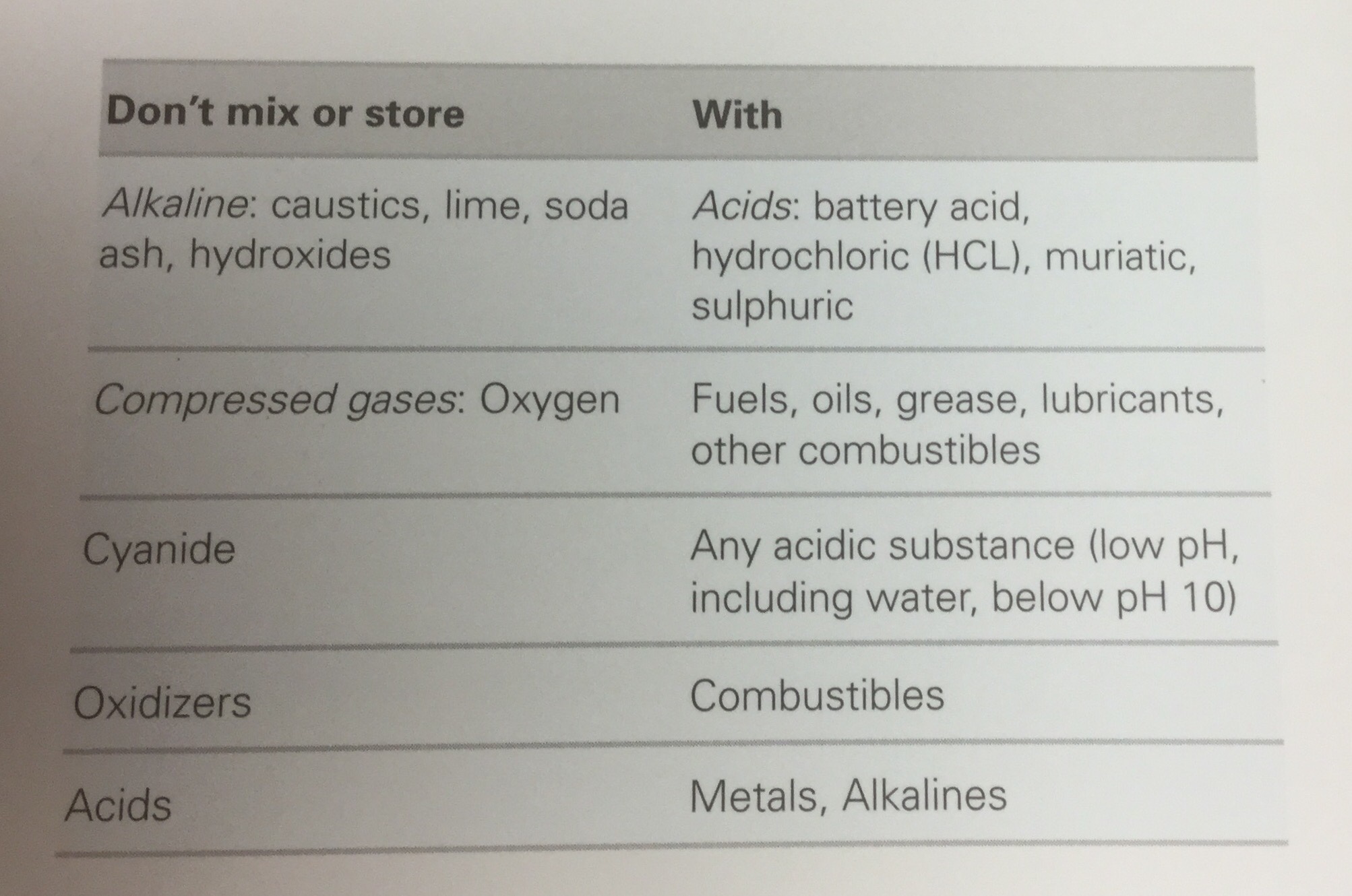
Don't mix or store guide:
-
How can the worker ensure that explosives are stored safely?
- Keep explosives in an orderly manner.
- Keep in an explosionproof area.
- Keep explosives from detonators.
- Secure aboveground magazines from unintended entry.
- Transport explosives in secure containters.
- Keep an up-to-date inventory.
- Always use old product first.
- Protect explosivies from energy sources.
- Dispose of unusable blasting materials in a secure manner.
-
Is crew working in accordance with our explosive procedures?
-
LIFE SAVING RULE: Never breach a blasting procedure!
-
Is crew working with non-compatible substances?
-
Is crew authorized and know what chemicals can mix safely? NEVER MIX UNKNOWN CHEMICALS.
-
Is crew handling and storing the hazardous substances safely?
-
List the proper requirements for handling the hazardous substances.
- Suit up. Always wear the required PPE
- Transfer Safely. Do not dispense flammable liquids without grounding or bonding.
- Store substances to prevent exposure.
- Ensure all containers are sealed and handled to manufacturer recomendations.
-
Is crew working around compressed gas or hazardous substances in pipes? If yes please take a picture and explain.
-
If crew is unsure, leave it alone. Do not open pipes or valves if you don't know what is inside .
-
Does the crew need to wear a personal detector, or monitor the area?
-
Is the ventilation system working and adequate? Please take a picture (always make sure that the ventilation system in your area is working, is not blocked, and does not have limited air flow.)
-
Does the crew know how much equipment can operate in my area?
-
Don't allow more equipment to operate in your area than the ventilation can handle. Don't idle your engine.
-
Does the crew smell or taste something unexpected? Trust your senses. If you smell, taste, hear, or see something unexpected leave the area immediately and notify your supervisor and warn other.
-
Please provide an explanation in detail of what was different in the area. RISK MANAGMENT: please describe what actions were taken to mitigate the risk.
-
Is the air dusty?
-
The worker must protect their self against harm. Ensure the following:
- Proper ventilation
- Dust suppressants
- Respirators
- Leave the area
-
What will the worker do if there is a spill, release or alarm that requires them to act immediately?
- Find emergency showers
- Find emergency eye wash stations
- Find evacuation point
- Barticade area
- evacuate if need
- Notify emergency response team
-
How can the worker protect their family from being exposed to hazardous substances from their workplace?
- Shower before going home
- not eating in work area
- Not taking contaminated cloths home
-
Does the crew know the risks associated with the substances You are handling and breathing?
-
Does the crew know where to find the Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) and labels?
Acknowledgements
-
Comments:
-
Actions:
-
Department:
-
Supervisor:
-
General Foreman:
-
Signature: