Information
-
Audit Title
-
Client / Site
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Location
-
Personnel
-
Building warrant of fitness certificate in place and current?
-
renewal date of building warrant of fitness license
1. Housekeeping
1.1 Housekeeping
-
All walkways clear?
-
No excess solvent / inks stored on floor? (staging area is 265L max, 8 meter distance to next staging area, Total amount limited to the press area is limited to 400L or less)
-
Solvent storage information
-
The amount of inks located within the press area should be limited to one shift’s needs and never exceed 265 L at one staging area.
The distance to the next staging area should be at least 8 m.
The total amount of flammable liquids (ink, solvent etc.) in the press area should be limited to 400 L.
Containment should be provided for all staging of flammable inks and liquids. The containment should be large enough to hold the content of the maximum expected spill, generally the largest container, plus a 50 mm freeboard.
The distance between staging areas for inks (distance measured from the curb) and press should be at least 5 m and the distance to any combustible in-process storage should be at least 8 m. -
Emergency exit doors signed and clear of any obstructions?
-
Emergency maps displayed throughout site?
-
Emergency response team displayed in key areas and is up to date? (notice boards, etc..)
-
Hazardous good clearly labelled and stored in the correct areas?
-
Fire equipment accessible and unobstructed? (1mtr clearance)
-
Equipment / tools observed in good condition and have designated areas when not in use
-
No excess tape / cardboard / paper on floor used for temporary fixes?
-
No plastic linings used as floor covering?
1.2 Battery Chargers
-
Battery chargers for mobile equipment in good condition?
-
Battery chargers placed in a good location (at least 1.5 mtr clearance)
-
Battery spill kits available?
-
Correct PPE in place and in good condition for checking and maintaining batteries?
-
Service and maintenance up to date? (check any log books and servicing dates)
-
Any followup items / comments for Housekeeping
2. Smoking
2.0 Smoking
2.1 Smoking
-
There is a designated area for smoking on site?
-
Any smoking in unauthorised areas? (persons smoking outside of these areas or evidence sighted during site survey)
-
Site covers smoking areas in induction ?
-
Area is suitable and has proper containment vessels?
-
Fire fighting equipment available in area?
3. Manual Fire-Fighting Equipment
3.1 Fire Extinguishers
-
Fire-fighting equipment up to date?<br>No items missing, all displaying good charge, none discharged / empty<br>
-
Checklist are in place to regularly check fire fighting equipment?
-
No damage / wear showing?
-
Safety pin is in place?
-
Secured with correct clip so can be readily accessed when needed (e.g not held in place with strapping material or devices that make it difficult to release fire extinguisher)
-
Show information for Fire Extinguishers
-
Fire Extinguishers
• Light Hazard Occupancy: (e.g. typically offices with limited combustibles, training rooms, auditoriums etc.) Those areas where, because of relatively small amount of combustibles, only incipient fires of minimum severity may be anticipated. Provide pressurized water extinguishers throughout on the basis of one of the 2A extinguishers every 550 m2 (6,000 ft2) of floor area or part thereof with no less than one per floor. Limit travel distance from any point to an extinguisher to 23 m (75m) maximum.
• Ordinary (medium) Hazard Occupancy: (e.g. typically workshops, manufacturing areas without flammable liquids, restaurants, garages etc.) Those areas where incipient fires of average severity may be anticipated. Provide pressurized water or loaded stream extinguishers throughout on the basis of one of the 2A extinguishers every 280 m2 (3,000 ft2) or a 3A extinguisher every 418 m2 (4,500 ft2) of floor area or part thereof. Limit travel distance from any point to an extinguisher to 23m (75ft) maximum.
• Extra Hazard Occupancy: (e.g. typically printing operations and areas handling flammable liquids, warehousing areas etc.) Those areas where, because of the character or quantity of combustibles, incipient fires of extra severity may be anticipated. (Typical: spray painting, woodworking, solvent areas, etc.) Provide multi-purpose dry chemical extinguishers throughout on the basis of one 3A:10B: C extinguisher every (3,000 ft2) 280 m2.
Signage
Fire extinguishers will be located in easily accessible locations and be identified by location signs. Where extinguishers are located in storage areas, high level signs may be required.
Types of extinguishers
Dry chemical
Dry chemical extinguishers will be avoided in printing areas and in electrical/computer rooms where sensitive electronic equipment may be affected due to clean up problems. Dry chemical and foam extinguishers may be used as secondary means of extinguishment in event of failure of CO2 extinguishers to deal with fire.
Pressurised water
Nine litre (2.4 US gallons) water extinguishers will be provided to fight small fires involving combustible materials such as plastics and paper. If fire hose reels are installed in the area, water extinguishers are not required.
CO2 and Dry Chemical extinguishers may also be used but water is preferable for general combustibles.
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) extinguishers will be provided near electrical equipment and printing presses, for use on fires involving flammable liquids and live electrical plant/equipment such as switchboards. Water extinguishers and hose reels can only be used if the equipment is de-energised and electrically isolated. If in doubt, these should not be used on electrical equipment.
3.2 Hoses & Reels
-
Hose reels in place are clearly marked and in appropriate box with nozzle?
-
Check of hoses found no damage or wear? (check 2 - 3 at random on site)
-
Staff during demonstration were able to set up and demonstrate its use correctly? (e.g set-up and test was done in a timely manner)
-
Seals and fittings are not cracked or showing wear?
-
Show information on Hose reels
-
Internal hose reels
a. Install internal hose reels in accordance with local codes or the following, whichever is more severe: On a basis so that every point in the building can be reached by at least one hose stream from a connection with 30m (100ft) of 25mm (1in) rubber hose.
b. Fire hose reels will be supplied direct from sprinkler systems, from unmetered or metered public water supplies, or from private supplies with automatic pumps. Which-ever system is used, ensure that the water supply is adequate and that the system complies with local requirements.
c. The hose reels should be provided at conspicuous locations and be adequately identified. High level signs should be provided for hose reels in warehouse areas.
d. Lay flat canvas hoses are not recommended.
e. If internal hose lines are fed by sprinkler systems consider feedings hoses from the ‘adjacent’ sprinkler system to the area in which the hoses are located. Doing this will help ensure ‘some’ water supply is available in an area should the ceiling sprinklers be impaired.
3.3 Fire Hydrants
-
Are there fire hydrants on site?
-
Are they in good condition and readily accessible on site?
-
Covers are present and in place to prevent insects / bugs / debris?
-
Hydrants are covered in training and there are trained persons on site?
-
Show information on fire hydrants
-
Fire Hydrants
Hydrants will be installed for use by the fire brigade as an immediate method to attack a large developing fire.
Employees will not use hydrants, unless specifically trained as part of a plant emergency organisation.
Due to the high water pressure in the hose, inexperienced use of a hydrant is dangerous.
4. Automatic Fire-fighing Equipment
4.0 Automatic fire fighting
4.1 automatic fire fighting
-
Process pumps must be interlocked with fire detection or automatic fire-extinguishing systems for the process to shutdown the pumps in case of fire. Are these in place?
-
Flame detection is recommended for ink mixing and storage areas even when these are protected by automatic sprinlers. Are these in place?
4.2 CO2 Gas Suppression
-
Does the site have CO2 installed on all Presses?
-
Any presses do solvent-less (water based printing?)
-
Gas discharge will protect printing heads including reservoirs and pumps, ventilation systems and ink storage next to the press. Are these in place?
-
Discharge will be automatic by operation of flame detectors, and shut ventilation systems / material supply to the press. Is this in place?
-
There is a manual operation button which allows the manual discharge of CO2?
-
Discharge should be over the entire press.
-
High value / modern presses will have 100% standby reserve supply of gas, except where replacement is possibl within 24 hours
-
Wet Sprinklers (where site is sprinklered) will protect under the shielded area of presses
-
Presses shall not be operated when CO2 system is inoperative
-
All nozzles and fittings are correctly installed (fixed properly and pointed in the right direction) on the press and present?
4.3 Flammable stores CO2
-
Existing CO2 systems (total flooding) must have: • a mechanically operated “lock out” device to prevent gas discharge when area is manned by personnel • adequate aisle and exit routes • emergency lighting and directional signs to ensure quick, safe evacuation • pre-discharge alarms to operate within protected areas immediately upon detection of fire • time delay in gas discharge sufficient to allow personnel to evacuate the area safely – minimum delay 30 seconds • continuous visual and audible alarms to operate at entry/exit points following gas discharge, until protected area is safe (a calibrated oxygen monitoring device may be used) • provision for rescue of personnel rendered unconscious due to a gas discharge • appropriate warning and instruction signs. Important: Total flooding CO2 systems will be converted to manual discharge where the above life safety features cannot be met.
5. Ventilation and Extraction
5.1 Ventilation
-
Exhaust air is removed through a system of blowers, fans and ductwork terminating out of doors away from air inlets, doorways and other openings?
-
Suction takes place close to the source of flammable vapours, near floor level, and in any nearby pits.
-
Exhaust fans are interlocked to insure their operation when equipment that generates flammable vapours is functioning?
-
Ventilation is monitored to provide an audible and visual alarm in event of failure?
-
Ventilation independent of the machine operation? (It should run even whenever there is an opportunity for a build-up of flammable vapours)
-
Low level ventilation in in place to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapours?
-
Low level extraction suction pickup is set up 300mm from the floor
-
Low level ventilation is set up correctly and tested to ensure the minimum extraction rate is 0.3 m3/min/m2 (1 ft3/min/ft2)<br>
-
Reading of extraction rate test:
-
Date extraction flow rate last tested
5.2 LEL's
-
LEL set up of 25%?<br>Where flammable liquids are used in process, ventilation will be installed to reduce the concentration of vapour to less than 25% lower explosion limit (LEL). The only exception is for evaporating ovens where there will be special control systems that monitor the vapour concentration and trigger shut down at 50% LEL or as specified by machine manufacturers.
-
Audible alarms? <br>An inter-lock should be provided between isolation of ventilation system and processing room equipment isolation with audible alarm to operators.
-
Show information on Ventilation
-
Ventilation:
Remove exhaust air through a system of blowers, fans and ductwork terminating out of doors away from air inlets, doorways and other openings. Suction should be taken close to the source of flammable vapours, near floor level, and in any nearby pits. Exhaust fans should be interlocked to insure their operation when equipment that generates flammable vapours is functioning. Run exhaust ducts as directly as possible to outdoors with a minimum of bends.
Ventilation should be monitored to provide an audible and visual alarm in event of failure. -
Where flammable liquids are used in process, ventilation will be installed to reduce the concentration of vapour to less than 25% lower explosion limit (LEL). The only exception is for evaporating ovens where there will be special control systems that monitor the vapour concentration and trigger shut down at 50% LEL or as specified by machine manufacturers.
Low level ventilation to prevent the accumulation of flammable vapours. The minimum extraction rate will be: 0.3 m3/min/m2 (1 ft3/min/ft2)
Design ventilation systems for continuous operation with pick-up exhaust points located within 300-mm of the floor. Minimum design based on ventilation of not less than 1 cfm/ft2 (0.305 m3/min/m2) of floor area. Design is to achieve a minimum Lower Explosive Limit (LEL) of 25% concentration. An inter-lock should be provided between isolation of ventilation system and processing room equipment isolation with audible alarm to operators. Make up air supply should ideally be located on the opposite side of the room to aid vapour removal from the floor.
All vents to be kept clear.
• Arrange the ventilation system to remove vapour directly from solvent-wetted surfaces of the presses, even while the presses are stopped.
• Ventilation needs to be independent of the machine operation. It should run even whenever there is an opportunity for a build-up of flammable vapours.
• Provide a separate room ventilation system along the floor directly under ink fountains and colour pans, and throughout spaces to remove flammable vapour-air mixtures that may exist under normal operations.
• Locate suction pickup within 12in. (300 mm) of the floor.
• Avoid concealed spaces, but if necessary, continuously vent them to prevent solvent vapour accumulation including printing press pits.
6. Solvent Rags & Bins
6.1 Waste bins for solvent rags
-
AFAP solvent waste policy for rags & gloves in place?
-
Waste bins for rags approved FM type?
-
Waste bins in good condition
-
Waste bins were not overflowing and emptied regularly
-
No plastic used as a liner inside bin?
-
Lids are in good condition and operating correctly?
-
Show information on FM approved Bins
-
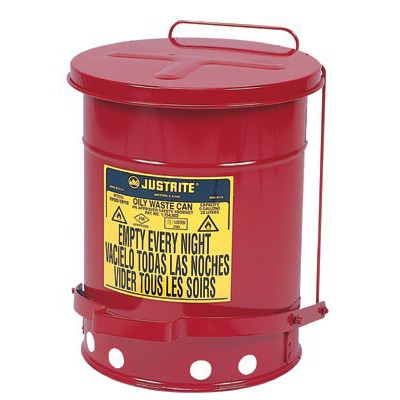
Oily Waste Cans which are FM Global approved are essential whenever cloths, wipes, cleaning rags and gloves are used to clean oil or solvents. Specially designed steel oily waste cans protect a facility from fires that can start due to spontaneous combustion, sparks, or careless use of smoking material.
-
The waste cans should not have plastic liners and they should be emptied daily.
7. Waste
7.2 Waste inks / solvents (inside plant)
-
Excessive waste inks on floor? (e.g ink / Paint pails stacked loose on floor around machinery
-
Waste inks stored correctly on pallets?
-
Spill kits in place to deal with any spill?
-
Spill kit items checked and are suitable for the possible size of spill?
7.3 Waste storage
-
Location is in good condition and clearly signed?
-
Waste store has license / certificate up to date?
-
enter expiry / renewal date of license
-
Waste store tidy?
-
Bunding and Spill kits in place?
-
Signage is in place and appropriate (showing PPE requirements, Fire warnings, etc..)
-
MSDS available and is up to date?
-
Emergency station nearby to deal with possible eye splash, spill (eye wash stations - shower units)
-
Local and Approved company remove waste ink / solvents from site?
-
Name of Provider
-
Defined limits for waste store? (capacity limits defined and known)
-
Limit allowed in waste store (litres)
-
information on solvent storage stored external to factory plant
-
External (preferred) Flammable liquids stored external to the factory will meet the following criteria:
• located at least 15 metres from factory walls or combustible materials
• where less than 15 metres distance, minimum 1 hour fire rated construction for walls facing
• main building without any directly opposing door or window openings
• Buildings should have damage-limiting construction – non-exposing walls and roofs are
• pressure relieving
• spillage containment/bunding that is sufficient to hold at least 25% of the contents of all
• containers or 100% of the largest container whichever is the greater
• earthing and bonding to prevent static electricity where decanting takes place
• weather protection for structures to avoid rainwater filling containment/bunding
• clearly marked by signs
• kept secure
8. Storage
8.0 Storage areas
8.1 Storage areas
-
Site has defined location to store flammable materials ?
-
Stacking heights throughout the plant should not exceed those that can be protected by the sprinkler system design. Excessive storage heights impair the ability of the sprinkler system to control a fire and therefore present a major hazard to the premises. Where practicable, goods in storage areas will be raised off the floor by storing on pallets to reduce the risk of water damage. A clearance of one metre (3.3 feet) will be maintained between the sprinkler head and the top of stacks so that water discharge will not be impaired.
-
Whenever possible, idle pallets should be stored in a separate, detached, low-value building. Only those quantities needed for immediate use should be stored in production, stores, warehouse and shipping areas. Internal storage should be restricted to a maximum of 1.8 metres in height, or as specified by sprinkler design. When stored in a main production building or warehouse, pallets not needed for immediate use shall be stored in a cut-off room, separated from the remainder of the building by walls having at least a two-hour fire resistance. Whenever possible the room should be located against outside walls.
8.2 Internal Storage
-
Area has fire door installed?
8.3 External Storage areas
-
Flammable liquids stored external to the factory will meet the following criteria: • located at least 15 metres from factory walls or combustible materials • where less than 15 metres distance, minimum 1 hour fire rated construction for walls facing main building without any directly opposing door or window openings • Buildings should have damage-limiting construction – non-exposing walls and roofs are pressure relieving • spillage containment/bunding that is sufficient to hold at least 25% of the contents of all containers or 100% of the largest container whichever is the greater • earthing and bonding to prevent static electricity where decanting takes place • weather protection for structures to avoid rainwater filling containment/bunding • clearly marked by signs • kept secure
9. Flammable goods handling & MSDS
9. Flammable goods handling
9.1 Liquid Transfer
-
Liquid Transfer<br>Transfer of liquids from their original shipping containers and process tanks, containers, or portable tanks within a building only by means of the following:<br>Containers with a capacity of 19 L (5 gal) or less?<br>Approved safety cans? (e.g FM approved type or similar)
-
Through a closed piping system?<br><br>
-
From a portable tank or container by means of an approved pump device drawing through an opening in the top of the tank or container?<br><br>
-
By gravity through a listed self-closing valve or self-closing faucet?<br>
-
Class I liquids are not dispensed into metal containers or process tanks unless the nozzle or fill pipe is in electrical contact with the container or process tank?
-
Process pumps interlocked with fire detection or automatic fire-extinguishing systems for the process to shutdown the pumps in case of fire?<br>
9.2 Flammable inks
-
Containers used are correctly labelled?
-
Inks around press area are able to be grounded by floor surface / bonding clamps?
-
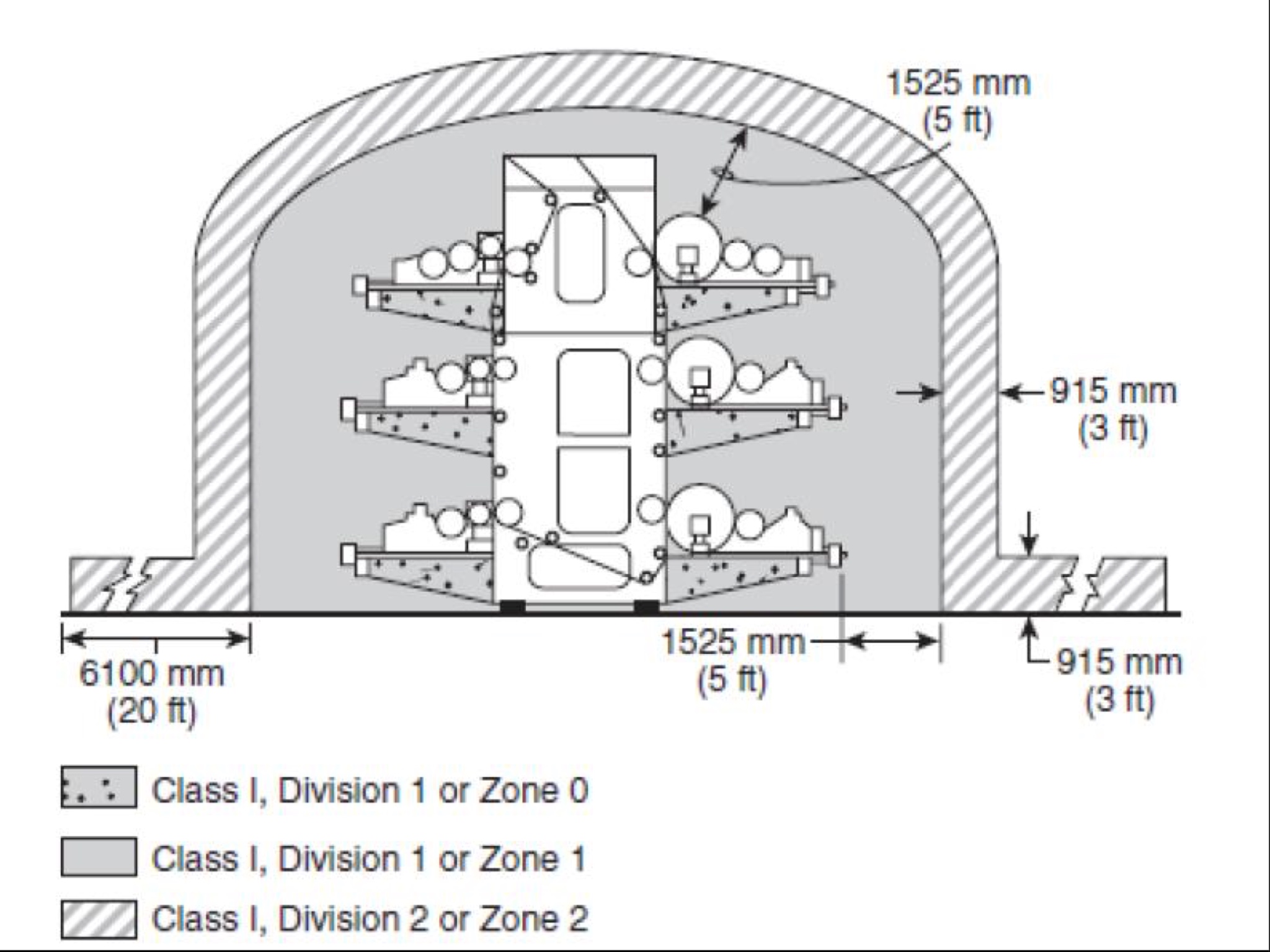
When flammable inks are used, protect as follows : • Use listed Class I, Group D, Division 1 or equivalent electrical equipment within the press frame • Use listed Class I, Group D, Division 1 or equivalent electrical equipment within a 5-ft (1.5-m) radius, measured from the perimeter of the surface of any ink fountain or colour pan • Use listed Class I, Group D, Division 1 or equivalent electrical equipment in areas where vapours accumulate • Use listed Class I, Group D, Division 2 or equivalent electrical equipment around ink fountains or colour pans, within a 25-ft (8-m) radius from the vapour source for a height of 3 ft (1 m) above the floor<br>Are these set out according to the guide?
-
Show Information
-
Refer housekeeping section:
The amount of inks located within the press area should be limited to one shift’s needs and never exceed 265 L at one staging area.
The distance to the next staging area should be at least 8 m.
The total amount of flammable liquids (ink, solvent etc.) in the press area should be limited to 400 L.
Containment should be provided for all staging of flammable inks and liquids. The containment should be large enough to hold the content of the maximum expected spill, generally the largest container, plus a 50 mm freeboard.
The distance between staging areas for inks (distance measured from the curb) and press should be at least 5 m and the distance to any combustible in-process storage should be at least 8 m. -
9.3 Trolleys / Transport
-
Trolleys used to transfer ink / solvents are in good condition?
-
Trolleys are able to be earthed / grounded?
9.4 Solvents
-
Solvents cans are correctly labelled?
-
Lids closed / containers secured?
9.5 MSDS
-
MSDS available in area where handling takes place?
-
Operators are aware of MSDS and how to use them?
-
MSDS up to date and manifest available?
10. Bonding and Earthing
General
-
Site has a work instruction around bonding and earthing?
-
AFAP Static control policy is in place?
10.1 Bonding and earthing (Clamping devices for solvent transfer)
-
Relevant co-workers are trained in the process to know how and where to apply?
-
Bonding clamps are in good order and condition?
-
Type of clamps: 1. Needle point or Alligator type? 2. Clamp spring is in good condition? (clamps firmly and not loose)
-
Clamps have been tested to ensure good earthing / bonding contact? Last reading checks available? <br>Resistance to ground checks for all grounding associated with presses and solvent storage / mixing rooms. <br>Resistance to ground reading should be <1megaohm.
10.2 Bonding and earthing (plant & equipment)
-
Because many printing presses are ideal generators of static electricity, it is important to eliminate static charges that may accumulate and become intense enough to ignite flammable vapour. Electrically ground the entire press framework. This includes the feeder device, spreader knives, doctor blades, metal rolls and containers for the flammable liquids, conveyor systems, ductwork, mills, and associated equipment. Spray booths, exhaust ducts, and piping should be similarly bonded and grounded. Are these in place?
-
11. Training & Emergency Trials
11.1 Fire Warden Training
-
Head fire warden and Deputy fire wardens have undergone external training on an approved course?
-
Training is current and up to date (no more than 2 years)
-
Fire extinguisher training is conducted regularly (no more than 2 years apart)
-
Hose fire fighting training is also covered?
11.2 Emergency Trials
-
Assembly points are clearly marked on site?
-
Trial are conducted every six months?
-
Records of trials are kept on record and maintained?
-
Results of trials are communicated to the site?
-
Any items found to address from a fire drill are tracked by the sites Management / OHSE committee?
11.3 Training
-
Site has a clear work instruction / process to follow for emergency evacuation?
-
Emergency evacuation is covered in the sites induction program for contractors, co-workers and visitors?
12. Security
12. Security
12.1 Site Security
-
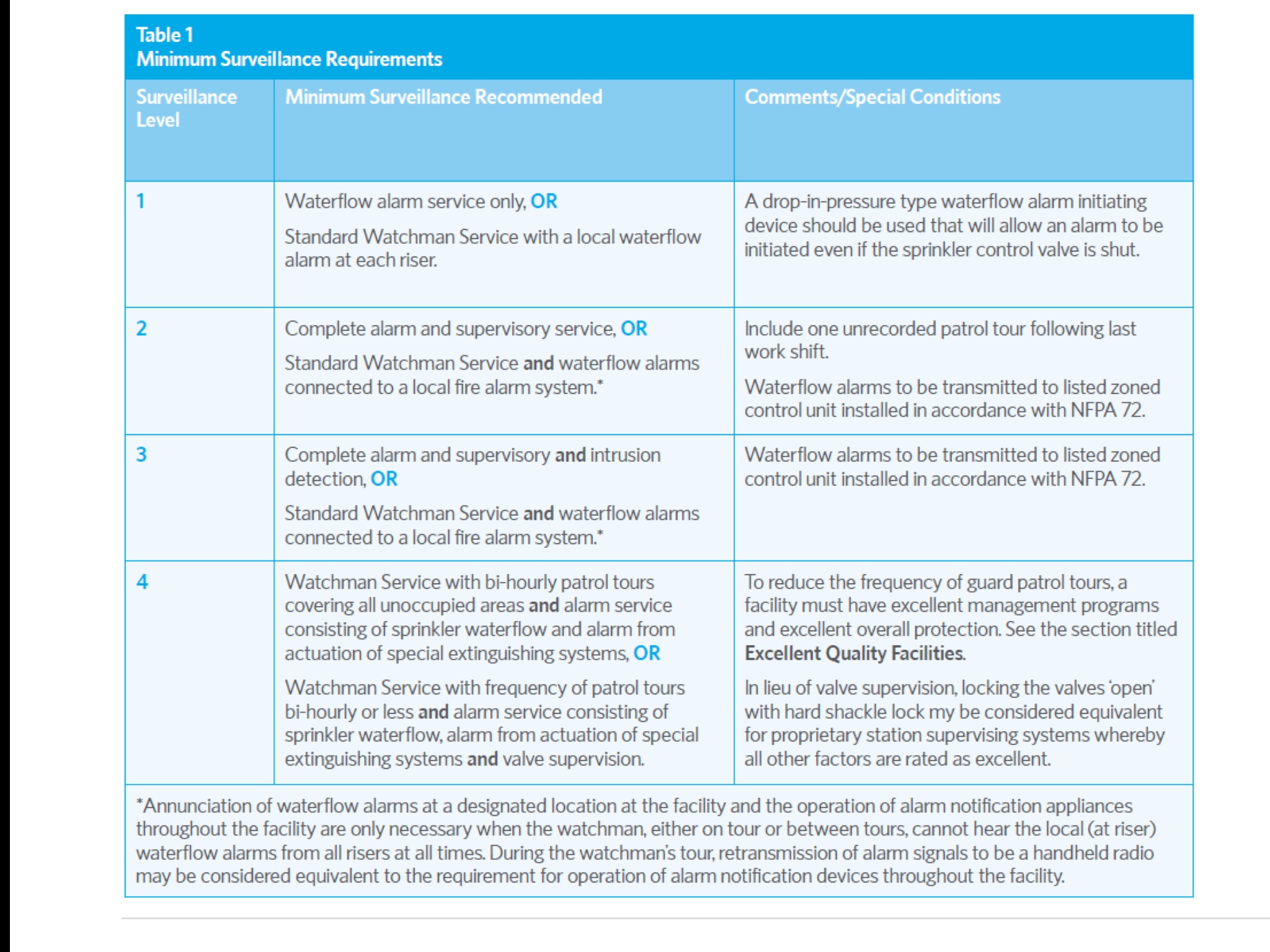
Management should develop a written surveillance plan for both fire protection and security to be certain that the facility is checked regularly during idle periods. To accomplish this, management should: • Determine which areas of the facility are unoccupied during both working and nonworking hours • Designate a management representative to be responsible for overseeing the surveillance program • This representative should review surveillance reports daily. Management control of surveillance is critical to maintaining program integrity • Evaluate changes in the facility that might require revising the surveillance plan.<br><br>Are these in place?
-
Document name / Information of security plan
-
Last review / Updated:
12.2 Guards
-
Where guards are in place, the initial and continued training of guards should be given as a formal, comprehensive written program covering all applicable protection procedures. Each guard must be: – Acquainted with the general nature of the facility’s operations and possess specific knowledge of those operations which are hazardous. – Familiar with the facility’s manual and automatic fire protection equipment and protective signaling systems. They should be especially aware of the location of all sprinkler valves and know which area each controls. – Familiar with the location and operation of manual fire alarm stations and other means of transmitting fire alarms. Such means should be provided throughout the facility to permit guards to easily report a fire. – Taught to notify the fire department before attempting to fight the fire. – Taught how to admit public fire apparatus to the property and how to direct fire department officers to the location of the fire. – Taught to properly notify company officials when an emergency occurs or when potential trouble is observed. – Taught to maintain a shift log and to prepare reports to management of observations made and action taken during tours.
12.3 Pump Room
-
Pump room is secured and locked?
12.4 Locks & valve switches
-
There are locks in place on valves / pipes to prevent tampering?
12.3 Security Information
13. Fire Alarms
13.1 Fire Alarm Panel
-
a. Fire alarm panels should be installed in accordance with NFPA 72, FM Data Sheet 5-40 “Fire Alarm Systems” Australian Standard or local equivalent.<br>b. The fire alarm panel should be in a constantly attended location, ideally a normally occupied guard house or control room.<br>c. Where the site is not constantly attended, the fire alarms should either be transmitted directly to the public fire brigade, or to an approved central station. Fire alarms include those from automatic fire detection systems, manual alarm points, sprinkler system water flow, and special extinguishing system discharge alarms.<br>d. Where the site is not constantly attended, supervisory / trouble alarms should be transmitted to an approved central station. Supervisory alarms include various faults in the alarm circuits, fire alarm panel isolated, power failure, valve tamper alarms, fire pump running, fire pump failure to start, fire pump engine trouble (high temp, overspeed, low oil pressure), fire pump control panel in OFF or MANUAL Position, power failure, phase reversal, low suction tank level, public water supply low pressure alarm and others.<br>e. The panel and components used in the fire detection and alarm system should be UL listed, FM Approved, LPC Approved, SSL Listed or listed by another independent, internationally recognized testing laboratory. <br>f. Unless required by local codes, there is no need to install smoke and heat detection in areas which are protected by automatic sprinklers<br>g. Smoke detection should be considered for all buildings which are not protected by automatic sprinklers. In some areas, due to dust, oil mist, or other air quality problem, heat detection may be used in lieu of smoke detection. Flame detection is recommended for ink mixing and storage areas even when these areas are protected by automatic sprinklers.<br>h. Smoke detection is required for all electrical switch rooms and transformer vaults.<br>i. Smoke detection is required in computer rooms and control rooms, above and below any raised floor.
-
Fire Alarm Panel Location
-
Monitored by:
-
Date last Checked:
-
Comments:
13.2 Fire Alarm
-
Fire alarm is audible at all areas of the site?
-
Areas considered where works may take place that alarm is audible or has visual systems in place to alert persons in these areas? (e.g working at the top of extruder lines or similar)
14. Pump Room
14. Pump Room
14.1 Fire Pump Testing
-
A weekly test of fire pumps should be undertaken. <br>Diesel Pumps = 30 mins running time<br>Electrical Pumps = 10 mins running time
-
Records are in place for the testing and current?
-
Testing done by:
-
Signage or lists clearly display pump pressure limits?
-
Servicing & Maintenance up to date?
-
Visual inspection of fire pump room found no issues?
15. Sprinklers
15. Sprinklers
15.1 Sprinkler plan
-
The site has a building plan showing the layout of the sprinklers?
-
The sprinklers system has an outlet on the far side of the design to allow the testing of the system?
15.2 Valves
-
All control valves will be listed and checked on a regular basis to ensure they are locked
-
Weekly visual inspection and monthly testing of Non-indicating valves?
16. Electrical
16.1 Electrical Cabinets
-
There is a regular schedule to check electrical cabinets? (preventative maintenance plans or similar)
-
Electrical cabinets are locked and secured?
-
Electrical cabinets do not have any flammable material stored next to it?
-
Electrical cabinets are accessible and no congestion or material or items placed on or nearby?
16.2 Thermography
-
Thermography / IR of electrical equipment is done and records on hand and any issues identified have been resolved?
16.3 Cords and leads
-
Electrical plugs / switches / PC / cords in area are in good condition with correct fittings? (no tape holding wires together)
-
Electrical leads are checked regularly?
-
There is a preventative maintenance schedule or similar to check leads / cords condition on site?
18. Hot Work & Impairment Process
18. Hot Work
18.1 Hot Work Permits
-
Hot work permits are in place with a work instruction?
-
Date of Work instruction review:
-
Date of last training:
18.2 Hot Work Permit Details
-
The Hot work permit will specify as a minimum: <br>1. The work to be done<br>2. Date and duration of the permit<br>3. Area where the work will take place<br>4. That sprinklers (if installed) are not isolated<br>5. How the area will be made safe before work occurs and after work has been completed<br>6. Who will undertake the work and with what supervision<br>7. Permit is authorised by a competent person and signed-off upon completion of the work<br><br>is the above in place?
-
The permit will also specify that the following precautions, as a minimum are met: • a suitable fire extinguisher will be provided nearby • a ‘runout’ fire hose reel or hydrant hose will be provided nearby • floors and surroundings will be swept clean and wetted down throughout the operation • any draught creating device such as fans and blowers will be turned off • all combustibles will be relocated at least 11 metres (35 feet) from the operation or the remainder will be protected with non- combustible curtains, metal guards or flame proofed covers (not ordinary tarpaulins) • all wall and floor openings covered.
-
Who signs off the permit?
19. BCP Plans
19.1 Business Continuity Plan
-
Where are the plans located?
-
Date of last BCP plan review
-
Show Amcor information on BCP plans
-
Following completion of a BIA and Threat Assessment each site will prepare a BCP that provides:
• a clear procedure for the escalation and control of an incident (incident response structure)
• communication guidelines for key stakeholders
• clear and specific plans to resume interrupted activities
Although the term ‘Business Continuity Plan’ implies a single document, in reality this covers a number of different activities and will usually consist of multiple plans. Generally, there are four types of plan corresponding to overlapping stages of the response, and any of these can appear in any BCP at any level.
The four stages are:
1. Emergency Response – the immediate response to an emergency, such as an Evacuation Plan
2. Incident/ Crisis Management – the management of the response to the incident
3. Continuity – the initial business response to ensure that essential activities can continue to operate at a minimum acceptable level
4. Recovery and Resumption – a plan to recover activities to a sustainable level and resume operations to what the organization defines as “normal”
The plan will be reviewed at least annually and adjusted as necessary for variations in vulnerabilities and organisational changes.
Note to Auditor:
Amcor Group Risk can be contacted for further information on this process. Guidelines and a BCP template are available on the intranet. -
The sites has established and documented a business continuity plan?
20. Fire Detection Systems
20.1 Fire Detection Systems
-
Fire detection systems will not normally be used as a substitute for sprinkler protection, especially for manufacturing and storage operations. Detection systems on their own will only be installed in: • fire separated office buildings • electrical switchrooms/substations, and in addition to sprinkler systems in low voltage ‘critical control equipment’ areas, such as computer rooms or process control equipment where early fire alarm response is desirable. • Detection systems may also operate other fire protection systems, particularly: • local application CO2 gas suppression systems on printing presses • total flooding gas suppression systems protecting flammable liquid stores. The detection system will comply with local legislative or code requirements. <br>Smoke detectors will be used in preference to heat/thermal detectors because of their superior alarm response times, subject to the environment being acceptable for their use. Flame detectors will be used on presses and in flammable liquid storage and mixing areas.
-
Local Requirements / Legislation: (if Known)
21. PPE and Clothing
21. PPE and Clothing
21.1 Footwear
-
The site has a policy / process in place to purchase anti-static shoes for any persons working in the printing / solvent / flammable areas?
-
-
Footwear should have an electrical resistance of less than 1000 megohm (1x10^9 ohms) at any time during its useful life.
21.2 Clothing
-
Clothing purchased for workers are specified to be 65% cotton 35% polyester to reduce static potential in co-workers.