Title Page
-
General guidance
Nonconformities can be defined as an issue that –
1. Impacts on product, quality, project performance and/or reliability & process
2. An issue that causes disruption to production or maintenance processes.
3. A repetitive issue in a process or activity.
4. A complex issue that requires root cause investigation or a team-based approach for resolution.
Non-conformities should be classed to show the scale of the impact upon project operations as follows –
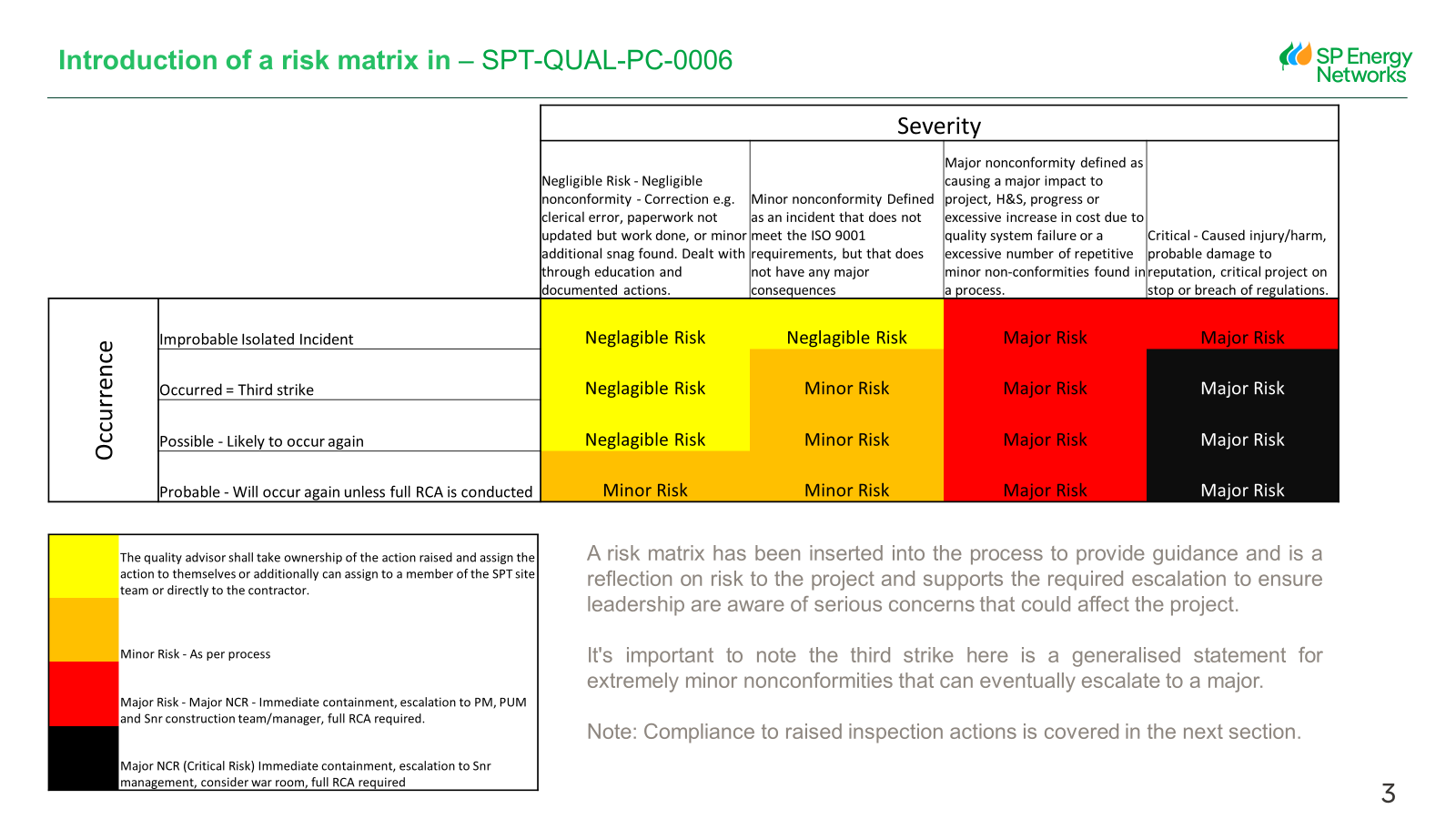
1. MAJOR – nonconformity causing a major impact to project progress or excessive increase in cost due to quality system failure: OR an excessive number of repetitive minor non-conformities found in a process.
2. MINOR – Defined as an incident that does not meet the ISO 9001 requirements, but that does not have any major consequences.
NCRs can be originate from the following sources (this list is not exhaustive)
1. 3rd party audit findings
2. Internal audit findings
3. Contractor inspections – if the criteria for nonconformities is met above.
4. Supplier delivery/equipment issues
5. Defect Liability Inspections
All HSEQ Nonconformities that have repeat actions from an audit/inspection will be classed as a Major Non-Conformance -
-
1 NCR Reference Number
-
- system generates a unique reference number automatically.
-
2 Name of person raising the NCR (the Originator)
-
- Originator will be poplulated automatically on raising
-
3. Recipient of the NCR
-
-The Originator to give as much information as possible. Name, Company, Contact information.
-
4 Name of Project & Project Code (If applicable)
-
- Originator to fill in
- please insert the name of the project as quoted on the Projectwise folder -
5. Date Identified
-
6. Date Raised
-
7. Area of NCR
-
-
8. Classification of the NCR
-
-Minor Nonconformities defined as an incident that does not meet the ISO 9001/14001/45001 requirements, but that does not have any major consequences.
-Major Nonconformities is an occurrence that could negatively impact the business and its intended operations and objectives. It’s classified as a significant failure to meet the requirements from ISO 9001/14001/45001
All HSEQ Nonconformities that have repeat actions from an audit will be classed as a Major Non-Conformance -
9. Non-Conformance details
-
-ORIGINATOR TO FILL IN - Describe the nonconformity in full, giving as much detail as possible. What exactly happened, where did it happen, When did it happen, How did it happen, How many times did it happen, Emphasise the risk.
-
-ORIGINATOR TO SHARE NCR open template with view and edit access with Recipient
-
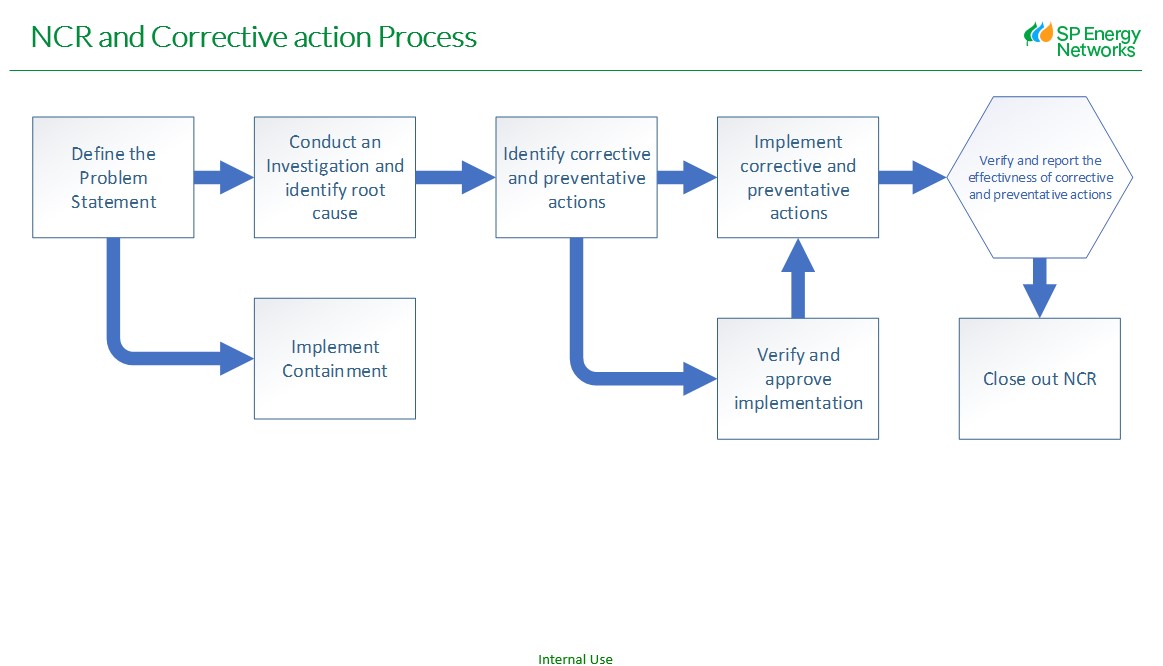
10. Containment
-
- RECIPIENT TO FILL IN
- describe the containment put in place to ensure defect is corrected and no repeat of error/defect is replicated in other works, processes or sites include information about segregation or quarantined items (required within 24 hours from date of raising)
- ORIGINATOR TO FILL IN- if on site inspection -
11. Root Cause Investigation (Recipient to complete)
-
-Method e.g. 5 Why's 3Q's - What happend?
- What must we do about it now?
- What must we do to prevent it happening again? - Required 10 days from the date of the raising the Non-Conformance
- Origanator to be contacted on completion of root cause -
12. Corrective Action (Recipient to complete)
-
- detail the corrective action put in place to ensure no repeat of the defect/error occurs. - Required 20 days from the date of raising the Non-Conformance
- Origanator to be contacted on completion of Corrective Action -
13.Preventative Action (Recipient to complete)
-
Identification and elimination of the cause(s) of potential nonconformances in order to prevent occurance nonconformance, unlike corrective action preventative action is a proactive approach that is taken to avoid any anticipated future that may appear in the product or at least capture reoccurrence of the failure mode. if root cause can not be identified it's imperative that preventative actions are considered to prevent similar or same fault modes. Preventive actions are often less tangible than corrective actions. They don't always involve a visible, physical change, but are more behind-the-scenes instead. Some examples include:
• Update processes and procedures to support capture or removal of nonconformities.
• Implementing new training programs for employees to capture similar failure modes.
• Conducting more frequent internal audits as a catch all.
• Performing increased maintenance on equipment and machinery.
• Increasing inspections/inspection criteria.
- Origanator to be contacted on completion of Preventative Action -
14. Is the root cause and corrective action effective? (Originator to complete)
-
- How has the corrective action been checked to ensure it has been effective? Add media to show verification, i.e. link to inspection, uncontrolled copy of updated document, audit report etc.
-
15. Method of verification of applied corrective actions (Originator to complete)
-
- Required 30 days from the date of raising the Non-Conformance
-
16. Name of person verifying the root cause and corrective action? (Originator to complete)
Approval
-
Date and time of approval
-
Approver's signature