Title Page
-
Location
-
Forest/Unit
-
R.D./Subunit
-
Facility/Compound
-
Date
-
Inspected by
-
INSTRUCTIONS:
-------------------------------------
1. Answer the questions below.
2. Add photos and notes by clicking on the paperclip icon.
3. To add a Corrective Measure click on the paperclip icon then "Add Action", provide a description, assign to a member, set priority and due date.
4. Complete audit by providing digital signature.
5. Share your report by exporting as PDF, Word, Excel or Web Link. -
(This form is compiled from regulations of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, USFS Health and Safety Code, and other relevant authorities. Users are encouraged to coordinate inspection activities with their Forest Safety Manager, and/or Forest Engineering Staff, which retains authority for facility inspections pursuant to FSM 6714.)
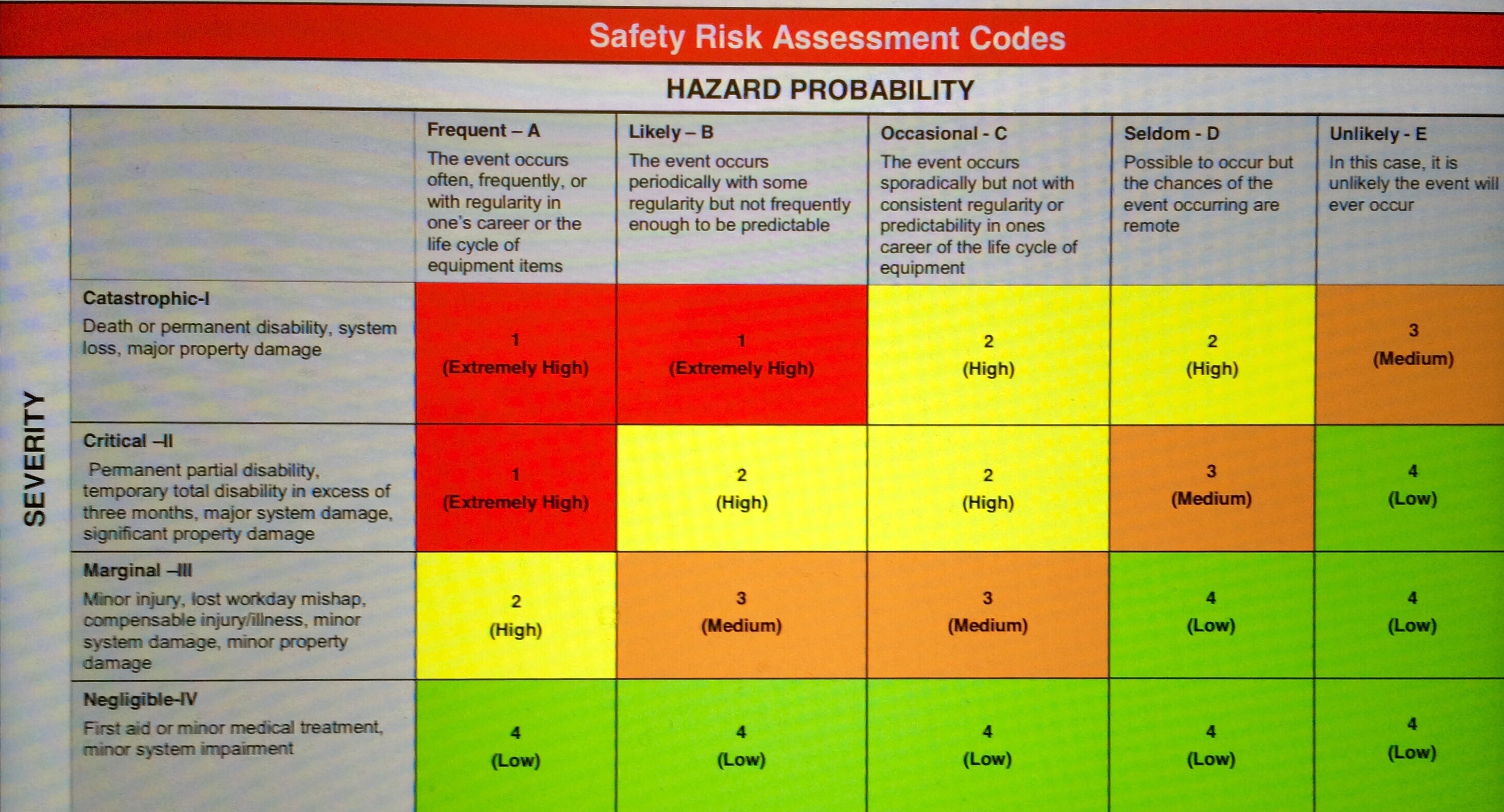
Hazard Classification:
A hazard class rating will be inserted by the inspector [Reference: 6709.12, 11.4]. Hazards found during
an inspection shall be classified so that managers can allocate time and dollars for their correction in
order of priority based on the degree of danger present. Hazards shall be classified as: imminent danger,
serious, and non-serious based on the following criteria:
1. Normal - No perceived hazard or risk.
2. Imminent danger hazards risk assessment code 1 (RAC 1) would likely cause death, severe injury or
high property losses immediately, or before the hazard can be eliminated through normal procedures.
Immediate employee protection and abatement is required. An example is a leaking propane gas cylinder
in crew quarters.
3. Serious hazards risk assessment code 2/3 (RAC 2/3) are those in which there is high probability that
serious injury, illness, or extensive property damage would result unless corrective action is taken.
Abatement shall be accomplished within 14 days. An example is a broken stair tread.
4. Non-serious hazards risk assessment code 4 (RAC 4) are those that could cause injury, illness, or
property damage. Abatement shall be accomplished in 30 days. An example is a broken window in a
workshop.
Note: In the event a hazard cannot be corrected in the time allotted (contractor not available or
contracting issues) a plan must be in place to correct the hazard as soon as possible. All employees must
be notified of the hazard to limit exposure.
Postings
-
Is the Summary of Occupational Illnesses and Injuries posted February thru April? 29CFR 1904.35
-
Are emergency telephone numbers posted where they can be readily found in case of emergency? 29 CFR 1910.38
-
Is the required OSHA workplace poster displayed in a prominent location where all employees are likely to see it? OSH Act 1970
I. GENERAL WORK ENVIRONMENT
-
1. Has this facility received a facility or workplace safety inspection within the past 12 months? | FSM 6714 FSH 7309.11, Ch.40 FSH 6709.11, 39.21, FSH 6709.12 Ch 10
-
2. Are all places of employment, passageways, and storerooms kept clean and orderly, and in a sanitary condition? | 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(1) 29, CFR 1910.141(a)(3)(i), H&SC 39.13.2.a
-
3. Are combustible waste materials and residues in a building or unit operating area kept to a minimum and disposed of daily. | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(iii), H&SC 34.2.8
-
4. Are covered metal waste cans used for oily and paint-soaked waste? 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(iii) H&SC 27.22e.2.a
-
5. Are grounds around buildings and operating areas free of weeds, trash, and other combustible materials? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(iv)
-
6. Are all enclosed workplaces constructed, equipped, and maintained, so far as reasonably practicable, as to prevent the entrance or harborage of rodents, insects, and other vermin? Is a continuing and effective extermination program instituted where their presence is detected.? | 29 CFR 1910.141(a)(5) and 1910.142(j) and 1910.176(c)
-
7. Is refuse properly collected & disposed of regularly? | 29 CFR 1910.141(a)(4)(ii)
-
8. Is all water provided for drinking, washing, and cooking potable? | 29 CFR 1910.141(b)(1)(i)
-
9. Are all outlets for water, not suitable for drinking, clearly identified? | 29 CFR 1910.141(b)(2)(i), H&SC 39.83.1.e
-
10. Are all work areas adequately lighted? | H&SC 37.23, H&SC 39.13.2.c
-
11. Are first aid supplies (including barrier kits) readily available and maintained, with no expired items? | 29 CFR 1910.151(b), H&SC 21.22
-
12. Are handwashing facilities or other appropriate antiseptic materials readily available to employees who may be subject to infectious materials exposure? | 29 CFR 1910.1030(d)(2)(iii-iv)
-
13. Are safety equipment items available, mounted, and current? (e.g., fire extinguishers, smoke and CO detectors, and first aid kits) 29 CFR 1910.157(c)(1) 29 CFR 1910.151(b) H&SC 34.2.1
-
14. Are smoke alarms installed and functional? Are sleeping areas protected by properly operating smoke detection/ alarm devices? | H&SC 34.2.1, NFPA 101
-
15. Is smoking prohibited inside all buildings, and within 25 feet of common ingress and egress points? | H&SC 39.13.1, FSM 6443.8, USDA 4400-6
-
16. Does an Emergency Action Plan exist for this facility? An emergency action plan must be in writing, kept in the workplace, and available to employees for review.| 29 CFR 1910.38(b), H&SC 39.12.1
-
17. Are toilets and washing facilities sanitary? | 29 CFR 1910.141(d) and 1910.22(a)(1) H&SC 39.13.2.c
II. WALKING and WORKING SURFACES
-
1. Is the floor of every workroom maintained in a clean and so far as possible, dry condition? Are appropriate means taken to ensure that surfaces are slip-resistant? | 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(2), H&SC 39.13.2.c
-
2. Are aisles or walkways that pass near moving or operating machinery, welding operations, or similar operations arranged so employees will not be subjected to hazards? 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(1) ANSI B11.19-2003
-
3. Is there safe clearance for walking in aisles where vehicles are operating? | 29 CFR 1910.176(a)
-
4. Are walking-working surfaces maintained free of hazards such as sharp or protruding objects, loose boards, corrosion, leaks, spills, snow, and ice? | 29 CFR 1910.22(a)(3)
-
5. Are changes of direction or elevations readily identifiable? | H&SC 39.13.4, H&SC 39.64.3.c
-
6. Are standard guardrails provided wherever aisle or walkway surfaces are elevated more than 4 feet above any adjacent floor or the ground? | 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(1)(i) and 1910.28(b)(1)(i)(A) H&SC 32.23.1
III. FLOOR and WALL OPENINGS
-
1. Are walking-working surfaces inspected, regularly and as necessary, and maintained in a safe condition? 29 CFR 1910.22(d)(1)
-
2. Are toeboards (minimum 3.5 inches) installed around the edges of a permanent floor opening (where persons may pass below the opening) or around open sides? H&SC 39.13.5 29 CFR1910.29(k)(1)(ii)
-
3. Are standard railings used where openings in floors, porches, abrupt edges of loading docks, etc. are present? | 29 CFR 1910.22(c), H&SC 39.13.5
-
4. Are grates or similar covers over floor openings, such as floor drains, of such design that the grate spacing will not catch foot traffic or rolling equipment? | OSH ACT of 1970 Section (5)(a)(1):
IV. INDUSTRIAL STAIRS and STAIRWAYS
-
1. Are standard stair railings and handrails present on all stairways having four or more risers? | 29 CFR1910.28(b)(11)(ii) H&SC 32.23.2, H&SC 39.13.6.c
-
2. Are stair railings provided on at least one side of a closed stairway? | 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(11)(ii)
-
3. Do all stairs have standard railings on all open sides of the stairways and stair platforms? | 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(11)(ii)
-
4. The height of handrails shall be not more than 37 inches (94 cm) nor less than 30 inches (76 cm) from the upper surface of the handrail to the surface of the tread, in line with the face of the riser at the forward edge of the tread. | 29 CFR 1926.1052(c)(6)
-
5. Handrails shall provide an adequate handhold for employees grasping them to avoid falling. | 29 CFR 1926.1052(c)(9)
-
6. Are handrails and the top rails of stair rail systems capable of withstanding, without failure, a force of at least 200 pounds (890 n) applied within 2 inches (5 cm) of the top edge, in any downward or outward direction, at any point along the top edge. | 29 CFR 1926.1052(c)(5) UBC 1607.3.4
-
7. Are stairs provided where there is a change in structure level, and operations require regular travel between those levels? | 29 CFR 1910.25(b)(7)
-
8. Do all stairways have a minimum width of 22 inches (56 cm) between vertical barriers ? | 29 CFR 1910.25(c)(4)
-
9. Do stairs have at least 6'8" feet of overhead clearance? | 29 CFR 1910.25(b)(2)
-
10. Do stairs angle no more than 50 degrees and no less than 30 degrees from horizontal? | 29 CFR 1910.25(c)(1)
-
11. Are step risers on stairs uniform from top to bottom, with no riser height greater than 9.5 inches? | 29 CFR 1910.25(c)(2) H&SC 39.13.6.d
-
12. Are these areas well lit? | H&SC 39.13.6.d
-
13. Are stair treads provided with a slip resistant surface, and the nosings of a no-slip surface? | 29 CFR 1910.22(d)(2) H&SC 39.13.6.a
-
14. Where stairs or stairways exit directly into any area where vehicles may be operated, are adequate barriers and warnings provided to prevent employees from stepping into the path of traffic? | OSH ACT of 1970 Section (5)(a)(1): 29 CFR1910.176(a)
-
15. Are stairways free of defects, rubbish, slippery substances, loose materials, or obstructions that may cause slips, trips, and falls? | H&SC 39.13.6b
V. ELEVATED SURFACES, STORAGE, and MATERIALS HANDLING
-
1. Are load limits posted, when appropriate, showing load capacity on elevated floors, storage shelves, bins, and racks? | 29 CFR 1910.22(b) H&SC 39.64.3
-
2. Are elevated surfaces (more than 4 feet above the floor or ground) provided with standard guardrails? | 29 CFR 1910.28(b)(1)(i) and 1910.28(b)(1)(i)(A)
-
3. Are all elevated surfaces above 4 feet (beneath which people or machinery could be exposed to falling objects) provided with standard toeboards? | 29 CFR 1910.28(c)(1)
-
4. Is a permanent means of access/egress provided to work all areas? | 29 CFR 1910.36(a)(1)
-
5. Are mechanical assist devices, such as handtrucks, available for moving equipment and supplies? | H&SC 39.63.2
-
6. Is material on elevated surfaces piled, stacked, or secured in a manner to prevent it from tipping, falling, collapsing, rolling, or spreading? | 29 CFR 1910.176(b)
-
7. Are storage areas kept free from accumulation of materials that could constitute hazards from tripping, fire, explosion, or pest harborage, and is vegetation controlled if necessary? | 29 CFR 1910.176(c), H&SC 32.12.6
-
8. Are materials or equipment stored so as to not create hazards to employees, with sharp objects not obstructing the walkway? | 29 CFR 1910.176(b)
-
9. Are tools and materials stored away from unguarded windows, aisles, heat sources, and electrical panels? | H&SC 39.64.3b
-
10. Are materials stored on tops of bookcases and file cabinets kept to a minimum? | H&SC 39.51a.1
-
11. Are shelving and storage racks secured as necessary (e.g., to floors and walls) to prevent tipping? | 29 CFR 1910.176(b) H&SC 35.51a.1.b
-
12. Are clearance signs posted to warn of clearance limits where needed (e.g., in low overhead areas)? | 29 CFR 1910.176(e)
-
13. Are materials stored to prevent sprain or strain injuries to employees when retrieving or accessing? | H&SC 39.64
-
14. Is there safe clearance for equipment through aisles and doorways? Are materials stored so as to allow safe passage of workers? | 29 CFR 1910.176(a), H&SC 39.64.3b(3)
-
15. Are chains, ropes, chokers or slings securing equipment or supplies of adequate strength/condition for the job performed | H&SC 42.1-3
VI. EXIT DOORS and ROUTES
-
1. Is a fire prevention/evacuation plan prepared for the site? Is an appropriately-detailed scale plan of the site posted in conspicuous location(s) at the site? | 29 CFR 1910.38 29 CFR 1910.39 H&SC 34.11
-
2. Are all personnel familiar with the plan, and are fire drills scheduled at least twice per year? | 29 CFR 1910.38(e) 29 CFR 1910.38(f) H&SC 34.11.2
-
3. Are the directions to exits, if not immediately apparent, marked with visible signs? | 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(4), H&SC 34.11.6
-
4. Are doors, passageways, or stairways that are neither exits nor access to exits, and which could be mistaken for exits, appropriately marked “NOT AN EXIT,” or “TO BASEMENT,” “STOREROOM,” etc.? | 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(5), H&SC 34.11.6.a
-
5. Are exit signs provided with the word “EXIT” in lettering at least 6 inches high and the stroke of the lettering at least ¾-inch wide? | 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(7)
-
6. Is there a sign reading “EXIT” with an arrow indicating the direction, in every location where the direction of travel is not apparent? | 29 CFR 1910.37(b)(4)
-
7. Are exit doors unlocked, with employees able to open them from the direction of exit travel without the use of a key or any special knowledge or effort? | 29 CFR 1910.36(d), (d)(1), H&SC 34.11.6.b
-
8. Are there sufficient exit routes to permit prompt escape in case of emergency? | 29 CFR 1910.36(b), H&SC 34.11.5
-
9. Are exit routes free of obstructions, with no material or equipment placed there, either permanently or temporarily? | 29 CFR 1910.37(a)(3)
-
10. Are exit accesses at least 28 inches in width? | 29 CFR 1910.36(g)(2)
-
11. Are all safeguards designed to protect employees during an emergency (sprinkler systems, alarm systems, fire doors, and exit lighting) in proper working order? | 29 CFR 1910.37(a)(4)
VII. ELECTRICAL SAFETY
-
1. Is all electrical work performed by a licensed contractor or Forest Service inspector in compliance with NEC and OSHA rules? | 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(1), H&SC 36.1 and 36.12
-
2. Is adequate clearance (36”) provided in front of electrical service panels and disconnects? | 29 CFR 1910.303(g)(1)(i-iv), H&SC 36.13.12.a
-
3. Do circuit breakers clearly indicate whether they are in the “on” or “off” position? | 29 CFR 1910.304(f)(1)(vi), H&SC 36.13.11
-
4. Are all disconnecting switches and circuit breakers labeled to indicate their use or equipment served? | 29 CFR 1910.303(f)(1), H&SC 36.13.11
-
5. Are circuit breakers used as switches in 120-volt fluorescent lighting circuits approved for the purpose and marked “SWD”? 29 CFR 1910.304(f)(1)(viii) NEC 240.83(D)
-
6. Are enclosures or guards installed, arranged, and strong enough to prevent damage to electrical equipment which may be exposed to such damage? | 29 CFR 1910.303(g)(2)(i), NEC 110.27(A)
-
7. Are conductors entering boxes, cabinets, or fittings protected from abrasion, and provided with undamaged, tight-fitting covers, or plates, including plugging unused opening (knockouts)? | 29 CFR 1910.305(b)(1)(i), 29 CFR 1910.305(b)(1)(ii), 29 CFR 1910.305(b)(2)(i), H&SC 36.13.5, NEC 110.12(A) and (B)
-
8. Are defective components promptly replaced? | H&SC 36.13.4
-
9. Are unused live electrical wires secured/removed? | 29 CFR 1910.303(b)(1)
-
10. Are electrical outlets prohibited above permanently installed baseboard electric heaters? See manufacturers instructions on installation. | NEC 424.9, NEC 210.52
-
11. Are flexible cords and cables prohibited as a substitute for fixed (permanent) wiring of a structure? Is it prohibited to run flexible cords through holes in walls, ceilings, floors, through doors and windows, or concealed behind building walls, ceilings, and floors? | 29 CFR 1910.305(g)(1)(iv)(A-F), H&SC 36.13.6.a
-
12. Do all extension cords have a grounding conductor?| 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(3)(i), H&SC 36.13.9.b
-
13. Are extension cords protected from abrasion, crushing, kinking, and pulling? | H&SC 36.13.6
-
14. Are portable cords and plug-connected equipment with frayed or deteriorated insulation repaired or replaced promptly? | 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(2)(i)
-
15. Are conductors spliced or joined by using suitable devices or by brazing, welding, or soldering? | 29 CFR 1910.303(c)
-
16. Are all splices, joints, and free ends of conductors covered with adequate insulation? | 29 CFR 1910.303(c)(3)(I)
-
17. Are electrical cords free of splices or taps? | 29 CFR 1910.305(g)(2)(ii), H&SC 36.13.6.e
-
18. Are electrical appliances such as vacuum cleaners, portable heaters, motor-operated appliances, handheld motor-operated tools, or that are used in wet or damp locations grounded? | 29 CFR 1910.304(g)(6)(vi)(C)(3), 29 CFR 1910.304(g)(6)(vi)(C)(5), 29 CFR 1910.304(g)(6)(vi)(C)(4)
-
19. Have all grounded conductors maintained the designated polarity when attached to a terminal or load, with no reversed polarity, open neutral, etc.? | 29 CFR 1910.304(a)(2)
-
20. Are all lights located within 7 feet of the floor, or exposed to being struck or damaged, protected? | H&SC 37.23a.1
-
21. Are replacement bulbs within a lighting fixture’s rating? | H&SC 37.23a.2
-
22. Are ground-fault circuit interrupters provided outside of buildings, and in damp areas (such as near kitchen countertop surfaces, in bathrooms, unfinished basements, shops, and garages)? | 29 CFR1910.304(b)(3)(i), NEC 210.8(A-E), H&SC 36.13.2.a.(1)
-
23. Is all equipment and associated wiring installations in hazardous (classified) locations intrinsically safe or approved for the location and its related combustibles? | 29 CFR 1910.307(b), 29 CFR 1910.307(b)(2)(i), NEC 500.7, NEC 504.1
VIII. PLUMBING, HEATING, VENTILATION, and AIR CONDITIONING
-
1. Does your HVAC system receive inspections from a competent person at least annually? | H&SC 37.11
-
2. Is preventive maintenance performed as recommended by the manufacturer, and records kept with the equipment? | H&SC 37.12.3
-
3. Are chimneys, flues, and masonry cleaned and inspected at least annually? | H&SC 34.33
-
4. Are indoor air quality complaints investigated with results effectively communicated to employees? | MLA, Article 27.10
-
5. Are air filters inspected monthly and changed as needed, or as recommended by the manufacturer? | H&SC 37.12.7
-
6. Are gas system shutoffs identified, and readily accessible? | NFPA 54:7.8.2.3, H&SC 37.12.6, CPC 1210.11.1, CPC 1210.11.2
-
7. Are gas appliances accessible for inspection and service by qualified individuals? | H&SC 37.12.6, NFPA 54: 4.1
-
8. Are gas water heaters and connectors protected from physical damage (e.g., in garages)? | NFPA 54:9.1.10.2, H&SC 39.9
-
9. In earthquake-prone locations, inspect to ensure that the water heater is secured to the wall studs in two locations (high and low) using appropriate metal strapping and bolts.| NFPA 54:G.6.3.4, CPC 507.2, H&SC 39.9,
-
10. Are temperature/pressure relief valves and drains installed on all water heaters? | NFPA 54:10.27.5, H&SC 39.9
-
11. Are water system shutoffs identified, accessible and operable? | Best Practice
IX. HAZARDOUS MATERIALS
-
1. Has a written Hazard Communication Plan been developed which covers this facility? | 29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(1), H&SC 61.13
-
2. Are employees made aware of hazards involved with the various chemicals they may be exposed to in their work environment, such as ammonia, chlorine, epoxies, and caustics? (Right-to-know) | 29 CFR 1910.1200(e), 29 CFR 1910.1200(h), H&SC 61.11
-
3. Does this facility have a current inventory of hazardous substances used here? | 29 CFR 1910.1200(e)(1)(i), H&SC 61.14.1
-
4. Are SDS’s readily available to employees at all times? | 29 CFR 1910.1200(b)(3)(ii), 29 CFR 1910.1200(b)(4)(ii), {29 CFR 1910.1200(b)(6) Exceptions}, 29 CFR 1910.1200(g)(1), 29 CFR 1910.1200(g)(6), H&SC 61.14.2-Employees shall not handle hazardous chemicals that do not have an SDS (Hazardous Chemical. Any chemical having either a physical or health hazard associated with its use.)<br>
-
5. Is each container for a hazardous substance (vats, bottles, storage tanks) labeled with product identity and a hazard warning that communicates specific health and physical hazards? | 29 CFR 1910.1200(f)(10), 29 CFR 1910.1200(f)(6)(ii)
-
6. Are hazardous or potentially hazardous conditions, equipment, or operations identified (through appropriate signing and tags) that may cause harm by inhalation, ingestion, skin absorption, or contact (e.g., lead-based paint, biohazards, radiation, etc.)? | 29 CFR 1910.145(a-f), H&SC 61.01(1)
-
7. Do you have a current Hazardous Material Spill Response Plan to manage spills in the office and field? | FSM 2100, Ch. 2160, 29 CFR 1910.120(q)(1)
-
8. Is the possible presence of asbestos determined prior to the beginning of any repair, demolition, construction, or reconstruction work? | 29 CFR 1910.1001(j)(3)(i-iii), H&SC 61.81
-
9. Are employees warned of the presence/ hazards of asbestos-containing materials and lead based paint where required? | 29 CFR 1910.1001(j)(2)(iii), 29 CFR 1910.1025(d) H&SC 61.81
-
10. Are eye wash stations provided (15 min./min flow) in areas where caustics (battery charging or corrosive liquids) are used? | 29 CFR 1910.151(c)
-
11. Are covered metal waste cans used for combustible waste materials (oily and paint-soaked rags)? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(iii), H&SC 27.22e.2
-
12. Are employees prohibited from eating in areas exposed to toxic materials? | 29 CFR 1910.141(g)(2), H&SC 61.26.3 {Toxic material means a material in concentration or amount which is of such toxicity so as to constitute a recognized hazard that is causing or is likely to cause death or serious physical harm. }
-
13. Are pipelines transporting hazardous substances through above-ground piping identified? | H&SC 38.12b
X. FLAMMABLE and COMBUSTIBLE MATERIALS
-
1. Are all flammable and combustible liquids stored in labeled, approved containers, tanks, or drums? | 29 CFR 1910.1200(f)(5)
-
2. Are flammable and combustible liquids stored in approved cabinets or storage buildings? | 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(3), H&SC 34.2.4
-
3. Are storage cabinets labeled “Flammable- Keep Fire Away”? | H&SC 61.51d.4.a
-
4. Are metal materials storage cabinets of appropriate design, with secondary containment, three-point door latches, and self-closing doors*? (*recommended for future procurement's) | 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(3)(ii)(a),
-
5. Do maintenance and operating procedures control leakage and prevent the accidental escape of flammable or combustible liquids, with spills being cleaned up promptly (e.g., in the bottom of cabinets)? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(9)(i)
-
6. Are tanks of gasoline and diesel (e.g., truck-mounted, or above-ground storage tanks) labeled “GASOLINE-FLAMMABLE” and “DIESEL-COMBUSIBLE” accordingly (durable material, with red lettering at least 3” high and characters at least ½” in width, on a white background)? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(6)(i), UFC 7901.9.2, UFC 7902.1.3.1
-
7. Are bulk drums of flammable liquids grounded and bonded to containers during dispensing? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(6)(ii), H&SC 61.51e.1.c
-
8. Are only approved containers used for storing flammable and combustible liquids? | 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(2)(i)
-
9. Are all containers of flammable or combustible liquids securely sealed or closed, except when in use? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(2)(iv)(a)
-
10. Are liquefied petroleum storage tanks, regulators, and piping guarded to prevent damage from impacts from vehicles? | 29 CFR 1910.110(d)(10), NFPA 54 9.1.13
-
11. Are above-ground storage tanks, piping, and fittings protected from vehicle impacts (e.g., bollards)? |29 CFR 1910.106(g)(3)(v)(b) NFPA 30 23.5.2.2
-
12. Are “NO SMOKING” signs posted on liquid propane gas tanks? | NFPA 1 10.9.1, NFPA 1 20.4.2.4.1
-
13. Are LP gas containers, including portable tanks, and compressed gas cylinders stored outside in a well-ventilated area that is protected from physical damage? | 29 CFR 1910.101(a), H&SC 61.62
-
14. Are “NO SMOKING” signs posted in areas where flammable or combustible materials are used/stored? | 29 CFR 1910.106(e)(6)(i)
XI. Fire Extinguishers
-
1. Are portable fire extinguishers located, mounted, and readily accessible at each work location? 29 CFR 1910.157(c)(1)
-
2. Are fire extinguishers provided for the type of materials they will extinguish, and placed in areas where they are to be used? (CLASS A: Ordinary combustible materials fires; CLASS B: Flammable liquid, gas, or grease fires; CLASS C: Energized-electrical equipment fires.) 29 CFR 1910.157(d), H&SC 35.11a
-
3. Are fire extinguishers charged and fully operable? 29 CFR 1910.157(c)(4)
-
4. Are fire extinguishers mounted so that employees do not have to travel more than 75 feet for a Class A fire or 50 feet for a Class B fire in all locations? 29 CFR 1910.157(d)(2), 29 CFR 1910.157(d)(4)
-
5. Are fire extinguishers visually inspected monthly? 29 CFR 1910.157(e)(2), NFPA 10 7.2.1.2.1
-
6. Are all fire extinguishers serviced, maintained, and tagged at intervals not to exceed one year? 29 CFR 1910.157(e)(3)
-
7. Are extinguishers located, mounted, and signed not less than 10’, or more than 25’ from any flammables/ combustibles storage area outside of a storage room, but inside of a building (e.g., storage lockers)? 29 CFR 1910.106(d)(7)(I)(b), 29 CFR 1910.157(c)(1)
-
8. Are fire extinguishers mounted 4 inches minimum off the ground maximum of 5 feet from the top of extinguisher weighing less then 40 lbs. and 3.5 feet from the top of extinguisher weighing more then 40 lbs. | NFPA 10 6.1.3.8<br>NFPA 10
XII. HAND TOOLS and EQUIPMENT
-
1. Are all hand tools and equipment present on site in good working condition? 29 CFR 1910.242(a) H&SC 41.04a.2
-
2. Are hand tools that develop mushroomed heads (e.g., chisels and punches) reconditioned or replaced as necessary? 29 CFR 1910.242(a), H&SC 41.13.2
-
3. Are broken or fractured handles on hammers, pulaskis, etc. replaced promptly? 29 CFR 1910.242(a), H&SC 41.13.4
-
4. Are tool handles free of splinters and cracks, and wedged tightly in the head of all tools? 29 CFR 1910.242(a), H&SC 41.13.4
-
5. Are tool-cutting edges kept sharp? 29 CFR 1910.242(a), H&SC 41.13.2
-
6. Are jacks inspected periodically to assure that they are in good operating condition? 29 CFR 1910.244(a)(2)(vi), H&SC 42.1.8
XIII. PORTABLE (POWER) TOOLS and EQUIPMENT
-
1. Are all tools (including personal tools) used by personnel maintained in a safe condition? 29 CFR 1910.242(a)
-
2. Does each portable circular saw or drill have a constant pressure switch (dead man switch) that will shut off the power when pressure is released? 29 CFR 1910.243(a)(2)
-
3. Are all cord-connected, electrically-operated tools and equipment effectively grounded or of the approved double- insulated type? 29 CFR 1910.334(a)(3)(i) H&SC 43.12.1.k NFPA 70 (NEC) 250.114
-
4. Are grinders, saws, and similar equipment provided with appropriate safety guards? 29 CFR 1910.243(c) H&SC 43.5 H&SC 43.7
-
5. Are guards and safety equipment provided by the manufacturer on the power tools; unless the manufacturer identifies specific uses? |H&SC 43.12.2 {Example: Some grinders may be used as buffers and the guards may removed per the manufacturer}
-
6. Are portable circular saws equipped with guards above and below the base plate or shoe? 29 CFR 1910.243(a)(1) H&SC 43.51.a.1.a
-
7. Are rotating parts of equipment such as sanders guarded at nip points to prevent physical contact? 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(1) H&SC 43.51a.6.a
-
8. Are effective guards in place over belts, pulleys, chains, and sprockets on equipment such as concrete mixers, air compressors, and the like? 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(1-3), H&SC 31.34(b)(2) H&SC 43.12.2
-
9. Are portable fans provided with full guards having openings of 1/2-inch or less? 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(5)
-
10. If hoisting equipment is used for lifting heavy objects, are hoist ratings appropriate for the task? H&SC 42.1.11
-
11. Are portable, waterproof ground-fault circuit interrupters (for all temporary 15, 20, and 30 ampere circuits) used for outside construction/ maintenance? 29 CFR 1910.304(b)(3)(ii)(A) H&SC 36.13.2
-
12. Are pneumatic and hydraulic hoses on power-operated tools checked regularly for deterioration or damage? H&SC 43.31.1.b
XIV. ABRASIVE WHEEL EQUIPMENT/ GRINDERS
-
1. Is appropriate PPE (including first aid kit, eye/face, and hearing protection) available for operating all equipment, and is eye/face protection always worn when grinding? | 29 CFR 1910.132(d)(1)(i-iii), H&SC 43.71 H&SC 43.71.2-3 H&SC 43.72.8
-
2. Are abrasive wheels closely inspected for cracks and defects and ring tested when mounting, and closely inspected thereafter? 29 CFR 1910.215(d)(1) H&SC 43.72.1
-
3. Is the maximum RPM rating of each abrasive wheel compatible with the RPM rating of the grinder motor? 29 CFR 1910.215(d)(1) H&SC 43.72.2
-
4. Are abrasive wheels oil-free and properly dressed? H&SC 43.72.10
-
5. Is the work rest on stationary grinders used and kept adjusted to within 1/8-inch of the wheel? 29 CFR 1910.215(a)(4) H&SC 43.72.4
-
6. Is the adjustable tongue on the top side of grinder used and kept adjusted to w/i 1/4-inch of the wheel? 29 CFR 1910.215(b)(9) H&SC 43.72.6
-
7. Do safety guards cover the spindle end, nut, flange projections? 29 CFR 1910.215(a)(2)(i)
-
8. Do guards limit grinding to no more than 90 degrees (one-fourth of the wheel’s periphery), with no more than 65 degrees above the horizontal plane of the wheel spindle? 29 CFR 1910.215(b)(3)
-
9. Are bench and pedestal grinders permanently mounted? 29 CFR 1910.212(b) H&SC 43.72.9
-
10. Are aisles and areas around grinders kept clear? 29 CFR 1910.22(a)
XV. MACHINE GUARDING
-
1. Are guards provided to protect the operator and other personnel from hazards created by point of operation, ingoing nip points, rotating parts, flying chips, and sparks? 29 CFR 1910.212(a)(1)
-
2. Are guards attached to the machine when possible, and if that is not possible, attached elsewhere? The guard shall be such that it does not offer an accident hazard in itself. |29 CFR 1910.212(a)(2)
-
3. Is the point of operation of any machine whose operation exposes an employee to injury, guarded and in conformance with appropriate standards? |29 CFR 1910.212(a)(3)(ii)
-
4. Is equipment and machinery securely placed and anchored when necessary to prevent tipping, walking, or other movement that could result in personal injury? 29 CFR 1910.212(b) H&SC 39.74.4
-
5. Are all belts, pulleys, gears, shafts, and moving parts properly guarded? Are guards and safety devices functional, adjusted, and in place? |29 CFR 1910.213(a)(9), 29 CFR 1910.219(d) 29 CFR 1910.219(e) H&SC 39.74.6 H&SC 39.74b.3
XVI. WOODWORKING MACHINERY
-
1. Is appropriate personal protective equipment (e.g., face, eye, and hearing protection) provided? 29 CFR 1910.132(a)
-
2. Are all stationary woodworking machines securely anchored to prevent movement? 29 CFR 1910.212(b)
-
3. Are all woodworking machines and portable electric hand tools properly grounded? 29 CFR 1910.213(a)(11)
-
4. Is equipment equipped such that power switches must be reset after power loss/interruption? 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(3) H&SC 43.51.12
-
5. Are electrical switches located within reach of the operator’s position, allowing the operator to secure the machinery without leaving his/her position, or reaching over the cutter? 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(1) H&SC 43.51.10 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(4)
-
6. Are foot-operated switches guarded to prevent accidental actuation by personnel or falling objects? 29 CFR 1910.213(b)(6)
-
7. Is emphasis is placed upon the importance of maintaining cleanliness around woodworking machinery, particularly as regards the effective functioning of guards and the prevention of fire hazards in switch enclosures, bearings, and motors.? 29 CFR 1910.213(s)(6) H&SC 39.74.5 H&SC 39.74b.5
-
8. Are all woodworking machines (such as table saws, radial arm saws, miter (chop) saws, band saws, jointers, planers, and other miscellaneous machinery) effectively guarded to protect personnel? 29 CFR 1910.212(a) H&SC 43.51a.1.a
-
9. Are hand-fed table saw blades guarded? 29 CFR 1910.213(d)(1) H&SC 43.51a.2.a(1)
-
10. Does the table saw guard adjust itself to thickness of, and remain in contact with, the material being cut? 29 CFR 1910.213(c)(1)
-
11. Do hand-fed table saws have a kerf-spreader? 29 CFR 1910.213(c)(2) H&SC 43.51a.2.a(2)
-
12. Do hand-fed table saws have anti-kick back dogs? 29 CFR 1910.213(c)(3) H&SC 43.51a.2.a(2)
-
13. Are feather boards available and used (such as in special operations such as molding, rabbeting, and dadoing when guards must be removed)? 29 CFR 1910.213(a)(15)
-
14. Are push sticks or blocks provided in several sizes, and suitable for the work being done? H&SC 43.51.20
-
15. Do radial arm saws have complete upper and lower blade guards? 29 CFR 1910.213(h)(1) H&SC 45.51a.3.c
-
16. Do radial arm saws have anti-kick-back dogs? 29 CFR 1910.213(h)(2) H&SC 45.51a.3.d
-
17. Do radial arm saws have a self-return mechanism? 29 CFR 1910.213(h)(4) H&SC 45.51a.3.f(2)
-
18. Is the direction of blade rotation marked on all radial arm saws? 29 CFR 1910.213(h)(5) H&SC 45.51a.3.e
-
19. Are circular saw blades completely guarded? 29 CFR 1910.213(a)(12) 29 CFR 1910.243(a)(1)
-
20. Do band saws have fully guarded wheels, self-adjusting guards, and tension control devices? 29 CFR 1910.213(i) H&SC 43.51a.4
-
21. Is the work area kept free of debris that may create tripping or fire hazards? H&SC 43.51.19
XVII. COMPRESSORS and COMPRESSED AIR
-
1. Are compressors equipped with pressure-relief valves and pressure gauges? 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(3)(i)
-
2. Are air intakes installed and equipped to ensure only clean, uncontaminated air enters the compressor? 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(2)
-
3. Are supply lines, hoses, and connections inspected regularly, and in good repair? H&SC 43.31.1.b
-
4. Are tank drain valves easily accessible, and opened frequently to prevent the accumulation of liquid? 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(2) H&SC 43.21.2
-
5. Is the system designed so that no valve is located between the compressor tank and the safety valve(s)? 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(3)(ii)
-
6. Are safety valves on compressed-air systems checked frequently? 29 CFR 1910.169(b)(3)(iv)
-
7. Are records of tank draining's and safety valve checks maintained? H&SC 43.21.3
-
8. Are compressors operated and lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations? H&SC 43.21.4
-
9. Are signs posted to warn of the automatic starting feature of the compressors? 29 CFR 1910.145(f)(3), 29 CFR 1910.145(f)(7)
-
10. Are all belts, pulleys, sprockets and chains, gears, shafts, and couplings less than 7 feet from the floor guarded? 29 CFR 1910.219(d)(1)
-
11. Is it strictly prohibited to direct compressed air toward a person? H&SC 43.31.1.j
-
12. Is it strictly prohibited to use compressed air for cleaning off clothing or parts of the body? H&SC 43.31.1.k
-
13. Has effective reduction of compressed air to less than 30 PSI for cleaning purposes been provided? Is effective chip guarding and PPE provided to protect personnel from flying chips? (E.g., protective barriers, shields, goggles, face shields.) ? 29 CFR 1910.242(b), H&SC 43.31.1.i
XVIII. PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT
-
1. Are workplace hazards assessed and documented via inspections? and necessary PPE selected and fitted to affected employees? 29 CFR 1910.132(d) H&SC 21.13a.2
-
2. Is there sufficient PPE provided and appropriate for the tasks assigned? 29 CFR 1910.132(a) H&SC 21.13a
-
3. Is PPE used and maintained in a reliable and sanitary condition, and not used if defective or damaged? 29 CFR 1910.132(a), 29 CFR 1910.132(e)
-
4. Is employee-provided PPE inspected and monitored to ensure its adequacy (including proper maintenance and sanitation)? 29 CFR 1910.132(b) H&SC 21.13a.1.c
-
5. Are filtering face pieces (dust masks) provided which are clean and uncontaminated? 29 CFR 1910.134(c)(2)(ii)
-
6. Do eye and face protection devices comply with ANSI/ISEA Z87.1-2010? 29 CFR 1910.133(b) H&SC 21.13b.1
-
7. Are suitable facilities for quick drenching or flushing of the eyes and body provided within the work area for immediate emergency use.? 29 CFR 1910.151(c)
-
8. Are approved hearing protection devices available to employees working in noisy areas? 29 CFR 1910.95(b)(1) 29 CFR 1910.95(i)(1) H&SC 21.13b.2
XIX. PORTABLE and FIXED LADDERS
-
1. Is the use of ladders limited to temporary uses wherever possible? H&SC 33.11
-
2. Are ladders used only for their intended purpose, and not for guys, braces, skids, gangways, etc.? 29 CFR 1910.23(b)(8)
-
3. Are all ladders inspected for defects before use and after any occurrence that could damage the ladder? 29 CFR 1910.23(b)(9), H&SC 33.11a
-
4. Are all ladders in good condition, joints between steps and side rails tight, all hardware and fittings securely attached, and movable parts operating freely without binding or undue play? H&SC 33.11a(1-6)
-
5. Are nonskid safety feet on all portable rung ladders where there is a hazard of slipping? 29 CFR 1910.23(c)(1), H&SC 33.11b.4
-
6. When ladders are used to access elevated surfaces, does the ladder always extend at least 3 feet above that surface? 29 CFR 1910.23(c)(11)
-
7. Are fixed ladders provided with grab bars installed adjacent to, or above, a ladder to provide a hand hold beyond the limits of the ladder? 29 CFR 1910.23(d)(7)
-
8. Are the ladder rungs, steps, and cleats spaced not less than 10 inches (25 cm) and not more than 14 inches (36 cm) apart, as measured between the center lines of the rungs, cleats, and steps? 29 CFR 1910.23(b)(2)
-
9. Are rungs, cleats, and steps free of splinters, sharp edges, burrs, or projections that may create a hazard on fixed ladders? 29 CFR 1910.23(b)(7), H&SC 33.11a.5
-
10. Is there at least 7” of clearance behind rungs on fixed ladders, except when unavoidable obstructions are encountered? 29 CFR 1910.23(d)(2)
-
11. Are all fixed ladders designed for a minimum single live load of at least 250 pounds? 29 CFR 1926.1053(a)(1)(iii)
-
12. Is the distance between rungs, cleats, and steps on fixed ladders between 10-14 inches, and uniform throughout the length of the ladder? 29 CFR 1910.23(d)(13)
-
13. Are rungs on fixed ladders at least a minimum of 16 inches in length? 29 CFR 1910.23(d)(13)
-
18. Are all fixed metal ladders painted or otherwise treated to resist corrosion or rusting? 29 CFR 1910.23(b)(6)
XX. COMPRESSED GAS and CYLINDERS
-
1. Are cylinders legibly marked to clearly identify the gas contained? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(1)(ii)
-
2. Are compressed gas cylinders inspected as required for corrosion, general distortion, cracks, or any other defect that might indicate a weakness or render them unfit for service? 29 CFR 1910.101(a) H&SC 61.62.3
-
3. Are cylinders with water-weight capacity over 30 pounds equipped (with means for connecting a valve protector or device, or with a collar or recess) to protect the valve? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(1)(iv)
-
4. Are valve protectors always placed on cylinders except when they are in use or connected for use? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2)(iv)
-
5. Are valves on empty cylinders closed when not in use? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2)(iii)
-
6. Are stored oxygen cylinders separated from heat sources, flammable/combustible materials, and gas cylinders a minimum of 20’, or by anon- combustible half-hour fire-rated barrier at least 5’ high? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(4)(iii) H&SC 27.23e.9.b
-
7. Are cylinders located or stored in well-ventilated dry areas where they will not be damaged by passing or falling objects, struck by vehicles, or be subject to tampering by unauthorized persons? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2)(ii) H&SC 27.23e.9.b
-
8. Are compressed-gas cylinders stored in an area protected from external heat sources (flames, intense radiant heat, electric arcs or high-temperature lines)? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(2)(i)
-
9. Unless secured on special trucks, are regulators removed and valve-protection caps put in place before moving cylinders? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(D) H&SC 27.23e.8.a
-
10. Are all gas cylinders stored and shipped with the valve end up and valve covers in place? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(iii)(A) H&SC 27.23e.8-9
-
11. Are acetylene cylinders stored valve end up? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(3)(ii)
-
12. Are cylinders stored, handled, or transported in a manner to prevent them from tipping, falling, or rolling? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(B) 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(iii)(B)
XXI. WELDING, CUTTING, and BRAZING
-
1. Are only authorized/ trained personnel allowed to use welding, cutting or brazing equipment? 29CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(xiii)(c) H&SC 27.23b
-
2. Is welding or cutting only permitted in areas made fire safe? 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(xv)
-
3. When the object to be welded cannot be moved and fire hazards cannot be removed, are shields used to confine heat, sparks, and slag? 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(1)(ii) H&SC 27.23e.4.a
-
4. Are fire watchers assigned when welding or cutting is performed in locations (within 35”) where a serious fire might develop? 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(iii)
-
5. Are fire watchers kept on site at least one-half hour after completion of operations? 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(B)
-
6. Is suitable fire-extinguishing equipment available for immediate use? 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(2)(ii)
-
7. Are employees exposed to the hazards created by welding, cutting, or brazing operations protected with PPE and appropriate required clothing? 29 CFR 1910.252(b)(3) H&SC 27.23c
-
8. Are eye-protection, helmets, hand shields, and goggles in good condition, and do they meet appropriate standards? 29 CFR 1910.252(b)(2) H&SC 27.23e.4.b
-
9. Is a check made for adequate ventilation where welding or cutting is performed? 29 CFR 1910.252(c)(2) H&SC 27.23e.1
-
10. Are cylinders, cylinder valves, couplings, regulators, hoses, and apparatus kept free of oily or greasy substances? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(i) H&SC 27.23e.7.c
-
11. Before hot work begins, are drums, barrels, tanks, and other containers thoroughly cleaned and tested so that no substances remain that could explode, ignite, or produce toxic vapors? 29 CFR 1910.252(a)(3)
-
12. Do cylinders without fixed hand wheels have keys, handles, or nonadjustable wrenches on stem valves when in service? 29 CFR 1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(E) H&SC 27.23e.7.d
-
13. Is open circuit (no load) voltage of arc welding and cutting machines as low as possible, and not in excess of the recommended limit? 29 CFR 1910.254(b)(3)(iii)
-
14. Are work and electrode lead cables frequently inspected for wear and damage and replaced when needed? 29 CFR 1910.254(d)(9)(iii)
-
15. Do means for connecting cable lengths have adequate insulation? 29 CFR 1910.254(d)(9)(iii)
-
16. Are power cables free of defects and splices within 10 feet of the operator? 29 CFR 1910.254(d)(8) H&SC 27.23e.5.b
-
17. Are employees required to shut off the electric power to the welder when work is stopped, or nobody is in attendance? H&SC 27.23e.5.d(4)
-
18. Are electrodes removed from the holders when not in use? 29 CFR 1910.252(b)(4)(v)
-
19. Are electrode holders, when not in use, placed so that they cannot make contact with persons, conducting objects, fuel, or compressed gas tanks? 29 CFR 1910.254(d)(7)
XXII. INDUSTRIAL TRUCKS / FORKLIFTS
-
1. Do industrial truck operators meet OSHA's industrial truck operator training requirements? 29 CFR 1910.178(l) H&SC 44.61-62
-
2. Are industrial trucks inspected by the operator prior to each shift? 29 CFR 1910.178(q)(7) H&SC 44.62a.1
-
3. Are industrial trucks taken out of service when found in need of repair, or in any way unsafe? 29 CFR 1910.178(p)(1) H&SC 44.62a.1
-
4. Are overhead guards used as a protection against falling objects? 29 CFR 1910.178(m)(9) H&SC 44.62a.31c
-
5. Are unauthorized personnel prohibited from riding on powered industrial trucks? 29 CFR 1910.178(m)(3) H&SC 44.62a.30
-
6. Are sufficient clearances allowed wherever turns or passage must be made? 29 CFR 1910.176(a)
-
7. Are operators prohibited from handling loads exceeding the truck’s rated capacity? 29 CFR 1910.178(o)(2) H&SC 44.62a.2
-
8. Are persons prohibited from standing or passing under the elevated portion of any truck? 29 CFR 1910.178(m)(2) H&SC 44.62a.16
-
9. Are horns used where vision is obstructed, and backup alarms used when traveling in reverse? 29 CFR 1910.178(n)(4), H&SC 44.62a.26-27
-
10. Are unattended industrial trucks shut off, loads lowered, controls neutralized, and brakes set? 29 CFR 1910.178(m)(5)(i) H&SC 44.62a.17
XXIII. LOCKOUT / TAGOUT
-
1. Has a hazardous energy control program (consisting of energy control procedures, employee training, and periodic inspections) been established where applicable? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(1) H&SC 38.3
-
2. Has appropriate training been provided to authorized employees? H&SC 38.3.1.a
-
3. Is all machinery or equipment (capable of movement) required to be de-energized or disengaged and locked out during cleaning, servicing, adjusting, or setting-up operations? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(1) 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(2)(i) H&SC 38.3.2
-
4. Does the lockout/tagout procedure require stored energy (i.e., mechanical, hydraulic, air) be released or blocked before equipment is locked out for repairs? 29 CFR 1910.147(d)(5)(i)
-
5. Are appropriate employees provided with protective materials and hardware for hazardous energy control? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(i)
-
6. Are lockout and tagout devices identifiable to the employee applying them? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(ii)(D)
-
7. Do tagout devices include a legend warning against hazardous conditions if the equipment is re-energized? 29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(iii)
-
8 Are authorized employees required to check the safety of the lockout by attempting to start up after making sure no one is exposed? 29 CFR 1910.147(d)(6)
General Duty Clause or other noted deficiencies, concerns, or safety issues
-
Note any violations or concerns that need to be addressed. Provide photos and reference to issue to be addressed. <br>
Completion
-
Inspected by