Title Page
-
Client Name
-
Client Address
-
Location of Services
-
Date
-
Company Contact
-
Prepared by
-
COMPLIANCE REPORT: PRIVILEGED DOCUMENT This Audit Report is made for the purpose of conducting a health and safety audit as defined by the Texas Safety Audit Privilege Act, Tex. Rev. Civ. Stat. Ann. 4447cc (Vernon 2003). This Audit Report and all exhibits attached hereto may be privileged from compelled disclosure, including litigation, pursuant to the above Act. Furthermore, this Act may prohibit persons with knowledge of the contents of this report, or attached exhibits, from disclosing that information to any third party. You should consult an attorney before voluntarily producing this report, any exhibits attached to it, or allowing persons to discuss its findings as the voluntary disclosure of this report’s contents may waive your rights under the Act. This Audit Report does not constitute a guarantee, warranty, or representation of any kind by the auditor that the audited company is in compliance with ANSI, OSHA, or any other applicable safety or health regulation. If the auditor finds deficiencies with compliance, the responsibility to initiate and pursue appropriate remedies to achieve compliance is solely that of the audited company
-
“EMPLOYER RESPONSIBILITY”
Employers have the responsibility to provide a safe workplace. Employers MUST provide their employees with a workplace that does not have serious hazards and must follow all OSHA safety and health standards. Employers must find and correct safety and health problems. Employers MUST also: • Inform employees about hazards through training, labels, alarms, color-coded systems, chemical information sheets and other
methods.
• Train employees in a language and vocabulary they can understand. This includes all new employees as well as current employees
who may have new tasks or have not demonstrated proficiency in their current tasks.
• Keep accurate records of work-related injuries and illnesses.
• Perform tests in the workplace, such as air sampling, required by some OSHA standards.
• Provide hearing exams or other medical tests required by OSHA standards.
• Post OSHA citations and injury and illness data where workers can see them.
• Notify OSHA within eight hours of a workplace fatality or when there or more workers are hospitalized.
• Prominently display the official OSHA poster that describes rights and responsibilities under the OSHA ACT
It is the employer’s responsibility to evaluate and/or certify an employee qualified, authorized and/or competent in the safe use and operation of tools, equipment, machinery, and procedures. It is the employer’s responsibility to evaluate the employees and determine the applicable requirement given the OSHA definitions:
• “Qualified Person” – Means a person who, by possession of a recognized degree, certificate, or professional standing, or who by extensive knowledge, training or experience, successfully demonstrated the ability to solve/resolve problems relating to the subject matter, the work or the project.
• “Authorized Person” – Means a person approved or assigned by the employer to perform a specific type of duty or duties or to be at a specific location or location at the job-site
• “Competent Person” – Means one who is capable of identifying existing and predictable hazards in the surroundings or working conditions which are unsanitary, hazardous, or dangerous to employees and who has authorization to take prompt corrective measures to eliminate them.
“PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT”
Please remember it is the responsibility of the employer to provide a safe workplace for all employees. The work site should be evaluated regularly to determine if hazards are present. This analysis or hazard assessment, should include all tasks, tools, and machinery. This review should include:
1. A check of the condition of all working parts, pinch points, guarding, and discharge of materials.
2. Confirmation of routine maintenance with documentation.
3. Continuous operator training, with documentation.
4. Confirmation that training, operation, and maintenance are performed according to the manufacturer’s recommendations or current standards for safe operating procedures.
If hazards are identified, then every effort should be made to eliminate the hazards by engineering and procedural means. If the hazards cannot be eliminated, then as a last resort personal protective equipment should be used. In all cases, the employer is required to train the employee. This includes: proper operation, use, maintenance, possible hazards, and proper use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) training includes the selection, use, limitations, cleaning, and possible disposing of the equipment. Safety meetings are a part of the communication process, yet in no way meet the training requirements of the federal standards. Documentation should include: the trainer, material taught, a written test to confirm employee knowledge and understanding, and a performance test to confirm the level of the employee’s skills.
“HAND & POWER TOOLS/MACHINERY”
Suggest doing a specific machine guarding survey to ensure all belts, pulleys, shafts, pinch points, chains, and sprockets are fully guarded to ensure someone may not be caught in it. Also, ensure employees do not wear loose clothing or have unrestrained hair while operating any of this equipment.
This safety survey in no way represents that the requirements of regulatory agencies were being met on the day of the safety survey. The responsibility for the interpretation of current regulatory agencies standards and the adherence to any such interpretation rests with the owner and/or employer.
Desktop Assessment
-
Desk Top Audit?
Employee Postings
-
Are the following postings found prominently posted in a location frequented by the employees? NOTE: OSHA Job Safety and Health; Federal Polygraph; Fair Labor Standards Act, including the current Minimum Wage; Family and Medical Leave Act; Equal Employment Opportunities; Child Labor Law; Pay Day; Human Rights and Equal Employment Opportunity; Workers' Compensation
-
Are the required postings and warning signs/labels available in a language that is understood?
-
All postings and warning signs/ labels should be made available in a language that all employees understand. 1910.145 - Specifications for accident prevention signs and tags.
-
Are required permits current and posted?
Recording and Reporting Occupational Injuries and Illnesses – 1904
-
Is it between February 1st and April 30th?
-
Is the OSHA 300 A posted in a conspicuous area?
-
Does the OSHA 300 form appear to be completed and/or maintained?
-
29 CFR 1904.4(a) Each employer required by this part to keep records of fatalities, injuries, and illnesses must record each fatality, injury and illness that Is work-related; and Is a new case; and Meets one or more of the general recording criteria of §1904.7 or the application to specific cases of §§1904.8 through 1904.12
-
Are job related injuries and illnesses recorded on this form within seven (7) days of occurrence?
-
1904.29(b)(3) You must enter each recordable injury or illness on the OSHA 300 Log and 301 Incident Report within seven (7) calendar days of receiving information that a recordable injury or illness has occurred.
-
Are OSHA 300 and 301 Forms maintained and retained for 5 years?
-
1904.33(a) Basic requirement. You must save the OSHA 300 Log, the privacy case list (if one exists), the annual summary, and the OSHA 301 Incident Report forms for five (5) years following the end of the calendar year that these records cover.
Policy and Procedure Review
-
Is a current copy of the Employee Policies and Safety Procedures manual available for all employees?
-
Is it documented that all new or transferred employees have received, read, and been given an opportunity to ask any questions which they might have concerning the Employee Policy and Safety Procedure information?
-
Does the Company health and safety program appear to be “active,” with the following activities occurring?<br>1. Routine safety meetings<br>2. Management and employees working together to eliminate hazards.<br>3. Routine review of the tasks and appropriate PPE.<br>4. Routine review of written programs for accuracy and completeness.<br>5. Regular training for affected employees.
-
Does an employee training program appear to be available for the appropriate areas of concern? <br>Reminder: Employee Training: Employee training programs should be designed to ensure that all employees understand and are aware of the hazards to which they may be exposed and the proper methods for avoiding such hazards
-
Are supervisors trained to understand the key role they play in job site safety and to enable them to carry out their safety and health responsibilities effectively?
-
Is one person or department clearly responsible for the health and safety program and/or individual written program?
-
Is there a safety incentive program in place to reward employees for reducing workplace injuries/illness?
-
Does the safety incentive program penalize workers for reporting work-related injuries or illnesses?
-
-
Is there a working procedure for addressing employee complaints regarding safety concerns?
Sub-Contractors
-
Do you employ Sub-Contractors?
-
Does your company have a Sub-Contractor program?
-
Do you have a sub-contractor prequalification form?
Incident Reporting Program
-
Does your company have an incident/accident reporting program?
-
Does your program include “Near Miss” reporting?
-
Does your company have incident/accident reporting, investigation, and near-miss forms?
-
Does your company conduct formal root cause investigations for all reported events?
-
What method is utilized?
-
Who participates in the investigations?
-
Does your company use a medical case management company?
Drug and Alcohol Program
-
Does your company have a written drug and alcohol program?
-
Do you drug test for DOT, Non-DOT, or both?
-
Who is your company subscribing with (lab/consortium) for drug and alcohol testing?
-
Describe disciplinary procedures for violations:
-
Do you have Supervisors/Managers trained in Reasonable Suspicion responsibilities?
-
Have Supervisors/Managers received Reasonable Suspicion training?
Safety Responsibilites
-
Does your company employ a full-time safety person?
-
Do you contract any of the safety training out?
Safety Meetings / Training
-
Does your company have regularly scheduled safety training?
-
Are training rosters or other forms of proof of training kept?
-
Do you provide refresher safety training?
-
Are tests given with all training to verify topic understanding?
-
Do you have a safety training matrix?
-
Are all of your employees fluent in the English language?
-
Do you provide training in a language that non-English speaking employees understand?
-
Does the company's new hire orientation process include safety training/topics?
-
Do you have a Short Service Employee program?
Safety Programs / Training
-
Does your company require a completed Job Safety Analysis (JSA) or a Job Hazard Analysis (JHA) that covers; job steps, hazards associated with each job step, and how to mitigate each hazard identified prior to starting work?
-
Has there been a Hazard Assessment conducted to determine PPE required?
-
1910.132(d) Hazard assessment and equipment selection.
1910.132(d)(1) The employer shall assess the workplace to determine if hazards are present, or are likely to be present, which necessitate the use of personal protective equipment (PPE). If such hazards are present, or likely to be present, the employer shall:
1910.132(d)(1)(i) Select, and have each affected employee use, the types of PPE that will protect the affected employee from the hazards identified in the hazard assessment;
1910.132(d)(1)(ii) Communicate selection decisions to each affected employee; and,
1910.132(d)(1)(iii) Select PPE that properly fits each affected employee. -
Does employer allow for Employee-Owned PPE?
-
1910.132(b) Employee-owned equipment. Where employees provide their own protective equipment, the employer shall be responsible to assure its adequacy, including proper maintenance, and sanitation of such equipment.
-
Are all employees required to use personal protective equipment (PPE) as needed that is functional and in good repair?
-
29 CFR 1910.132(a) Application. Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, shall be provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition wherever it is necessary by reason of hazards of processes or environment, chemical hazards, radiological hazards, or mechanical irritants encountered in a manner capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through absorption, inhalation or physical contact.
1910.132(b) Employee-owned equipment. Where employees provide their own protective equipment, the employer shall be responsible to assure its adequacy, including proper maintenance, and sanitation of such equipment. -
Does the employer purchase PPE as required by 1910.132(H)
-
1910.132(h)(1) Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment (PPE), used to comply with this part, shall be provided by the employer at no cost to employees.
1910.132(h)(2) The employer is not required to pay for non-specialty safety-toe protective footwear (including steel-toe shoes or steel-toe boots) and non-specialty prescription safety eyewear, provided that the employer permits such items to be worn off the job-site.
1910.132(h)(4) The employer is not required to pay for: The logging boots required by 29 CFR 1910.266(d)(1)(v); Everyday clothing, such as long-sleeve shirts, long pants, street shoes, and normal work boots; or Ordinary clothing, skin creams, or other items, used solely for protection from weather, such as winter coats, jackets, gloves, parkas, rubber boots, hats, raincoats, ordinary sunglasses, and sunscreen.
1910.132(h)(5) The employer must pay for replacement PPE, except when the employee has lost or intentionally damaged the PPE. -
Has the company documented that PPE training has been done, who has received it, and when?
-
1910.132(f) Training. The employer shall provide training to each employee who is required by this section to use PPE. Each such employee shall be trained to know at least the following: When PPE is necessary; What PPE is necessary; How to properly don, doff, adjust, and wear PPE; The limitations of the PPE; and, The proper care, maintenance, useful life and disposal of the PPE.
1910.132(f)(2) Each affected employee shall demonstrate an understanding of the training specified in paragraph (f)(1) of this section, and the ability to use PPE properly, before being allowed to perform work requiring the use of PPE. -
Do you have a Behavior-Based Safety Program with Observations?
-
Do you perform Abrasive Blasting?
-
Are your employees exposed to lead?
-
Do you have a Lead Awareness or Lead Abatement and Removal Program?
-
Do you have a Respiratory Protection program?
-
Respirators used on location?
-
Is there voluntary (Non-Mandatory) use of respirators allowed by employer?
-
Appendix D to Sec. 1910.134 (Mandatory) Information for Employees Using Respirators When Not Required Under the Standard
Respirators are an effective method of protection against designated hazards when properly selected and worn. Respirator use is encouraged, even when exposures are below the exposure limit, to provide an additional level of comfort and protection for workers. However, if a respirator is used improperly or not kept clean, the respirator itself can become a hazard to the worker. Sometimes, workers may wear respirators to avoid exposures to hazards, even if the amount of hazardous substance does not exceed the limits set by OSHA standards. If your employer provides respirators for your voluntary use, or if you provide your own respirator, you need to take certain precautions to be sure that the respirator itself does not present a hazard.
You should do the following:
1. Read and heed all instructions provided by the manufacturer on use, maintenance, cleaning and care, and warnings regarding the respirators limitations.
2. Choose respirators certified for use to protect against the contaminant of concern. NIOSH, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, certifies respirators. A label or statement of certification should appear on the respirator or respirator packaging. It will tell you what the respirator is designed for and how much it will protect you.
3. Do not wear your respirator into atmospheres containing contaminants for which your respirator is not designed to protect against. For example, a respirator designed to filter dust particles will not protect you against gases, vapors, or very small solid particles of fumes or smoke.
4. Keep track of your respirator so that you do not mistakenly use someone else's respirator. -
Are respirators observed during this survey cleaned appropriately?
-
1910.134(h)(1) Cleaning and disinfecting. The employer shall provide each respirator user with a respirator that is clean, sanitary, and in good working order. The employer shall ensure that respirators are cleaned and disinfected using the procedures in Appendix B-2 of this section, or procedures recommended by the respirator manufacturer, provided that such procedures are of equivalent effectiveness. The respirators shall be cleaned and disinfected at the following intervals: Respirators issued for the exclusive use of an employee shall be cleaned and disinfected as often as necessary to be maintained in a sanitary condition; Respirators issued to more than one employee shall be cleaned and disinfected before being worn by different individuals; Respirators maintained for emergency use shall be cleaned and disinfected after each use; and Respirators used in fit testing and training shall be cleaned and disinfected after each use.
-
Do you conduct fit testing using the procedures set forth in Appendix A to 1910.134?
-
Appendix A to §1910.134—Fit Testing Procedures (Mandatory)
-
Fit Testing Procedures
-
Are all respirators observed during this survey packed and stored to prevent deformation of the facepiece and exhalation valve?
-
1910.134(h)(2)(i) All respirators shall be stored to protect them from damage, contamination, dust, sunlight, extreme temperatures, excessive moisture, and damaging chemicals, and they shall be packed or stored to prevent deformation of the facepiece and exhalation valve.
-
Do you provide comprehensive and understandable training annually (or more often if necessary) to employees who are required to use respirators?
-
1910.134(k)(1) The employer shall ensure that each employee can demonstrate knowledge of at least the following: Why the respirator is necessary and how improper fit, usage, or maintenance can compromise the protective effect of the respirator; What the limitations and capabilities of the respirator are; How to use the respirator effectively in emergency situations, including situations in which the respirator malfunctions; How to inspect, put on and remove, use, and check the seals of the respirator; What the procedures are for maintenance and storage of the respirator; How to recognize medical signs and symptoms that may limit or prevent the effective use of respirators; and The general requirements of this section.
-
Is the training provided before employees are required to use a respirator in the workplace?
-
1910.134(k)(2) The training shall be conducted in a manner that is understandable to the employee.
The employer shall provide the training prior to requiring the employee to use a respirator in the workplace. -
Are the fit test records retained for respirator users until the next fit test is administered?
-
1910.134(m)(1) Medical evaluation. Records of medical evaluations required by this section must be retained and made available in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020.
-
Respirators used on location?
-
Is there voluntary (Non-Mandatory) use of respirators allowed by employer?
-
Appendix D to Sec. 1910.134 (Mandatory) Information for Employees Using Respirators When Not Required Under the Standard
Respirators are an effective method of protection against designated hazards when properly selected and worn. Respirator use is encouraged, even when exposures are below the exposure limit, to provide an additional level of comfort and protection for workers. However, if a respirator is used improperly or not kept clean, the respirator itself can become a hazard to the worker. Sometimes, workers may wear respirators to avoid exposures to hazards, even if the amount of hazardous substance does not exceed the limits set by OSHA standards. If your employer provides respirators for your voluntary use, or if you provide your own respirator, you need to take certain precautions to be sure that the respirator itself does not present a hazard.
You should do the following:
1. Read and heed all instructions provided by the manufacturer on use, maintenance, cleaning and care, and warnings regarding the respirators limitations.
2. Choose respirators certified for use to protect against the contaminant of concern. NIOSH, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, certifies respirators. A label or statement of certification should appear on the respirator or respirator packaging. It will tell you what the respirator is designed for and how much it will protect you.
3. Do not wear your respirator into atmospheres containing contaminants for which your respirator is not designed to protect against. For example, a respirator designed to filter dust particles will not protect you against gases, vapors, or very small solid particles of fumes or smoke.
4. Keep track of your respirator so that you do not mistakenly use someone else's respirator. -
Do you conduct fit testing using the procedures set forth in Appendix A to 1910.134?
-
Appendix A to §1910.134—Fit Testing Procedures (Mandatory)
-
Fit Testing Procedures
-
Do you provide comprehensive and understandable training annually (or more often if necessary) to employees who are required to use respirators?
-
1910.134(k)(1) The employer shall ensure that each employee can demonstrate knowledge of at least the following: Why the respirator is necessary and how improper fit, usage, or maintenance can compromise the protective effect of the respirator; What the limitations and capabilities of the respirator are; How to use the respirator effectively in emergency situations, including situations in which the respirator malfunctions; How to inspect, put on and remove, use, and check the seals of the respirator; What the procedures are for maintenance and storage of the respirator; How to recognize medical signs and symptoms that may limit or prevent the effective use of respirators; and The general requirements of this section.
-
Is the training provided before employees are required to use a respirator in the workplace?
-
1910.134(k)(2) The training shall be conducted in a manner that is understandable to the employee.
The employer shall provide the training prior to requiring the employee to use a respirator in the workplace. -
Are the fit test records retained for respirator users until the next fit test is administered?
-
1910.134(m)(1) Medical evaluation. Records of medical evaluations required by this section must be retained and made available in accordance with 29 CFR 1910.1020.
-
Do you have a Confined Space program?
-
Do you have a Hearing Conservation program?
-
1910.95(d)(1)
When information indicates that any employee's exposure may equal or exceed an 8-hour time-weighted average of 85 decibels, the employer shall develop and implement a monitoring program. -
Do you have an Electrical Safety program?
-
If qualified employees only work on company owned equipment, are they trained by the manufacturer?
-
Does your company train you qualified employees in Arc Flash & Shock protection?
-
Do you have a Lockout/Tagout program?
-
Are documented procedures for the control of potentially hazardous energy, covering the scope, purpose, responsibility, authorization, rules, and techniques available?
-
1910.147(c)(1) Energy control program. The employer shall establish a program consisting of energy control procedures, employee training and periodic inspections to ensure that before any employee performs any servicing or maintenance on a machine or equipment where the unexpected energizing, startup or release of stored energy could occur and cause injury, the machine or equipment shall be isolated from the energy source and rendered inoperative.1910.147(c)(4)
Energy control procedure.
1910.147(c)(4)(i) Procedures shall be developed, documented and utilized for the control of potentially hazardous energy when employees are engaged in the activities covered by this section.
1910.147(c)(4)(ii) The procedures shall clearly and specifically outline the scope, purpose, authorization, rules, and techniques to be utilized for the control of hazardous energy, and the means to enforce compliance including, but not limited to, the following:
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(A) A specific statement of the intended use of the procedure;
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(B) Specific procedural steps for shutting down, isolating, blocking and securing machines or equipment to control hazardous energy;
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(C) Specific procedural steps for the placement, removal and transfer of lockout devices or tagout devices and the responsibility for them; and
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(D) Specific requirements for testing a machine or equipment to determine and verify the effectiveness of lockout devices, tagout devices, and other energy control measures. -
Is employee LOTO training conducted and documented?
-
1910.147(c)(7)(i) The employer shall provide training to ensure that the purpose and function of the energy control program are understood by employees and that the knowledge and skills required for the safe application, usage, and removal of the energy controls are acquired by employees. The training shall include the following:
1910.147(c)(7)(i)(A) Each authorized employee shall receive training in the recognition of applicable hazardous energy sources, the type and magnitude of the energy available in the workplace, and the methods and means necessary for energy isolation and control.
1910.147(c)(7)(i)(B) Each affected employee shall be instructed in the purpose and use of the energy control procedure.
1910.147(c)(7)(i)(C) All other employees whose work operations are or may be in an area where energy control procedures may be utilized, shall be instructed about the procedure, and about the prohibition relating to attempts to restart or reenergize machines or equipment which are locked out or tagged out. -
Are documented procedures for the control of potentially hazardous energy, covering the scope, purpose, responsibility, authorization, rules, and techniques available?
-
1910.147(c)(1) Energy control program. The employer shall establish a program consisting of energy control procedures, employee training and periodic inspections to ensure that before any employee performs any servicing or maintenance on a machine or equipment where the unexpected energizing, startup or release of stored energy could occur and cause injury, the machine or equipment shall be isolated from the energy source and rendered inoperative.1910.147(c)(4)
Energy control procedure.
1910.147(c)(4)(i) Procedures shall be developed, documented and utilized for the control of potentially hazardous energy when employees are engaged in the activities covered by this section.
1910.147(c)(4)(ii) The procedures shall clearly and specifically outline the scope, purpose, authorization, rules, and techniques to be utilized for the control of hazardous energy, and the means to enforce compliance including, but not limited to, the following:
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(A) A specific statement of the intended use of the procedure;
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(B) Specific procedural steps for shutting down, isolating, blocking and securing machines or equipment to control hazardous energy;
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(C) Specific procedural steps for the placement, removal and transfer of lockout devices or tagout devices and the responsibility for them; and
1910.147(c)(4)(ii)(D) Specific requirements for testing a machine or equipment to determine and verify the effectiveness of lockout devices, tagout devices, and other energy control measures. -
Is employee LOTO training conducted and documented?
-
1910.147(c)(7)(i) The employer shall provide training to ensure that the purpose and function of the energy control program are understood by employees and that the knowledge and skills required for the safe application, usage, and removal of the energy controls are acquired by employees. The training shall include the following:
1910.147(c)(7)(i)(A) Each authorized employee shall receive training in the recognition of applicable hazardous energy sources, the type and magnitude of the energy available in the workplace, and the methods and means necessary for energy isolation and control.
1910.147(c)(7)(i)(B) Each affected employee shall be instructed in the purpose and use of the energy control procedure.
1910.147(c)(7)(i)(C) All other employees whose work operations are or may be in an area where energy control procedures may be utilized, shall be instructed about the procedure, and about the prohibition relating to attempts to restart or reenergize machines or equipment which are locked out or tagged out. -
Do you have an H2S (Hydrogen Sulfide) program?
-
Do you have a Hazard Communication (HAZCOM) program?
-
1910.1200(e)(1) Employers shall develop, implement, and maintain at each workplace, a written hazard communication program which at least describes how the criteria specified in paragraphs (f), (g), and (h) of this section for labels and other forms of warning, safety data sheets, and employee information and training will be met.
-
Do you have a Hazardous Waste Operations and Emergency Response (HAZWOPER) program?
-
Do you have a Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Program?
-
Do you have a Hot Work program?
-
Do you have a Fire Safety program?
-
Do you have an Excavation program?
-
Do you have a Heavy Equipment program?
-
Do you have a Crane program?
-
Are monthly, frequent, and periodic inspections documented?
-
1910.179(j)(1)(ii) Inspection procedure for cranes in regular service is divided into two general classifications based upon the intervals at which inspection should be performed. The intervals in turn are dependent upon the nature of the critical components of the crane and the degree of their exposure to wear, deterioration, or malfunction. The two general classifications are herein designated as "frequent" and "periodic" with respective intervals between inspections as defined below:
1910.179(j)(1)(ii)(a) Frequent inspection—Daily to monthly intervals.
1910.179(j)(1)(ii)(b) Periodic inspection—1 to 12-month intervals. -
Are monthly hoist chain and running rope and hook inspection records kept?
-
1910.179(j)(2)(iii) Hooks with deformation or cracks. Visual inspection daily; monthly inspection with a certification record which includes the date of inspection, the signature of the person who performed the inspection and the serial number, or other identifier, of the hook inspected. For hooks with cracks or having more than 15 percent in excess of normal throat opening or more than 10° twist from the plane of the unbent hook refer to paragraph (l)(3)(iii)(a) of this section.
1910.179(j)(2)(iv) Hoist chains, including end connections, for excessive wear, twist, distorted links interfering with proper function, or stretch beyond manufacturer's recommendations. Visual inspection daily; monthly inspection with a certification record which includes the date of inspection, the signature of the person who performed the inspection and an identifier of the chain which was inspected. -
Do you operate cranes?
-
Are monthly, frequent, and periodic inspections documented?
-
1910.179(j)(1)(ii) Inspection procedure for cranes in regular service is divided into two general classifications based upon the intervals at which inspection should be performed. The intervals in turn are dependent upon the nature of the critical components of the crane and the degree of their exposure to wear, deterioration, or malfunction. The two general classifications are herein designated as "frequent" and "periodic" with respective intervals between inspections as defined below:
1910.179(j)(1)(ii)(a) Frequent inspection—Daily to monthly intervals.
1910.179(j)(1)(ii)(b) Periodic inspection—1 to 12-month intervals. -
Are monthly hoist chain and running rope and hook inspection records kept?
-
1910.179(j)(2)(iii) Hooks with deformation or cracks. Visual inspection daily; monthly inspection with a certification record which includes the date of inspection, the signature of the person who performed the inspection and the serial number, or other identifier, of the hook inspected. For hooks with cracks or having more than 15 percent in excess of normal throat opening or more than 10° twist from the plane of the unbent hook refer to paragraph (l)(3)(iii)(a) of this section.
1910.179(j)(2)(iv) Hoist chains, including end connections, for excessive wear, twist, distorted links interfering with proper function, or stretch beyond manufacturer's recommendations. Visual inspection daily; monthly inspection with a certification record which includes the date of inspection, the signature of the person who performed the inspection and an identifier of the chain which was inspected. -
Do you have a Rigging program?
-
Do you have a Forklift program?
-
Does the company have training documentation for Powered Industrial Truck (forklift) operators?
-
1910.178(l)(1)(i) The employer shall ensure that each powered industrial truck operator is competent to operate a powered industrial truck safely, as demonstrated by the successful completion of the training and evaluation specified in this paragraph (l).
1910.178(l)(1)(ii) Prior to permitting an employee to operate a powered industrial truck (except for training purposes), the employer shall ensure that each operator has successfully completed the training required.
1910.178(l)(2)(ii)
Training shall consist of a combination of formal instruction (e.g., lecture, discussion, interactive computer learning, video tape, written material), practical training (demonstrations performed by the trainer and practical exercises performed by the trainee), and evaluation of the operator's performance in the workplace.
1910.178(l)(2)(iii)
All operator training and evaluation shall be conducted by persons who have the knowledge, training, and experience to train powered industrial truck operators and evaluate their competence. -
Are inspection and maintenance records kept?
-
1910.178(q)(7) Industrial trucks shall be examined before being placed in service, and shall not be placed in service if the examination shows any condition adversely affecting the safety of the vehicle. Such examination shall be made at least daily. Where industrial trucks are used on a round-the-clock basis, they shall be examined after each shift. Defects when found shall be immediately reported and corrected.
-
Do you have an Aerial lift program?
-
Do you have a Fall Protection program?
-
Do you have a Scaffolds/Platforms program?
-
Do you have a First Aid/CPR program? <br>OSHA recommends but does not require, that every workplace include one or more employees who are trained and certified in first aid, including CPR. The other option for employers is to rely upon the reasonable proximity of an infirmary, clinic, or hospital.
-
Do you have a Bloodborne Pathogens program?
-
Blood Borne Pathogens written exposure control plan been developed if required?
-
1910.1030(c)(1)(i) Each employer having an employee(s) with occupational exposure as defined by paragraph (b) of this section shall establish a written Exposure Control Plan designed to eliminate or minimize employee exposure.
-
Blood Borne Pathogens training records maintained for 3 years from the date on which the training occurred?
-
1910.1030(h)(2)(ii) Training records shall be maintained for 3 years from the date on which the training occurred.
-
Is blood borne pathogen training provided before or at the time of initial assignment where contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials is possible?
-
1910.1030(g)(2)(ii)(A) At the time of initial assignment to tasks where occupational exposure may take place
-
Are hepatitis B vaccinations made available to all workers with occupational exposure?
-
This vaccination must be offered after the worker has received the required bloodborne pathogens training and within 10 days of initial assignment to a job with occupational exposure.
-
Is blood borne pathogen refresher training provided at least annually?
-
1910.1030(g)(2)(ii)(B) At least annually thereafter.
-
Do you have an Emergency Action Plan that covers employees in the field?
-
Do you have a NORM program?
-
Do you have an Asbestos program?
-
Do you have a Stop Work Authority program?
General Industry (29 CFR 1910)
-
General Industry (1910) Assessment?
Walking Working Surface
-
Are there fixed ladders?
-
Do the side rails of through or side-step ladder extensions which were observed extend 42 inches above parapets and landings?
-
29 CFR 1910.23(d)(4) The side rails of through or sidestep ladders extend at least 42 inches (1.1 m) above the top of the access level or landing platform served by the ladder.
-
Are step ladders and/or extension ladders used?
-
Wood Ladders in use?
-
Is it coated with any material that may obscure structural defects?
-
1910.23(b)(5) Wooden ladders are not coated with any material that may obscure structural defects
-
Are ladders free of punctures and lacerations?
-
1910.23(b)(7) Ladder surfaces are free of puncture and laceration hazards
-
Are ladders being used for their designed purpose?
-
1910.23(b)(8) Ladders are used only for the purposes for which they were designed
-
Are ladders inspected before initial use and defective ladders removed from service?
-
1910.23(b)(9) Ladders are inspected before initial use in each work shift, and more frequently as necessary, to identify any visible defects that could cause employee injury;
1910.23(b)(10) Any ladder with structural or other defects is immediately tagged "Dangerous: Do Not Use" or with similar language in accordance with § 1910.145 and removed from service until repaired in accordance with § 1910.22(d), or replaced;
1910.23(c) Portable ladders. The employer must ensure:
1910.23(c)(1) Rungs and steps of portable metal ladders are corrugated, knurled, dimpled, coated with skid-resistant material, or otherwise treated to minimize the possibility of slipping;
1910.23(c)(2) Each stepladder or combination ladder used in a stepladder mode is equipped with a metal spreader or locking device that securely holds the front and back sections in an open position while the ladder is in use;
1910.23(c)(4) Ladders are used only on stable and level surfaces unless they are secured or stabilized to prevent accidental displacement; -
Employees properly using ladders?
-
1910.23(b)(11) Each employee faces the ladder when climbing up or down it;
1910.23(b)(12) Each employee uses at least one hand to grasp the ladder when climbing up and down it; and
1910.23(b)(13) No employee carries any object or load that could cause the employee to lose balance and fall while climbing up or down the ladder.
1910.23(c)(4) Ladders are used only on stable and level surfaces unless they are secured or stabilized to prevent accidental displacement;
1910.23(c)(6) No ladder is moved, shifted, or extended while an employee is on it;
1910.23(c)(7) Ladders placed in locations such as passageways, doorways, or driveways where they can be displaced by other activities or traffic:
1910.23(c)(7)(i) Are secured to prevent accidental displacement; or
1910.23(c)(7)(ii) Are guarded by a temporary barricade, such as a row of traffic cones or caution tape, to keep the activities or traffic away from the ladder;
1910.23(c)(8) The cap (if equipped) and top step of a stepladder are not used as steps;
1910.23(c)(9) Portable ladders used on slippery surfaces are secured and stabilized;
1910.23(c)(10) The top of a non-self-supporting ladder is placed so that both side rails are
supported unless the ladder is equipped with a single support attachment;
1910.23(c)(11) Portable ladders used to gain access to an upper landing surface have side rails that extend at least 3 feet (0.9 m) above the upper landing surface -
Fall Protection required?
-
Are sides and edges 4 feet or more above a lower level protected?
-
1910.28(b)(1)(i) Except as provided elsewhere in this section, the employer must ensure that each employee on a walking-working surface with an unprotected side or edge that is 4 feet (1.2 m) or more above a lower level is protected from falling by one or more of the following:
1910.28(b)(1)(i)(A) Guardrail systems;
1910.28(b)(1)(i)(B) Safety net systems; or
1910.28(b)(1)(i)(C) Personal fall protection systems, such as personal fall arrest, travel restraint or positioning systems -
Stairs in use?
-
Does every stairway observed during this survey having 4 or more treads have stair railings of standard height? (30" - 34" above surface)
-
1910.28(b)(11)(ii) Each flight of stairs having at least 3 treads and at least 4 risers is equipped with stair rail systems and handrails.
-
Are risers observed during this survey uniform in height and conform to proper height?
-
1910.25(b)(3) Stairs have uniform riser heights and tread depths between landings.
1910.25(c) Standard stairs. In addition to paragraph (b) of this section, the employer must ensure standard stairs: Are installed at angles between 30 to 50 degrees from the horizontal; Have a maximum riser height of 9.5 inches (24 cm); Have a minimum tread depth of 9.5 inches (24 cm); and Have a minimum width of 22 inches (56 cm) between vertical barriers. -
Are standard railings observed during this survey provided on the open side of exposed stairs?
-
1910.28(b)(11)(ii) Each flight of stairs having at least 3 treads and at least 4 risers is equipped with stair rail systems and handrails.
-
Where doors or gates open directly on a stairway observed during this survey, is there a platform provided so the swing of the door does not reduce the effective width to less than 20 inches?
-
1910.25(b)(5)(i) Less than 20 inches (51 cm) for platforms installed before January 17, 2017; and 1910.25(b)(5)(ii)
Less than 22 inches (56 cm) for platforms installed on or after January 17, 2017 .
Temporary Labor Camps
-
Do you have employees that live on-site in temporary labor camps "man-camps"?
-
Does the site have adequate drainage and not subject to periodic flooding?
-
1910.142(a)(1)
All sites used for camps shall be adequately drained. They shall not be subject to periodic flooding, nor located within 200 feet of swamps, pools, sink holes, or other surface collections of water unless such quiescent water surfaces can be subjected to mosquito control measures. The camp shall be located so the drainage from and through the camp will not endanger any domestic or public water supply. All sites shall be graded, ditched, and rendered free from depressions in which water may become a nuisance. -
Is there any livestock within 500 ft. of the camp?
-
1910.142(a)(2)
All sites shall be adequate in size to prevent overcrowding of necessary structures. The principal camp area in which food is prepared and served and where sleeping quarters are located shall be at least 500 feet from any area in which livestock is kept. -
Is the campgrounds and open areas surrounding the shelters shall be maintained in a clean and sanitary condition free from rubbish, debris, waste paper, garbage, or other refuse?
-
910.142(a)(3)
The grounds and open areas surrounding the shelters shall be maintained in a clean and sanitary condition free from rubbish, debris, waste paper, garbage, or other refuse. -
Are beds spaced not closer than 36 inches both laterally and end to end, and elevated at least 12 inches from the floor? If double-deck bunks are used, they shall be spaced not less than 48 inches both laterally and end to end. The minimum clear space between the lower and upper bunk shall be not less than 27 inches. Triple-deck bunks are prohibited.
-
1910.142(b)(3)
Beds, cots, or bunks, and suitable storage facilities such as wall lockers for clothing and personal articles shall be provided in every room used for sleeping purposes. Such beds or similar facilities shall be spaced not closer than 36 inches both laterally and end to end, and shall be elevated at least 12 inches from the floor. If double-deck bunks are used, they shall be spaced not less than 48 inches both laterally and end to end. The minimum clear space between the lower and upper bunk shall be not less than 27 inches. Triple-deck bunks are prohibited. -
Are floors in good repair?
-
1910.142(b)(4)1910.142(b)(4)
The floors of each shelter shall be constructed of wood, asphalt, or concrete. Wooden floors shall be of smooth and tight construction. The floors shall be kept in good repair.
1910.142(b)(5)
All wooden floors shall be elevated not less than 1 foot above the ground level at all points to prevent dampness and to permit free circulation of air beneath. -
Does each window open at least 50% for ventilation?
-
1910.142(b)(7)
All living quarters shall be provided with windows the total of which shall be not less than one-tenth of the floor area. At least one-half of each window shall be so constructed that it can be opened for purposes of ventilation. -
All exterior openings are effectively screened with 16-mesh material. All screen doors shall be equipped with self-closing devices.
-
1910.142(b)(8)
All exterior openings shall be effectively screened with 16-mesh material. All screen doors shall be equipped with self-closing devices. -
Is the kitchen area sanitary with clean food storage and a minimum of 1 stove for every 10 employees?
-
1910.142(b)(9)
In a room where workers cook, live, and sleep a minimum of 100 square feet per person shall be provided. Sanitary facilities shall be provided for storing and preparing food.
1910.142(b)(10)
In camps where cooking facilities are used in common, stoves (in ratio of one stove to 10 persons or one stove to two families) shall be provided in an enclosed and screened shelter. Sanitary facilities shall be provided for storing and preparing food.
1910.142(b)(11)
All heating, cooking, and water heating equipment shall be installed in accordance with State and local ordinances, codes, and regulations governing such installations. If a camp is used during cold weather, adequate heating equipment shall be provided. -
There is an adequate and convenient water supply, approved by the appropriate health authority, provided in each camp for drinking, cooking, bathing, and laundry purposes. NOTE: A water supply shall be deemed adequate if it is capable of delivering 35 gallons per person per day to the campsite at a peak rate of 2 1/2 times the average hourly demand.
-
1910.142(c)(1)
An adequate and convenient water supply, approved by the appropriate health authority, shall be provided in each camp for drinking, cooking, bathing, and laundry purposes.
1910.142(c)(2)
A water supply shall be deemed adequate if it is capable of delivering 35 gallons per person per day to the campsite at a peak rate of 2 1/2 times the average hourly demand. -
Bathrooms are accessible without any individual passing through any sleeping room and are at least 100 feet from any sleeping room, dining room, lunch area, or kitchen.
-
1910.142(d)(1)
Toilet facilities adequate for the capacity of the camp shall be provided.
1910.142(d)(2)
Each toilet room shall be located so as to be accessible without any individual passing through any sleeping room. Toilet rooms shall have a window not less than 6 square feet in area opening directly to the outside area or otherwise be satisfactorily ventilated. All outside openings shall be screened with 16-mesh material. No fixture, water closet, chemical toilet, or urinal shall be located in a room used for other than toilet purposes.
1910.142(d)(3)
A toilet room shall be located within 200 feet of the door of each sleeping room. No privy shall be closer than 100 feet to any sleeping room, dining room, lunch area, or kitchen. -
Are all trash cans and dumpsters fly-tight, rodent-tight, impervious, cleanable, or single service containers, approved by the appropriate health authority shall be provided for the storage of garbage. NOTE: At least one such container shall be provided for each family shelter and shall be located within 100 feet of each shelter on a wooden, metal, or concrete stand.
-
1910.142(h)(1)
Fly-tight, rodent-tight, impervious, cleanable or single service containers, approved by the appropriate health authority shall be provided for the storage of garbage. At least one such container shall be provided for each family shelter and shall be located within 100 feet of each shelter on a wooden, metal, or concrete stand. -
Garbage containers are kept clean and emptied when full.
-
1910.142(h)(2)
Garbage containers shall be kept clean.
1910.142(h)(3)
Garbage containers shall be emptied when full, but not less than twice a week. -
Effective measures have been taken to prevent infestation by and harborage of animal or insect vectors or pests.
-
1910.142(j)
"Insect and rodent control." Effective measures shall be taken to prevent infestation by and harborage of animal or insect vectors or pests.
Housekeeping
-
Are washing facilities observed during this survey maintained in a sanitary condition?
-
1910.141(d)(1) General. Washing facilities shall be maintained in a sanitary condition.
-
Is hot and cold running water, or tepid running water, available for use?
-
1910.141(d)(2)(ii) Each lavatory shall be provided with hot and cold running water, or tepid running water.
-
Hand soap or cleansing agents available?
-
1910.141(d)(2)(iii) Hand soap or similar cleansing agents shall be provided.
-
Are individual hand towels (cloth or paper), warm air blowers, or continuous cloth toweling and handsoap or a similar cleansing agent available for use?
-
29 CFR 1910.141(d)(2)(iv) Individual hand towels or sections thereof, of cloth or paper, air blowers or clean individual sections of continuous cloth toweling, convenient to the lavatories, shall be provided.
-
Is potable water provided for drinking?
-
29 CFR 1910.141(b)(1)(i) Potable water shall be provided in all places of employment, for drinking, washing of the person, cooking, washing of foods, washing of cooking or eating utensils, washing of food preparation or processing premises, and personal service rooms.
1910.141(b)(1)(iii) Portable drinking water dispensers shall be designed, constructed, and serviced so that sanitary conditions are maintained, shall be capable of being closed, and shall be equipped with a tap. -
Does the employer prohibit the common drinking cup and other common utensils?
-
1910.141(b)(1)(v) Open containers such as barrels, pails, or tanks for drinking water from which the water must be dipped or poured, whether or not they are fitted with a cover, are prohibited.
1910.141(b)(1)(vi) A common drinking cup and other common utensils are prohibited. -
Is the consumption of food and beverages allowed on premises?
-
Are employees observed eating or storing food in toilet rooms or around toxic materials?
-
1910.141(g)(2) Eating and drinking areas. No employee shall be allowed to consume food or beverages in a toilet room nor in any area exposed to a toxic material.
1910.141(g)(4) Sanitary storage. No food or beverages shall be stored in toilet rooms or in an area exposed to a toxic material. -
Is the work area, floors, walkways, and other surfaces observed during this survey clean and orderly?
-
29 CFR 1910.22(a)(1) All places of employment, passageways, storerooms, service rooms, and walking-working surfaces are kept in a clean, orderly, and sanitary condition.
1910.141(a)(3)(iii) To facilitate cleaning, every floor, working place, and passageway shall be kept free from protruding nails, splinters, loose boards, and unnecessary holes and openings.
Recommend keeping all surfaces free from combustible dust. Note the following from OSHA National Emphasis Program on Combustible Dust; If the lab results indicate that the dust is combustible, and the combustible dust accumulations not contained within dust control systems or other containers, such as storage bins, are extensive enough to pose a deflagration, explosion, or other fire hazard, then citations under 29 CFR 1910.22 (housekeeping) or, where appropriate, 29 CFR 1910.176(c) (housekeeping in storage areas) may generally be issued. -
Are mats or grating used where drainage is needed?
-
29 CFR 1910.22(a)(2) The floor of each workroom is maintained in a clean and, to the extent feasible, in a dry condition. When wet processes are used, drainage must be maintained and, to the extent feasible, dry standing places, such as false floors, platforms, and mats must be provided.
-
Waste disposal containers available and cleaned daily?
-
1910.141(g)(3) Waste disposal containers. Receptacles constructed of smooth, corrosion-resistant, easily cleanable, or disposable materials, shall be provided and used for the disposal of waste food. The number, size, and location of such receptacles shall encourage their use and not result in overfilling. They shall be emptied not less frequently than once each working day, unless unused, and shall be maintained in a clean and sanitary condition. Receptacles shall be provided with a solid tight-fitting cover unless sanitary conditions can be maintained without use of a cover.
1910.141(a)(4)(i) Any receptacle used for putrescible solid or liquid waste or refuse shall be so constructed that it does not leak and may be thoroughly cleaned and maintained in a sanitary condition. Such a receptacle shall be equipped with a solid tight-fitting cover, unless it can be maintained in a sanitary condition without a cover. This requirement does not prohibit the use of receptacles which are designed to permit the maintenance of a sanitary condition without regard to the aforementioned requirements.
1910.141(a)(4)(ii) All sweepings, solid or liquid wastes, refuse, and garbage shall be removed in such a manner as to avoid creating a menace to health and as often as necessary or appropriate to maintain the place of employment in a sanitary condition. -
Are building grounds free from pests, trash, and overgrown vegetation?
-
1910.106(e)(9)(iv) "Clear zone." The ground area around buildings and unit operating areas shall be kept free of weeds, trash, or other unnecessary combustible materials.
1910.141(a)(5) Vermin control. Every enclosed workplace shall be so constructed, equipped, and maintained, so far as reasonably practicable, as to prevent the entrance or harborage of rodents, insects, and other vermin. A continuing and effective extermination program shall be instituted where their presence is detected.
1910.176(c) Housekeeping. Storage areas shall be kept free from accumulation of materials that constitute hazards from tripping, fire, explosion, or pest harborage. Vegetation control will be exercised when necessary.
Exit Routes, Emergency Action Plans & Fire Prevention Plans
-
Emergency Action Plan in place?
-
Recommend that your Emergency Action Plan be implemented as required in OSHA
1910.38. The use of floor plans or workplace maps that clearly show the emergency escape
routes should be included in the emergency action plan according to Appendix to Subpart E. -
Exit lead directly outside or to a street, walkway, refuge area, public way, or open space with access to the outside?
-
1910.36(c)(1) Each exit discharge must lead directly outside or to a street, walkway, refuge area, public way, or open space with access to the outside.
-
Exit door freely open and clear of obstructions and unlocked?
-
1910.36(d)(1) Employees must be able to open an exit route door from the inside at all times without keys, tools, or special knowledge. A device such as a panic bar that locks only from the outside is permitted on exit discharge doors.
1910.36(d)(2) Exit route doors must be free of any device or alarm that could restrict emergency use of the exit route if the device or alarm fails.
1910.36(d)(3) An exit route door may be locked from the inside only in mental, penal, or correctional facilities and then only if supervisory personnel are continuously on duty and the employer has a plan to remove occupants from the facility during an emergency. -
Does the exit route meet minimum height and width requirements?
-
1910.36(g)(1) The ceiling of an exit route must be at least seven feet six inches (2.3 m) high. Any projection from the ceiling must not reach a point less than six feet eight inches (2.0 m) from the floor.
1910.36(g)(2) An exit access must be at least 28 inches (71.1 cm) wide at all points. Where there is only one exit access leading to an exit or exit discharge, the width of the exit and exit discharge must be at least equal to the width of the exit access.
1910.36(g)(3) The width of an exit route must be sufficient to accommodate the maximum permitted occupant load of each floor served by the exit route.
1910.36(g)(4) Objects that project into the exit route must not reduce the width of the exit route to less than the minimum width requirements for exit routes. -
Lighting and marking must be adequate and appropriate.
-
1910.37(b)(1) Each exit route must be adequately lighted so that an employee with normal vision can see along the exit route.
1910.37(b)(2) Each exit must be clearly visible and marked by a sign reading "Exit."
1910.37(b)(3) Each exit route door must be free of decorations or signs that obscure the visibility of the exit route door.
1910.37(b)(4) If the direction of travel to the exit or exit discharge is not immediately apparent, signs must be posted along the exit access indicating the direction of travel to the nearest exit and exit discharge. Additionally, the line-of-sight to an exit sign must clearly be visible at all times.
1910.37(b)(5) Each doorway or passage along an exit access that could be mistaken for an exit must be marked "Not an Exit" or similar designation, or be identified by a sign indicating its actual use (e.g., closet).
1910.37(b)(6) Each exit sign must be illuminated to a surface value of at least five foot-candles (54 lux) by a reliable light source and be distinctive in color. Self-luminous or electroluminescent signs that have a minimum luminance surface value of at least .06 footlamberts (0.21 cd/m2) are permitted.
1910.37(b)(7) Each exit sign must have the word "Exit" in plainly legible letters not less than six inches (15.2 cm) high, with the principal strokes of the letters in the word "Exit" not less than three-fourths of an inch (1.9 cm) wide.
Powered Platforms, Man-lifts and Vehicle Mounted Work Platforms
-
Are there Powered Platforms, Man-lifts and Vehicle Mounted Work Platforms on location?
-
Are extendable and articulating boom platform upper and lower controls observed during this survey tested each day before use to determine safe working condition?
-
1910.67(c)(2)(i) Lift controls shall be tested each day prior to use to determine that such controls are in safe working condition.
1910.67(c)(2)(ix) Articulating boom and extensible boom platforms, primarily designed as personnel carriers, shall have both platform (upper) and lower controls. Upper controls shall be in or beside the platform within easy reach of the operator. Lower controls shall provide for overriding the upper controls. Controls shall be plainly marked as to their function. Lower level controls shall not be operated unless permission has been obtained from the employee in the lift, except in case of emergency. -
Are only trained and authorized persons allowed to operate aerial lifts?
-
1910.67(c)(2)(ii) Only trained persons shall operate an aerial lift.
-
Warning labels, placards observed during this survey legible and in place?
-
1910.68(c)(7)(i) Instruction signs at landings or belts. Signs of conspicuous and easily read style giving instructions for the use of the manlift shall be posted at each landing or stenciled on the belt.
Occupational Health and Environmental Control
Ventilation
-
Abrasive blasting, grinding, polishing, buffing, and/or spray finishing operations?
-
Abrasive Blasting?
-
Rate of exhaust sufficient for task?
-
1910.94(a)(3)(i) Blast-cleaning enclosures shall be exhaust ventilated in such a way that a continuous inward flow of air will be maintained at all openings in the enclosure during the blasting operation.
1910.94(a)(3)(i)(a) All air inlets and access openings shall be baffled or so arranged that by the combination of inward air flow and baffling the escape of abrasive or dust particules into an adjacent work area will be minimized and visible spurts of dust will not be observed.
1910.94(a)(3)(i)(b) The rate of exhaust shall be sufficient to provide prompt clearance of the dust-laden air within the enclosure after the cessation of blasting -
Ventilation Systems
-
Dust leaks observed?
-
1910.94(a)(4)(i)(a) When dust leaks are noted, repairs shall be made as soon as possible.
Hearing Conservation
-
Are employees exposed to noise at or above 85 decibels averaged over 8 working hours, or an 8-hour time-weighted average (TWA)?
-
Are exposed employees fitted with hearing protection?
-
1910.95(i)(1)
Employers shall make hearing protectors available to all employees exposed to an 8-hour time-weighted average of 85 decibels or greater at no cost to the employees. Hearing protectors shall be replaced as necessary.
1910.95(i)(2) - 1910.95(i)(5)
Employers shall ensure that hearing protectors are worn:
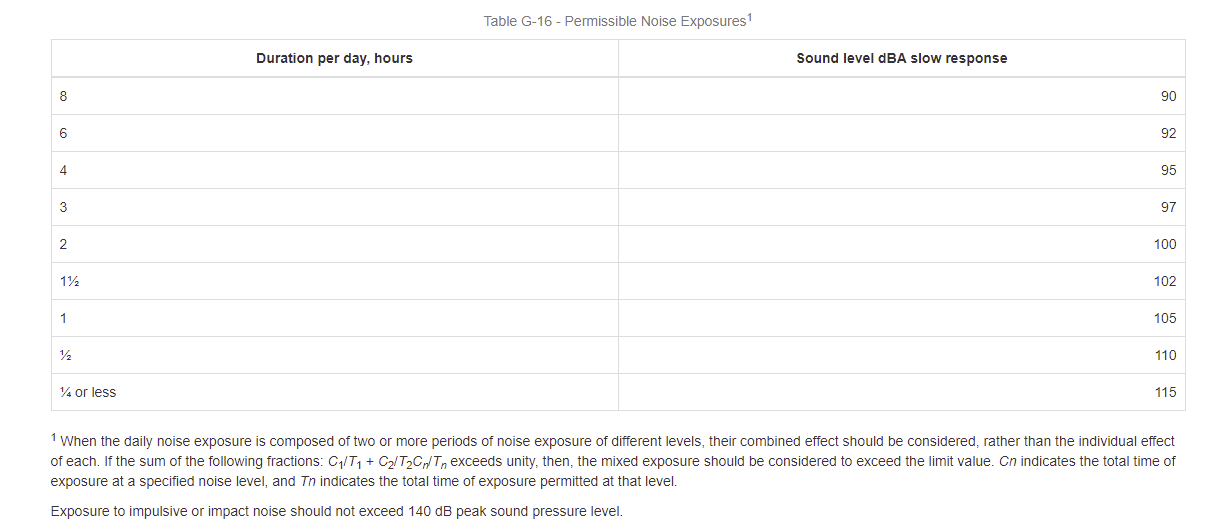
By an employee who is subjected to sound exceeding those listed in Table G-16, feasible administrative or engineering controls shall be utilized. If such controls fail to reduce sound levels within the levels of Table G-16, personal protective equipment shall be provided and used to reduce sound levels within the levels of the table. wear personal protective equipment; and
By any employee who is exposed to an 8-hour time-weighted average of 85 decibels or greater, and who:
Has not yet had a baseline audiogram established pursuant to paragraph (g)(5)(ii); or
Has experienced a standard threshold shift.
Employees shall be given the opportunity to select their hearing protectors from a variety of suitable hearing protectors provided by the employer.
The employer shall provide training in the use and care of all hearing protectors provided to employees.
The employer shall ensure proper initial fitting. -
Is approved hearing protective equipment available to every employee working in noisy (where noise levels exceed 85 dBA) areas observed during this survey?
-
1910.95(i)(1) Employers shall make hearing protectors available to all employees exposed to an 8-hour time-weighted average of 85 decibels or greater at no cost to the employees. Hearing protectors shall be replaced as necessary.
-
Have engineering controls been used to reduce excessive noise levels? Where engineering controls are determined to not be feasible, are administrative controls (that is, worker rotation) being used to minimize individual employee exposure to noise?
-
1910.95(b)(1) When employees are subjected to sound exceeding those listed in Table G-16, feasible administrative or engineering controls shall be utilized. If such controls fail to reduce sound levels within the levels of Table G-16, personal protective equipment shall be provided and used to reduce sound levels within the levels of the table.
Hazardous Materials
-
Are there Compressed Gas Cylinders?
-
Are compressed gas cylinders inspected?
-
1910.101(a) Each employer shall determine that compressed gas cylinders under his control are in a safe condition to the extent that this can be determined by visual inspection. Visual and other inspections shall be conducted as prescribed in the Hazardous Materials Regulations of the Department of Transportation (49 CFR parts 171-179 and 14 CFR part 103). Where those regulations are not applicable, visual and other inspections shall be conducted in accordance with Compressed Gas Association Pamphlets C-6-1968 and C-8-1962, which is incorporated by reference as specified in Sec. 1910.6.
-
Are all valve protectors always placed on cylinders observed during this survey when the cylinders are not in use or connected for use?
-
1910.253(b)(2)(iv) Valve protection caps, where cylinder is designed to accept a cap, shall always be in place, hand-tight, except when cylinders are in use or connected for use.
-
Are compressed gas cylinders observed during this survey stored in areas which are protected from external heat sources such as flame impingement, intense radiant heat, electric arcs, or high temperature lines and stored or located in a manner to prevent them from creating a hazard by tipping, falling or rolling?
-
1910.253(b)(2)(i) Cylinders shall be kept away from radiators and other sources of heat.
1910.253(b)(2)(ii) Inside of buildings, cylinders shall be stored in a well-protected, well-ventilated, dry location, at least 20 feet (6.1 m) from highly combustible materials such as oil or excelsior. Cylinders should be stored in definitely assigned places away from elevators, stairs, or gangways. Assigned storage spaces shall be located where cylinders will not be knocked over or damaged by passing or falling objects, or subject to tampering by unauthorized persons. Cylinders shall not be kept in unventilated enclosures such as lockers and cupboards. -
Are cylinders observed during this survey legibly marked to clearly identify the gas contained?
-
1910.253(b)(1)(ii) Compressed gas cylinders shall be legibly marked, for the purpose of identifying the gas content, with either the chemical or the trade name of the gas. Such marking shall be by means of stenciling, stamping, or labeling, and shall not be readily removable. Whenever practical, the marking shall be located on the shoulder of the cylinder.
-
Dispense Flammable and combustible liquids?
-
Are only approved pumps (i.e., grounded and non-spark producing), drawing from the top of the storage container observed during this survey, used to transfer flammable liquids?
-
29 CFR 1910.106(e)(2)(iv)(d) flammable liquids shall be drawn from or transferred into vessels, containers, or portable tanks within a building only through a closed piping system, from safety cans, by means of a device drawing through the top, or from a container or portable tanks by gravity through an approved self-closing valve. Transferring by means of air pressure on the container or portable tanks shall be prohibited.
-
Are approved containers and portable tanks in use?
-
1910.106(d)(2)(i) "General." Only approved containers and portable tanks shall be used. Metal containers and portable tanks meeting the requirements of and containing products authorized by chapter I, title 49 of the Code of Federal Regulations (regulations issued by the Hazardous Materials Regulations Board, Department of Transportation), shall be deemed to be acceptable.
-
Are containers and portable tanks observed during this survey used for flammable liquids electrically bonded or grounded during transfers?
-
1910.106(e)(6)(ii) Grounding. Category 1 or 2 flammable liquids, or Category 3 flammable liquids with a flashpoint below 100 °F (37.8 °C), shall not be dispensed into containers unless the nozzle and container are electrically interconnected. Where the metallic floorplate on which the container stands while filling is electrically connected to the fill stem or where the fill stem is bonded to the container during filling operations by means of a bond wire, the provisions of this section shall be deemed to have been complied with.
-
Are leaks and spills of flammable or combustible liquids observed during this survey?
-
1910.106(e)(9)(i) "General." Maintenance and operating practices shall be in accordance with established procedures which will tend to control leakage and prevent the accidental escape of flammable liquids. Spills shall be cleaned up promptly.
-
Is the use of flames or sources of ignition observed during this survey prohibited in areas where flammable vapors may be present?
-
1910.106(b)(6) "Sources of ignition." In locations where flammable vapors may be present, precautions shall be taken to prevent ignition by eliminating or controlling sources of ignition. Sources of ignition may include open flames, lightning, smoking, cutting and welding, hot surfaces, frictional heat, sparks (static, electrical, and mechanical), spontaneous ignition, chemical and physical-chemical reactions, and radiant heat.
-
Store Flammable and combustible liquids?
-
Are containers of flammable and combustible liquids observed during this survey closed if not being used?
-
1910.106(e)(2)(ii) "Containers." flammable liquids shall be stored in tanks or closed containers.
-
Are storage areas for flammable or combustible liquids observed during this survey free of combustible materials?
-
1910.106(e)(9)(iv) "Clear zone." Ground area around buildings and unit operating areas shall be kept free of weeds, trash, or other unnecessary combustible materials.
-
Are combustible waste materials observed during this survey being stored in covered metal receptacles?
-
1910.106(e)(9)(iii) "Waste and residue." Combustible waste material and residues in a building or unit operating area shall be kept to a minimum, stored in covered metal receptacles and disposed of daily.
-
Are flammable and combustible liquids observed during this survey stored in their original container or in an approved safety can?
-
1910.106(e)(2)(iv)(d) flammable liquids shall be drawn from or transferred into vessels, containers, or portable tanks within a building only through a closed piping system, from safety cans, by means of a device drawing through the top, or from a container or portable tanks by gravity through an approved self-closing valve. Transferring by means of air pressure on the container or portable tanks shall be prohibited.
-
Are there flammable and combustible liquids storage cabinets?
-
Is there more than 60 gallons of Category 1, 2, or 3 flammable liquids, nor more than 120 gallons of Category 4 flammable liquids in a cabinet?
-
1910.106(d)(3)(i) Maximum capacity. Not more than 60 gallons of Category 1, 2, or 3 flammable liquids, nor more than 120 gallons of Category 4 flammable liquids may be stored in a storage cabinet.
-
Are all cabinets observed during this survey provided with a three-point lock and labeled in conspicuous lettering: “FLAMMABLE–KEEP FIRE AWAY”?
-
1910.106(d)(3)(ii) "Fire resistance." Storage cabinets shall be designed and constructed to limit the internal temperature to not more than 325 deg. F. when subjected to a 10-minute fire test using the standard time-temperature curve as set forth in Standard Methods of Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials, NFPA 251-1969, which is incorporated by reference as specified in Sec. 1910.6. All joints and seams shall remain tight and the door shall remain securely closed during the fire test. Cabinets shall be labeled in conspicuous lettering, "Flammable - Keep Fire Away."
1910.106(d)(3)(ii)(a) Metal cabinets constructed in the following manner shall be deemed to be in compliance. The bottom, top, door, and sides of cabinet shall be at least No. 18 gage sheet iron and double walled with 1 1/2 - inch air space. Joints shall be riveted, welded or made tight by some equally effective means. The door shall be provided with a three-point lock, and the door sill shall be raised at least 2 inches above the bottom of the cabinet. -
Are safety cans or other portable containers of flammable liquids having a flash point at or below 80º F Painted red with clearly visible identification either in the form of a yellow band around the can or the name of the contents conspicuously stenciled or painted on the can in yellow?
-
1910.106(d)(3)(ii) "Fire resistance." Storage cabinets shall be designed and constructed to limit the internal temperature to not more than 325 deg. F. when subjected to a 10-minute fire test using the standard time-temperature curve as set forth in Standard Methods of Fire Tests of Building Construction and Materials, NFPA 251-1969, which is incorporated by reference as specified in Sec. 1910.6. All joints and seams shall remain tight and the door shall remain securely closed during the fire test. Cabinets shall be labeled in conspicuous lettering, "Flammable - Keep Fire Away."
1910.144(a)(1)(ii) Danger. Safety cans or other portable containers of flammable liquids having a flashpoint at or below 80º F, table containers of flammable liquids (open cup tester), excluding shipping containers, shall be painted red with some additional clearly visible identification either in the form of a yellow band around the can or the name of the contents conspicuously stenciled or painted on the can in yellow. Red lights shall be provided at barricades and at temporary obstructions. Danger signs shall be painted red.
Personal Protective Equipment
-
Are employees observed during this survey who are exposed to the hazards created by welding, cutting, or brazing operations protected with personal protective equipment and clothing?
-
29 CFR 1910.252(b)(3) Protective clothing - General requirements. Employees exposed to the hazards created by welding, cutting, or brazing operations shall be protected by personal protective equipment in accordance with the requirements of 1910.132. Appropriate protective clothing required for any welding operation will vary with the size, nature and location of the work to be performed.
-
Are all workers observed during this survey using the required protective clothing or equipment as needed?
-
29 CFR 1910.132(a) Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, shall be provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition wherever it is necessary by reason of hazards of processes or environment, chemical hazards, radiological hazards, or mechanical irritants encountered in a manner capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through absorption, inhalation or physical contact.
-
Is Hand Protection Required?
-
If special hand tools are used for placing and removing material, do they protect the operator's hands?
-
29 CFR 1910.212(a)(3)(iii) Special handtools for placing and removing material shall be such as to permit easy handling of material without the operator placing a hand in the danger zone. Such tools shall not be in lieu of other guarding required by this section, but can only be used to supplement protection provided.
-
Is appropriate hand protection required where there is the risk of hand injury observed during this survey?
-
1910.138(a) General requirements. Employers shall select and require employees to use appropriate hand protection when employees' hands are exposed to hazards such as those from skin absorption of harmful substances; severe cuts or lacerations; severe abrasions; punctures; chemical burns; thermal burns; and harmful temperature extremes
1910.138(b) Selection. Employers shall base the selection of the appropriate hand protection on an evaluation of the performance characteristics of the hand protection relative to the task(s) to be performed, conditions present, duration of use, and the hazards and potential hazards identified. -
Is foot protection worn where there is risk of foot injuries as observed during this survey?
-
1910.136(a) General requirements. The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses protective footwear when working in areas where there is a danger of foot injuries due to falling or rolling objects, or objects piercing the sole, or when the use of protective footwear will protect the affected employee from an electrical hazard, such as a static-discharge or electric-shock hazard, that remains after the employer takes other necessary protective measures.
-
Are hard hats worn where danger of falling objects exists as observed during this survey?
-
1910.135(a)(1) The employer shall ensure that each affected employee wears a protective helmet when working in areas where there is a potential for injury to the head from falling objects.
-
Are protective safety glasses, goggles or face shields worn where there is danger of flying particles, be subject to breakage, corrosive materials, punctures, abrasions, contusions, or burns as observed during this survey?
-
1910.133(a)(1) The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses appropriate eye or face protection when exposed to eye or face hazards from flying particles, molten metal, liquid chemicals, acids or caustic liquids, chemical gases or vapors, or potentially injurious light radiation.
29 CFR 1910.133(a)(2) The employer shall ensure that each affected employee uses eye protection that provides side protection when there is a hazard from flying objects. Detachable side protectors (e.g. clip-on or slide-on side shields) meeting the pertinent requirements of this section are acceptable. -
Respirators used on location?
-
Are respirators observed during this survey cleaned appropriately?
-
1910.134(h)(1) Cleaning and disinfecting. The employer shall provide each respirator user with a respirator that is clean, sanitary, and in good working order. The employer shall ensure that respirators are cleaned and disinfected using the procedures in Appendix B-2 of this section, or procedures recommended by the respirator manufacturer, provided that such procedures are of equivalent effectiveness. The respirators shall be cleaned and disinfected at the following intervals: Respirators issued for the exclusive use of an employee shall be cleaned and disinfected as often as necessary to be maintained in a sanitary condition; Respirators issued to more than one employee shall be cleaned and disinfected before being worn by different individuals; Respirators maintained for emergency use shall be cleaned and disinfected after each use; and Respirators used in fit testing and training shall be cleaned and disinfected after each use.
-
Are respirators observed during this survey properly stored?
-
1910.134(h)(2)
Storage. The employer shall ensure that respirators are stored as follows:
1910.134(h)(2)(i)
All respirators shall be stored to protect them from damage, contamination, dust, sunlight, extreme temperatures, excessive moisture, and damaging chemicals, and they shall be packed or stored to prevent deformation of the facepiece and exhalation valve.
1910.134(h)(2)(ii)
In addition to the requirements of paragraph (h)(2)(i) of this section, emergency respirators shall be:
1910.134(h)(2)(ii)(A)
Kept accessible to the work area;
1910.134(h)(2)(ii)(B)
Stored in compartments or in covers that are clearly marked as containing emergency respirators; and
1910.134(h)(2)(ii)(C)
Stored in accordance with any applicable manufacturer instructions.
General Environmental Controls
-
Control of Hazardous Energy (Lock Out Tag Out)
-
Are locks, tags, chains, wedges, key blocks, adapter pins, self-locking fasteners, or other hardware provided for isolating, securing, or blocking of machines or equipment from energy sources?
-
29 CFR 1910.147(c)(5)(i) Locks, tags, chains, wedges, key blocks, adapter pins, self-locking fasteners, or other hardware shall be provided by the employer for isolating, securing or blocking of machines or equipment from energy sources.
1910.147(c)(5)(ii) Lockout devices and tagout devices shall be singularly identified; shall be the only devices(s) used for controlling energy; shall not be used for other purposes; -
Is a periodic inspection conducted and documented of the energy control procedure at least annually?
-
1910.147(c)(6) Periodic inspection. The employer shall conduct a periodic inspection of the energy control procedure at least annually to ensure that the procedure and the requirements of this standard are being followed. The periodic inspection shall be performed by an authorized employee other than the ones(s) utilizing the energy control procedure being inspected. The periodic inspection shall be conducted to correct any deviations or inadequacies identified. Where lockout is used for energy control, the periodic inspection shall include a review, between the inspector and each authorized employee, of that employee's responsibilities under the energy control procedure being inspected. Where tagout is used for energy control, the periodic inspection shall include a review, between the inspector and each authorized and affected employee, of that employee's responsibilities under the energy control procedure being inspected, and the elements set forth in paragraph (c)(7)(ii) of this section. The employer shall certify that the periodic inspections have been performed. The certification shall identify the machine or equipment on which the energy control procedure was being utilized, the date of the inspection, the employees included in the inspection, and the person performing the inspection.
-
Signs and Safety Color Coding
-
Is the color Red used to indicate "Danger"?
-
1910.144(a)(1) Red shall be the basic color for the identification of:
1910.144(a)(1)(i) Fire protection equipment and apparatus.
1910.144(a)(1)(ii) Danger. Safety cans or other portable containers of flammable liquids having a flashpoint at or below 80º F, table containers of flammable liquids (open cup tester), excluding shipping containers, shall be painted red with some additional clearly visible identification either in the form of a yellow band around the can or the name of the contents conspicuously stenciled or painted on the can in yellow. Red lights shall be provided at barricades and at temporary obstructions. Danger signs shall be painted red.
1910.144(a)(1)(iii) Stop. Emergency stop bars on hazardous machines such as rubber mills, wire blocks, flatwork ironers, etc., shall be red. Stop buttons or electrical switches which letters or other markings appear, used for emergency stopping of machinery shall be red. -
Is the color yellow used for "Caution" area's?
-
1910.144(a)(3) Yellow shall be the basic color for designating caution and for marking physical hazards such as: Striking against, stumbling, falling, tripping, and "caught in between."
-
Are Accident Prevention Signs used?
-
1910.145(c)(1) Danger signs.
1910.145(c)(1)(i) There shall be no variation in the type of design of signs posted to warn of specific dangers and radiation hazards.
1910.145(c)(1)(ii) All employees shall be instructed that danger signs indicate immediate danger and that special precautions are necessary.
1910.145(c)(2) Caution signs.
1910.145(c)(2)(i) Caution signs shall be used only to warn against potential hazards or to caution against unsafe practices.
1910.145(c)(2)(ii) All employees shall be instructed that caution signs indicate a possible hazard against which proper precaution should be taken. -
Are Accident Prevention Tags used?
-
1910.145(f)(3) Use. Tags shall be used as a means to prevent accidental injury or illness to employees who are exposed to hazardous or potentially hazardous conditions, equipment or operations which are out of the ordinary, unexpected or not readily apparent. Tags shall be used until such time as the identified hazard is eliminated or the hazardous operation is completed. Tags need not be used where signs, guarding or other positive means of protection are being used.
1910.145(f)(4) General tag criteria. All required tags shall meet the following criteria:
1910.145(f)(4)(i) Tags shall contain a signal word and a major message.
1910.145(f)(4)(i)(A) The signal word shall be either "Danger," "Caution," or "Biological Hazard," "BIOHAZARD," or the biological hazard symbol.
1910.145(f)(4)(i)(B) The major message shall indicate the specific hazardous condition or the instruction to be communicated to the employee.
1910.145(f)(4)(ii) The signal word shall be readable at a minimum distance of five feet (1.52 m) or such greater distance as warranted by the hazard.
1910.145(f)(4)(iii) The tag's major message shall be presented in either pictographs, written text or both.
1910.145(f)(4)(iv) The signal word and the major message shall be understandable to all employees who may be exposed to the identified hazard.
1910.145(f)(4)(v) All employees shall be informed as to the meaning of the various tags used throughout the workplace and what special precautions are necessary.
1910.145(f)(4)(vi) Tags shall be affixed as close as safely possible to their respective hazards by a positive means such as string, wire, or adhesive that prevents their loss or unintentional removal.
1910.145(f)(5) Danger tags. Danger tags shall be used in major hazard situations where an immediate hazard presents a threat of death or serious injury to employees. Danger tags shall be used only in these situations.
1910.145(f)(6) Caution tags. Caution tags shall be used in minor hazard situations where a non-immediate or potential hazard or unsafe practice presents a lesser threat of employee injury. Caution tags shall be used only in these situations.
1910.145(f)(7) Warning tags. Warning tags may be used to represent a hazard level between "Caution" and "Danger," instead of the required "Caution" tag, provided that they have a signal word of "Warning," an appropriate major message, and otherwise meet the general tag criteria of paragraph (f)(4) of this section.
1910.145(f)(8) Biological hazard tags.
1910.145(f)(8)(i) Biological hazard tags shall be used to identify the actual or potential presence of a biological hazard and to identify equipment, containers, rooms, experimental animals, or combinations thereof, that contain or are contaminated with hazardous biological agents -
Are all emergency stop buttons observed during this survey colored red?
-
1910.144(a)(1)(iii) Emergency stop bars on hazardous machines such as rubber mills, wire blocks, flat work ironers, etc., shall be red. Stop buttons or electrical switches which letters or other markings appear, used for emergency stopping of machinery shall be red.
-
Are there Permit-Required Confined Spaces?
-
Has the permit space observed during this survey been tested to determine if acceptable entry conditions exist prior to entry?
-
1910.146(c)(5)(ii)(C) Before an employee enters the space, the internal atmosphere shall be tested, with a calibrated direct-reading instrument, for oxygen content, for flammable gases and vapors, and for potential toxic air contaminants, in that order. Any employee who enters the space, or that employee's authorized representative, shall be provided an opportunity to observe the pre-entry testing required by this paragraph.
Is the permit space observed during this survey being tested or monitored as necessary to determine if acceptable entry conditions are being maintained during the course of entry operations? -
Is the written permit-required confined space entry program available to employees?
-
29 CFR 1910.146(c)(4) If the employer decides that its employees will enter permit spaces, the employer shall develop and implement a written permit space program that complies with this section. The written program shall be available for inspection by employees and their authorized representatives.
1910.146(d)(3) Develop and implement the means, procedures, and practices necessary for safe permit space entry operations, including, but not limited to, the following: Specifying acceptable entry conditions; Providing each authorized entrant or that employee's authorized representative with the opportunity to observe any monitoring or testing of permit spaces; Isolating the permit space; Purging, inerting, flushing, or ventilating the permit space as necessary to eliminate or control atmospheric hazards; Providing pedestrian, vehicle, or other barriers as necessary to protect entrants from external hazards; and Verifying that conditions in the permit space are acceptable for entry throughout the duration of an authorized entry. -
Are authorized entrants or their representatives provided an opportunity to observe any monitoring or testing of permit spaces?
-
1910.146(d)(3)(ii) Providing each authorized entrant or that employee's authorized representative with the opportunity to observe any monitoring or testing of permit spaces.
Medical and First Aid
-
Are first aid kits with required supplies available and easily accessible?
-
Recommend keeping a fully stocked first aid kit to reduce the risk of a minor injury becoming more severe. 1910.266 App A The following list sets forth the minimally acceptable number and type of first-aid supplies for first-aid kits required under paragraph (d)(2) of the logging standard. The contents of the first-aid kit listed should be adequate for small work sites, consisting of approximately two to three employees. When larger operations or multiple operations are being conducted at the same location, additional first-aid kits should be provided at the work site or additional quantities of supplies should be included in the first-aid kits:
1. Gauze pads (at least 4 x 4 inches).
2. Two large gauze pads (at least 8 x 10 inches).
3. Box adhesive bandages (band-aids).
4. One package gauze roller bandage at least 2 inches wide.
5. Two triangular bandages.
6. Wound cleaning agent such as sealed moistened towelettes.
7. Scissors.
8. At least one blanket.
9. Tweezers.
10. Adhesive tape.
11. Latex gloves.
12. Resuscitation equipment such as resuscitation bag, airway, or pocket mask.
13. Two elastic wraps.
14. Splint.
15. Directions for requesting emergency assistance. -
1910.266 App A The following list sets forth the minimally acceptable number and type of first-aid supplies for first-aid kits required under paragraph (d)(2) of the logging standard. The contents of the first-aid kit listed should be adequate for small work sites, consisting of approximately two to three employees. When larger operations or multiple operations are being conducted at the same location, additional first-aid kits should be provided at the work site or additional quantities of supplies should be included in the first-aid kits:
1. Gauze pads (at least 4 x 4 inches).
2. Two large gauze pads (at least 8 x 10 inches).
3. Box adhesive bandages (band-aids).
4. One package gauze roller bandage at least 2 inches wide.
5. Two triangular bandages.
6. Wound cleaning agent such as sealed moistened towelettes.
7. Scissors.
8. At least one blanket.
9. Tweezers.
10. Adhesive tape.
11. Latex gloves.
12. Resuscitation equipment such as resuscitation bag, airway, or pocket mask.
13. Two elastic wraps.
14. Splint.
15. Directions for requesting emergency assistance. -
Are emergency phone numbers posted where they can be readily found in case of an emergency?
-
If medical and first aid facilities are not in proximity (4 minutes ore less) of your workplace, is at least one employee on each shift currently qualified to render first aid?
-
29 CFR 1910.151(b) In the absence of an infirmary, clinic, or hospital in near proximity to the workplace which is used for the treatment of all injured employees, a person or persons shall be adequately trained to render first aid. Adequate first aid supplies shall be readily available.
OSHA recommends that every workplace include one or more employees who are trained and certified in first aid, including CPR. -
Are there Eye Wash and Showers adjacent to and within 10 seconds of caustic or strong acid hazards?
-
29 CFR 1910.151(c) Where the eyes or body of any person may be exposed to injurious corrosive materials, suitable facilities for quick drenching or flushing of the eyes and body shall be provided within the work area for immediate emergency use.
Fire Protection
-
Have you established procedures for sounding emergency alarms in the workplace?
-
1910.165(b)(5) The employer shall establish procedures for sounding emergency alarms in the workplace. For those employers with 10 or fewer employees in a particular workplace, direct voice communication is an acceptable procedure for sounding the alarm provided all employees can hear the alarm. Such workplaces need not have a back-up system.
-
Are approved portable fire extinguishers observed during this survey provided, mounted, located, and identified so that they are readily accessible to workers?
-
29 CFR 1910.157(c)(1) The employer shall provide portable fire extinguishers and shall mount, locate and identify them so that they are readily accessible to employees without subjecting the employees to possible injury.
To prevent fire extinguishers from being moved or damaged, they should be mounted on brackets or in wall cabinets with the carrying handle placed 3-1/2 to 5 feet above the floor. Larger fire extinguishers need to be mounted at lower heights with the carrying handle about 3 feet from the floor. -
Are portable fire extinguishers observed during this survey inspected (monthly & annually), maintained, fully charged, operating properly, and kept in designated places?
-
1910.157(c)(4) The employer shall assure that portable fire extinguishers are maintained in a fully charged and operable condition and kept in their designated places at all times except during use.
1910.157(e)(1) The employer shall be responsible for the inspection, maintenance and testing of all portable fire extinguishers in the workplace.
1910.157(e)(2) Portable extinguishers or hose used in lieu thereof under paragraph (d)(3) of this section shall be visually inspected monthly.
1910.157(e)(3) The employer shall assure that portable fire extinguishers are subjected to an annual maintenance check. Stored pressure extinguishers do not require an internal examination. The employer shall record the annual maintenance date and retain this record for one year after the last entry or the life of the shell, whichever is less. The record shall be available to the Assistant Secretary upon request. -
Are there Class D fire hazards?
-
Has an ongoing educational program been provided (new hires, annual, follow-up and those designated to use) to familiarize employees with the general principles of fire extinguisher use and the hazards involved with incipient stage firefighting?
-
1910.157(g)(1) Where the employer has provided portable fire extinguishers for employee use in the workplace, the employer shall also provide an educational program to familiarize employees with the general principles of fire extinguisher use and the hazards involved with incipient stage fire fighting.
1910.157(g)(4) The employer shall provide the training required upon initial assignment to the designated group of employees and at least annually thereafter.
Compressed Air
-
Compressed Air Equipment?
-
Is maintenance and testing performed on compressed air equipment per OSHA and manufacturer guidelines?
-
1910.169(b)(3)(iv) All safety valves shall be tested frequently and at regular intervals to determine whether they are in good operating condition.
-
Are air receivers observed during this survey installed so that they are easily accessible?
-
1910.169(b)(1) Installation. Air receivers shall be so installed that all drains, handholes, and manholes therein are easily accessible. Under no circumstances shall an air receiver be buried underground or located in an inaccessible place.
-
Are gauges observed during this survey located in such a way that they are readily visible?
-
1910.169(b)(3)(i) Every air receiver shall be equipped with an indicating pressure gauge (so located as to be readily visible) and with one or more spring-loaded safety valves. The total relieving capacity of such safety valves shall be such as to prevent pressure in the receiver from exceeding the maximum allowable working pressure of the receiver by more than 10 percent.
-
Is compressed air equipment observed during this survey constructed and installed so that it is cannot be readily rendered inoperative by any means, including the elements?
-
1910.169(b)(3)(iii) Safety appliances, such as safety valves, indicating devices and controlling devices, shall be constructed, located, and installed so that they cannot be readily rendered inoperative by any means, including the elements.
-
Are worm-gear type clamps for securing air nozzles and other equipment to compressed air hoses
-
1910.243(b)(2) Airhose. Hose and hose connections used for conducting compressed air to utilization equipment shall be designed for the pressure and service to which they are subjected.
Material Handling and Storage
-
Permanent aisles and passageways appropriately marked?
-
1910.176(a) Use of mechanical equipment. Where mechanical handling equipment is used, sufficient safe clearances shall be allowed for aisles, at loading docks, through doorways and wherever turns or passage must be made. Aisles and passageways shall be kept clear and in good repair, with no obstruction across or in aisles that could create a hazard. Permanent aisles and passageways shall be appropriately marked.
-
Material securely stored?
-
1910.176(b) Secure storage. Storage of material shall not create a hazard. Bags, containers, bundles, etc., stored in tiers shall be stacked, blocked, interlocked and limited in height so that they are stable and secure against sliding or collapse.
1910.176(c) Housekeeping. Storage areas shall be kept free from accumulation of materials that constitute hazards from tripping, fire, explosion, or pest harborage. Vegetation control will be exercised when necessary. -
Open pits, tanks, vats, etc. have guarding?
-
1910.176(g) Guarding. Covers and/or guard- rails shall be provided to protect personnel from the hazards of open pits, tanks, vats, ditches, etc.
-
Are Powered Industrial Trucks (Forklift) used on location?
-
Do the forklifts observed have all labels, nameplates, and markings as required?
-
1910.178(a)(3)Approved trucks shall bear a label or some other identifying mark indicating approval by the testing laboratory. See paragraph (a)(7) of this section and paragraph 405 of "American National Standard for Powered Industrial Trucks, Part II, ANSI B56.1-1969", which is incorporated by reference in paragraph (a)(2) of this section and which provides that if the powered industrial truck is accepted by a nationally recognized testing laboratory it should be so marked.
1910.178(a)(6) The user shall see that all nameplates and markings are in place and are maintained in a legible condition. -
Are seat belts utilized when operating the forklift?
-
Recommend all forklift operators follow OSHA forklift operator safety guidelines. This must be enforced by the company.
-
Are operators observed lowering forks, neutralizing the controls, setting the brake, and shutting off equipment when dismounting?
-
Was the operator more than 25 feet from Forklift?
-
1910.178(m)(5)(i) When a powered industrial truck is left unattended, load engaging means shall be fully lowered, controls shall be neutralized, power shall be shut off, and brakes set. Wheels shall be blocked if the truck is parked on an incline.
1910.178(m)(5)(ii) A powered industrial truck is unattended when the operator is 25 ft. or more away from the vehicle which remains in his view, or whenever the operator leaves the vehicle and it is not in his view. -
1910.178(m)(5)(iii) When the operator of an industrial truck is dismounted and within 25 ft. of the truck still in his view, the load engaging means shall be fully lowered, controls neutralized, and the brakes set to prevent movement.
-
Cranes, Hoists, or Derricks in use at location?
-
Are elevators, hoists, and man cages observed during this survey have capacities posted?
-
1910.179(b)(5) Rated load marking. The rated load of the crane shall be plainly marked on each side of the crane, and if the crane has more than one hoisting unit, each hoist shall have its rated load marked on it or its load block and this marking shall be clearly legible from the ground or floor.
-
Are operators observed during this survey qualified or certified?
-
1910.179(b)(8) Designated personnel-Only designated personnel shall be permitted to operate a crane.
-
Are pendant control boxes observed during this survey clearly marked for identification of functions?
-
1910.179(g)(1)(v) Pendant control boxes shall be constructed to prevent electrical shock and shall be clearly marked for identification of functions.
-
Are Slings and cables used on location?
-
Are Alloy Chains used?
-
Are records kept of the most recent month in which each alloy steel chain sling was thoroughly inspected?
-
1910.184(e)(3)(ii) The employer shall make and maintain a record of the most recent month in which each alloy steel chain sling was thoroughly inspected, and shall make such record available for examination.
-
Is a thorough inspection made of the alloy steel chain sling at least once every 12 months?
-
1910.184(e)(3)(i) In addition to the inspection required by paragraph (d) of this section, a thorough periodic inspection of alloy steel chain slings in use shall be made on a regular basis, to be determined on the basis of (A) frequency of sling use; (B) severity of service conditions; (C) nature of lifts being made; and (D) experience gained on the service life of slings used in similar circumstances. Such inspections shall in no event be at intervals greater than once every 12 months.
-
Are thorough inspections of alloy steel chain slings performed by competent persons?
-
1910.184(e)(3)(iii) The thorough inspection of alloy steel chain slings shall be performed by a competent person designated by the employer, and shall include a thorough inspection for wear, defective welds, deformation and increase in length. Where such defects or deterioration are present, the sling shall be immediately removed from service.
-
Do alloy steel chain slings observed during this survey have permanently affixed durable identification stating the size, grade, rated capacity, and reach?
-
1910.184(e)(1) Sling identification. Alloy steel chain slings shall have permanently affixed durable identification stating size, grade, rated capacity, and reach.
-
Wire rope rigging used?
-
Are wire ropes observed during this survey that are removed from service plainly marked as being unfit for use?
-
1910.184(f)(5) Removal from service. Wire rope slings shall be immediately removed from service if any of the following conditions are present:
1910.184(f)(5)(i) Ten randomly distributed broken wires in one rope lay, or five broken wires in one strand in one rope lay.
1910.184(f)(5)(ii) Wear or scraping of one-third the original diameter of outside individual wires.
1910.184(f)(5)(iii) Kinking, crushing, bird caging or any other damage resulting in distortion of the wire rope structure.
1910.184(f)(5)(iv) Evidence of heat damage.
1910.184(f)(5)(v) End attachments that are cracked, deformed or worn.
1910.184(f)(5)(vi) Hooks that have been opened more than 15 percent of the normal throat opening measured at the narrowest point or twisted more than 10 degrees from the plane of the unbent hook.
1910.184(f)(5)(vii) Corrosion of the rope or end attachments. -
Synthetic slings used?
-
Is each synthetic web sling observed during this survey marked or coded to show the rated capacity for each type of hitch and synthetic web material?
-
1910.184(i)(1) Sling identification. Each sling shall be marked or coded to show the rated capacities for each type of hitch and type of synthetic web material.
-
Are all slings, fasteners, and attachments observed during this survey inspected for damage or defects by a competent person each day before they are used?
-
1910.184(d) Inspections. Each day before being used, the sling and all fastenings and attachments shall be inspected for damage or defects by a competent person designated by the employer. Additional inspections shall be performed during sling use, where service conditions warrant. Damaged or defective slings shall be immediately removed from service.
-
Are damaged or defective slings observed during this survey immediately taken out of service?
-
1910.184(c)(1) Slings that are damaged or defective shall not be used.
-
Are slings observed during this survey securely attached to their loads?
-
1910.184(c)(6) Slings shall be securely attached to their loads.
-
Are slings observed during this survey padded or protected from the sharp edges of their loads?
-
1910.184(c)(7) Slings shall be padded or protected from the sharp edges of their loads.
-
Are suspended loads observed during this survey kept clear of all obstructions?
-
1910.184(c)(8) Suspended loads shall be kept clear of all obstructions.
-
Are employees observed during this survey kept clear of loads to be lifted and suspended?
-
1910.184(c)(9) All employees shall be kept clear of loads about to be lifted and of suspended loads.
-
Are slings observed during this survey stored in a clean, dry place?
-
Recommend a competent person designated by the company perform daily checks of all slings before use to make sure they do not show signs of damage or wear
-
When possible, are slings observed during this survey stored by hanging on a rack or wall?
-
Store slings in an area where they will not be subjected to mechanical, chemical, or ultraviolet damage, or to extreme temperatures, when slings are exposed to extreme temperatures, follow the guidance provided by the sling manufacturer or qualified person.
Consult the sling manufacturer for recommended inspection procedures when nylon or polyester webbing slings are extensively exposed to sunlight or ultraviolet light. -
Are rack columns observed during this survey anchored to the floor?
-
ANSI MH16.1: 2012 1.4.7 Column Base Plates and Anchors
The bottom of all columns shall be furnished with column base plates. All rack columns shall be anchored to the floor with anchor bolts to resist all applicable forces as described in Section 2.1 or Section 2.2. -
Is decking observed during this survey fastened to the beams to prevent deck dropping?
-
ANSI MH16.1: 2012 1.4.6 Movable-Shelf Rack Stability
The stability of movable-shelf racks is not to depend on the presence, absence or location of the movable shelves. Those components which do provide stability, such as the permanently bolted or welded top shelves and the longitudinal and
transverse diagonal bracing, are to be clearly indicated on the rack drawings (Section 1.4.4). For specific movable-shelf rack installations in which the overall rack height is a controlling element, a conspicuous warning is to be placed in the owner’s utilization instruction manual stating any restrictions to shelf placement or shelf removal. Such restrictions are to be permanently posted in locations clearly visible to forklift operators. -
Do storage racks observed during this survey display a conspicuously located permanent plaque that indicates load capacity?
-
ANSI MH16.1: 2012 1.4.2 Plaque The owner is responsible for displaying in one or more conspicuous locations a permanent plaque(s). Each plaque shall have an area of not less than 50 square inches. Plaques shall show in clear, legible print (a) the maximum permissible unit load and/or maximum uniformly distributed load per level, (b) the average unit load, if applicable and (c) maximum total load per bay. The unit load is usually a single pallet or container and its contents that is mechanically transported. Storage levels having multiple stacking of unit loads shall be so identified. It is the responsibility of the owner to ensure that the rack system is not altered in a manner that the plaque information is invalidated.
Machinery and Machine Guarding
-
Are there floor and bench-grinding machines?
-
Are floor- and bench-mounted abrasive wheels observed during this survey equipped with safety guards?
-
1910.215(a)(1) Machine guarding. Abrasive wheels shall be used only on machines provided with safety guards.
-
Are work rests observed during this survey kept adjusted closely to the wheel with a maximum opening of 1/8 inch to prevent the work from being jammed between the wheel and the rest?
-
1910.215(a)(4) Work rests. On offhand grinding machines, work rests shall be used to support the work. They shall be of rigid construction and designed to be adjustable to compensate for wheel wear. Work rests shall be kept adjusted closely to the wheel with a maximum opening of one-eighth inch to prevent the work from being jammed between the wheel and the rest, which may cause wheel breakage. The work rest shall be securely clamped after each adjustment. The adjustment shall not be made with the wheel in motion.
-
Do the safeguards observed during this survey prevent workers’ hands, arms, and other body parts from making contact with dangerous moving parts?
-
1910.212(a)(1) Types of guarding. One or more methods of machine guarding shall be provided to protect the operator and other employees in the machine area from hazards such as those created by point of operation, ingoing nip points, rotating parts, flying chips and sparks. Examples of guarding methods are-barrier guards, two-hand tripping devices, electronic safety devices, etc.
-
Are the safeguards observed during this survey firmly secured and not easily removable?
-
1910.212(a)(2) General requirements for machine guards. Guards shall be affixed to the machine where possible and secured elsewhere if for any reason attachment to the machine is not possible. The guard shall be such that it does not offer an accident hazard in itself.
-
Are Portable saws equipment observed during this survey provided with appropriate safety guards?
-
1910.243(a)(1)(i) All portable, power-driven circular saws having a blade diameter greater than 2 in. shall be equipped with guards above and below the base plate or shoe. The upper guard shall cover the saw to the depth of the teeth, except for the minimum arc required to permit the base to be tilted for bevel cuts. The lower guard shall cover the saw to the depth of the teeth, except for the minimum arc required to allow proper retraction and contact with the work. When the tool is withdrawn from the work, the lower guard shall automatically and instantly return to covering position.
-
Are Portable grinders observed during this survey provided with appropriate safety guards?
-
Portable Grinder Guarding
-
1910.243(c)(1) Abrasive wheels shall be used only on machine provided with safety guards.
1910.243(c)(3) Vertical portable grinders. Safety guards used on machines known as right angle head or vertical portable grinders shall have a maximum exposure angle of 180 deg., and the guard shall be so located so as to be between the operator and the wheel during use. Adjustment of guard shall be such that pieces of an accidentally broken wheel will be deflected away from the operator. (See Figure P-4.)
Welding Cutting and Brazing
-
Are there welding, cutting or brazing operations on location?
-
Are terminals for welding leads observed during this survey protected from contact?
-
1910.254(b)(4)(iv) Terminals for welding leads should be protected from accidental electrical contact by personnel or by metal objects i.e., vehicles, crane hooks, etc. Protection may be obtained by use of: Dead-front receptacles for plug connections; recessed openings with nonremovable hinged covers; heavy insulating sleeving or taping or other equivalent electrical and mechanical protection. If a welding lead terminal which is intended to be used exclusively for connection to the work is connected to the grounded enclosure, it must be done by a conductor at least two AWG sizes smaller than the grounding conductor and the terminal shall be marked to indicate that it is grounded.
-
Are electrode cables observed during this survey free from splices within 10 feet from holders?
-
1910.254(d)(8) Electric shock. Cables with splices within 10 feet (3 m) of the holder shall not be used. The welder should not coil or loop welding electrode cable around parts of his body.
-
Are cables observed during this survey with damaged insulation or exposed bare conductors replaced?
-
1910.254(d)(9)(iii) Cables with damaged insulation or exposed bare conductors shall be replaced. Joining lengths of work and electrode cables shall be done by the use of connecting means specifically intended for the purpose. The connecting means shall have insulation adequate for the service conditions.
-
Is flash-back protection provided by an approved device that will prevent flame from passing into the fuel-gas system?
-
1910.253(e)(3)(ii)(C)(3) Flash-back protection shall be provided by an approved device that will prevent flame from passing into the fuel-gas system.
-
Are leaking, defective, burned, or worn hoses observed during this survey removed, repaired, or replaced?
-
1910.253(e)(5)(v) Hose showing leaks, burns, worn places, or other defects rendering it unfit for service shall be repaired or replaced.
-
Are cylinders observed during this survey kept far enough away from the welding or cutting operation so that sparks, hot slag, or flames will not reach them? Or, are fire-resistant shields provided?
-
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(I) Cylinders shall be kept far enough away from the actual welding or cutting operation so that sparks, hot slag, or flame will not reach them, or fire-resistant shields shall be provided.
-
Are cylinders observed during this survey placed where they cannot become part of an electrical circuit?
-
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(J) Cylinders shall not be placed where they might become part of an electric circuit. Contacts with third rails, trolley wires, etc., shall be avoided. Cylinders shall be kept away from radiators, piping systems, layout tables, etc., that may be used for grounding electric circuits such as for arc welding machines. Any practice such as the tapping of an electrode against a cylinder to strike an arc shall be prohibited.
-
Is using cylinders as rollers or supports prohibited?
-
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(K) Cylinders shall never be used as rollers or supports, whether full or empty.
-
Are fuel-gas cylinders observed during this survey placed with the valve end up whenever they are in use?
-
1910.253(b)(5)(iii)(A) Fuel-gas cylinders shall be placed with valve end up whenever they are in use. Liquefied gases shall be stored and shipped with the valve end up.
-
Inside buildings, are cylinders observed during this survey stored in well-protected, well-ventilated, dry locations at least 20 feet from highly combustible material such as oil?
-
1910.253(b)(2)(ii) Inside of buildings, cylinders shall be stored in a well-protected, well-ventilated, dry location, at least 20 feet (6.1 m) from highly combustible materials such as oil or excelsior. Cylinders should be stored in definitely assigned places away from elevators, stairs, or gangways. Assigned storage spaces shall be located where cylinders will not be knocked over or damaged by passing or falling objects, or subject to tampering by unauthorized persons. Cylinders shall not be kept in unventilated enclosures such as lockers and cupboards.
-
Is storage of fuel gas cylinders inside a building observed during this survey limited to a total gas capacity of 2,000 cubic feet or 300 pounds of liquefied petroleum gas (except for those being used or attached and ready to use)?
-
1910.253(b)(3) Fuel-gas cylinder storage. Inside a building, cylinders, except those in actual use or attached ready for use, shall be limited to a total gas capacity of 2,000 cubic feet (56 m3) or 300 pounds (135.9 kg) of liquefied petroleum gas.
-
Is a separate, specially constructed room or compartment provided to store cylinders that have more than 2,000 cubic feet total gas capacity or 300 pounds of liquefied petroleum gas?
-
1910.253(b)(3)(i) For storage in excess of 2,000 cubic feet (56 m3) total gas capacity of cylinders or 300 (135.9 kg) pounds of liquefied petroleum gas, a separate room or compartment conforming to the requirements specified in paragraphs (f)(6)(i)(H) and (f)(6)(i)(I) of this section shall be provided, or cylinders shall be kept outside or in a special building. Special buildings, rooms or compartments shall have no open flame for heating or lighting and shall be well ventilated. They may also be used for storage of calcium carbide in quantities not to exceed 600 (271.8 kg) pounds, when contained in metal containers complying with paragraphs (g)(1)(i) and (g)(1)(ii) of this section.
-
Are stored oxygen cylinders observed during this survey separated from fuel-gas cylinders or combustible materials (especially oil or grease) by at least 20 feet, or by a noncombustible barrier at least 5 feet high with a fire-resistance rating of at least one-half hour?
-
1910.253(b)(4)(iii) Oxygen cylinders in storage shall be separated from fuel-gas cylinders or combustible materials (especially oil or grease), a minimum distance of 20 feet (6.1 m) or by a noncombustible barrier at least 5 feet (1.5 m) high having a fire-resistance rating of at least one-half hour.
-
Unless the cylinders observed during this survey are secured on a special truck, are regulators removed and valve-protection caps installed before cylinders are moved?
-
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(D) Unless cylinders are secured on a special truck, regulators shall be removed and valve-protection caps, when provided for, shall be put in place before cylinders are moved.
-
Are cylinder valves observed during this survey closed when work is finished and before cylinders are moved?
-
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(F) Cylinder valves shall be closed before moving cylinders.
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(G) Cylinder valves shall be closed when work is finished.
1910.253(b)(5)(ii)(H) Valves of empty cylinders shall be closed. -
Are all moveable fire hazards and combustibles moved to at least 35 feet away from areas or objects to be welded?
-
1910.252(a)(1)(i) Fire hazards. If the object to be welded or cut cannot readily be moved, all movable fire hazards in the vicinity shall be taken to a safe place.
1910.252(a)(2)(vi)(C) In the presence of explosive atmospheres (mixtures of flammable gases, vapors, liquids, or dusts with air), or explosive atmospheres that may develop inside uncleaned or improperly prepared tanks or equipment which have previously contained such materials, or that may develop in areas with an accumulation of combustible dusts. -
When welding or cutting operations are performed within 35 feet of combustible materials or floor, ceiling, or wall openings, are guards, barriers, or other precautions used to confine heat sparks and slag or is a fire watch assigned?
-
1910.252(a)(1)(ii) Guards. If the object to be welded or cut cannot be moved and if all the fire hazards cannot be removed, then guards shall be used to confine the heat, sparks, and slag, and to protect the immovable fire hazards.
1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(A) Fire watchers shall be required whenever welding or cutting is performed in locations where other than a minor fire might develop, or any of the following conditions exist:
1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(A)(1) Appreciable combustible material, in building construction or contents, closer than 35 feet (10.7 m) to the point of operation.
1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(A)(2) Appreciable combustibles are more than 35 feet (10.7 m) away but are easily ignited by sparks.
1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(A)(3) Wall or floor openings within a 35-foot (10.7 m) radius expose combustible material in adjacent areas including concealed spaces in walls or floors.
1910.252(a)(2)(iii)(A)(4) Combustible materials are adjacent to the opposite side of metal partitions, walls, ceilings, or roofs and are likely to be ignited by conduction or radiation -
Is local or general exhaust ventilation provided during welding to maintain concentrations of toxic materials such as fluorides, cadmium, zinc, beryllium, lead, or mercury within acceptable limits?
-
1910.252(c)(1)(iii) Maximum allowable concentration. Local exhaust or general ventilating systems shall be provided and arranged to keep the amount of toxic fumes, gases, or dusts below the maximum allowable concentration as specified in 1910.1000.
-
Are adequate controls in place to protect workers from exposures to hexavalent chromium Cr(VI), which can occur when welding or cutting operations are performed on stainless steel, other metals containing Cr(VI), or surfaces coated with Cr(VI) paint?
-
1910.1026(f)(1)(i) Except as permitted in paragraph (f)(1)(ii) and paragraph (f)(1)(iii) of this section, the employer shall use engineering and work practice controls to reduce and maintain employee exposure to chromium (VI) to or below the PEL unless the employer can demonstrate that such controls are not feasible. Wherever feasible engineering and work practice controls are not sufficient to reduce employee exposure to or below the PEL, the employer shall use them to reduce employee exposure to the lowest levels achievable, and shall supplement them by the use of respiratory protection that complies with the requirements of paragraph (g) of this section.
-
Are welding cables and hoses observed during this survey kept clear of passageways, ladders, and stairways?
-
1910.252(b)(1)(ii) Welding cable. Welders shall place welding cable and other equipment so that it is clear of passageways, ladders, and stairways.
-
Are employees observed during this survey who are working nearby protected from arc welding rays by screens, booths, or shields?
-
1910.252(b)(2)(iii) Protection from arc welding rays. Where the work permits, the welder should be enclosed in an individual booth painted with a finish of low reflectivity such as zinc oxide (an important factor for absorbing ultraviolet radiations) and lamp black, or shall be enclosed with noncombustible screens similarly painted. Booths and screens shall permit circulation of air at floor level. Workers or other persons adjacent to the welding areas shall be protected from the rays by noncombustible or flameproof screens or shields or shall be required to wear appropriate goggles.
Electrical
-
Are all over-current devices observed during this survey (circuit breakers, fuses, etc.) legibly marked to indicate their purpose?
-
1910.303(e)(1) Identification of manufacturer and ratings. Electric equipment may not be used unless the following markings have been placed on the equipment:
1910.303(e)(1)(i) The manufacturer's name, trademark, or other descriptive marking by which the organization responsible for the product may be identified; and
1910.303(e)(1)(ii) Other markings giving voltage, current, wattage, or other ratings as necessary. -
Are two or more employees trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) methods available at field locations where employees are working on or associated with exposed lines or equipment energized at 50 volts or more?
-
1910.269(b)(1) First-aid training. When employees are performing work on, or associated with, exposed lines or equipment energized at 50 volts or more, persons with first-aid training shall be available
-
Are portable cord and plug-connected equipment and flexible cord sets (extension cords) observed during this survey visually inspected before use every day? <br>Note: Cord and plug-connected equipment and flexible cord sets that remain connected (once they are put in place) and are not exposed to damage need not be visually inspected until they are relocated.
-
1910.334(a)(2)(i) Portable cord and plug connected equipment and flexible cord sets (extension cords) shall be visually inspected before use on any shift for external defects (such as loose parts, deformed and missing pins, or damage to outer jacket or insulation) and for evidence of possible internal damage (such as pinched or crushed outer jacket). Cord and plug connected equipment and flexible cord sets (extension cords) which remain connected once they are put in place and are not exposed to damage need not be visually inspected until they are relocated.
-
If a defect might expose employees to injury, is the defective or damaged item removed from service and are employees prohibited from using it until repairs and tests have been made?
-
1910.334(a)(2)(ii) If there is a defect or evidence of damage that might expose an employee to injury, the defective or damaged item shall be removed from service, and no employee may use it until repairs and tests necessary to render the equipment safe have been made.
-
Do flexible cords used with grounding-type equipment observed during this survey contain an equipment grounding conductor?
-
1910.334(a)(3)(i) A flexible cord used with grounding type equipment shall contain an equipment grounding conductor.
-
Are receptacles installed in damp locations observed during this survey suitable for that location? <br>Note: Ground-fault circuit interrupters are recommended in these types of locations.
-
1910.305(j)(2)(iv) A receptacle installed in a wet or damp location shall be suitable for the location..
1910.305(j)(2)(v) A receptacle installed outdoors in a location protected from the weather or in other damp locations shall have an enclosure for the receptacle that is weatherproof when the receptacle is covered (attachment plug cap not inserted and receptacle covers closed). -
Is the width of working space in front of the electric equipment observed during this survey the width of the equipment or 30 inches, whichever is greater? 600 Volts or Less
-
1910.303(g)(1)(i)(B) The width of working space in front of the electric equipment shall be the width of the equipment or 762 mm (30 in.), whichever is greater. In all cases, the working space shall permit at least a 90-degree opening of equipment doors or hinged panels; and
1910.303(g)(1)(i)(C) The work space shall be clear and extend from the grade, floor, or platform to the height required by paragraph (g)(1)(vi) of this section. However, other equipment associated with the electrical installation and located above or below the electric equipment may extend not more than 153 mm (6 in.) beyond the front of the electric equipment.
1910.303(g)(1)(ii) Working space required by this standard may not be used for storage. When normally enclosed live parts are exposed for inspection or servicing, the working space, if in a passageway or general open space, shall be suitably guarded. -
Electrical equipment installed neat and in a workman-like manner?
-
1910.303(b)(7) Mechanical execution of work. Electric equipment shall be installed in a neat and workmanlike manner.
-
Is electrical panels, pull boxes, housing, and other electrical enclosures effectively enclosed?
-
1910.303(b)(7)(i) Unused openings in boxes, raceways, auxiliary gutters, cabinets, equipment cases, or housings shall be effectively closed to afford protection substantially equivalent to the wall of the equipment.
-
Are there contaminates near or damage to electrical parts?
-
1910.303(b)(7)(iii) Internal parts of electrical equipment, including busbars, wiring terminals, insulators, and other surfaces, may not be damaged or contaminated by foreign materials such as paint, plaster, cleaners, abrasives, or corrosive residues.
1910.303(b)(7)(iv) There shall be no damaged parts that may adversely affect safe operation or mechanical strength of the equipment, such as parts that are broken, bent, cut, or deteriorated by corrosion, chemical action, or overheating.
Toxic and Hazardous Substances
-
Are there Above Ground Storage Tanks?
-
Are all ASTs observed during this survey properly labeled?
-
1910.1200(f)(6) Workplace labeling. The employer shall ensure that each container of hazardous chemicals in the workplace is labeled, tagged or marked.
-
Does each tank observed during this survey have appropriate secondary containment?
-
40 CFR 265.193(b) 40 CFR 265.193(c) 40 CFR 265.193(d)
-
Is all leak detection equipment observed during this survey in satisfactory condition?
-
40 CFR 265.193(c)(3) 40 CFR 265.193(e)(3)(iii)
-
Does the company maintain all employee exposure and medical records for at least the duration of employment plus 30 years?
-
1910.1020(d)(1)(ii) "Employee exposure records." Each employee exposure record shall be preserved and maintained for at least thirty (30) years
-
Is each container/containers of hazardous chemicals in the workplace observed during this survey labeled, tagged or marked identifying the chemical it contains? HAZCOM
-
1910.1200(f)(6) Workplace labeling. The employer shall ensure that each container of hazardous chemicals in the workplace is labeled, tagged or marked
-
Are copies of the required safety data sheets for each hazardous chemical in the workplace observed during this survey readily accessible to employees in the work area during each work shift?
-
1910.1200(g)(8) The employer shall maintain in the workplace copies of the required safety data sheets for each hazardous chemical, and shall ensure that they are readily accessible during each work shift to employees when they are in their work area(s). (Electronic access and other alternatives to maintaining paper copies of the safety data sheets are permitted as long as no barriers to immediate employee access in each workplace are created by such options.)
Construction (29 CFR 1926)
-
Construction Site Assessment?
General Safety and Health Provisions - Subpart C - 1926.20
-
Scrap Lumber with protruding nails and other debris regularly cleared from work areas and from around structures?
-
Jobsite properly fenced, signed, and secured?
-
Emergency action plan is on site?
-
Adequate dumpsters for trash and recyclables?
-
Housekeeping; Is the job site clean?
-
Exits were clear and unobstructed?
-
Pre-task/Daily Safety Brief and/or Plans are being done regularly?
-
Site safety inspections being conducted routinely by client?
-
Conducting weekly toolbox talks?
Occupational Health and Environmental Controls - Subpart D - 1926.50
-
Medical Services and First Aid Available?
-
1926.50(a) The employer shall insure the availability of medical personnel for advice and consultation on matters of occupational health.
1926.50(b) Provisions shall be made prior to commencement of the project for prompt medical attention in case of serious injury.
1926.50(c) In the absence of an infirmary, clinic, hospital, or physician, that is reasonably accessible in terms of time and distance to the worksite, which is available for the treatment of injured employees, a person who has a valid certificate in first-aid training from the U.S. Bureau of Mines, the American Red Cross, or equivalent training that can be verified by documentary evidence, shall be available at the worksite to render first aid. -
First aid kits available and stocked?
-
1926.50(d)(2)
The contents of the first aid kit shall be placed in a weatherproof container with individual sealed packages for each type of item, and shall be checked by the employer before being sent out on each job and at least weekly on each job to ensure that the expended items are replaced. -
All work areas adequately illuminated?
-
1926.56(a)
General. Construction areas, ramps, runways, corridors, offices, shops, and storage areas shall be lighted to not less than the minimum illumination intensities listed in Table D-3 while any work is in progress:
TABLE D-3 - MINIMUM ILLUMINATION INTENSITIES IN FOOT-CANDLES
____________________________________________________________________
|
Foot-Candles | Area of Operation
_______________|____________________________________________________
|
5............. | General construction area lighting.
3............. | General construction areas, concrete placement,
| excavation and waste areas, access ways, active
| storage areas, loading platforms, refueling, and
| field maintenance areas.
5............. | Indoors: warehouses, corridors, hallways, and
| exitways.
5............. | Tunnels, shafts, and general underground work areas:
| (Exception: minimum of 10 foot-candles is required
| at tunnel and shaft heading during drilling,
| mucking, and scaling. Bureau of Mines approved cap
| lights shall be acceptable for use in the tunnel
| heading)
10............ | General construction plant and shops (e.g., batch
| plants, screening plants, mechanical and
| electrical equipment rooms, carpenter shops,
| rigging lofts and active store rooms, mess halls,
| and indoor toilets and workrooms.)
30............ | First aid stations, infirmaries, and offices.
_______________|____________________________________________________ -
Adequate supply of water and individual drinking containers provided?
-
1926.51(a)(1) An adequate supply of potable water shall be provided in all places of employment.
1926.51(a)(2) Portable containers used to dispense drinking water shall be capable of being tightly closed, and equipped with a tap. Water shall not be dipped from containers.
1926.51(a)(3) Any container used to distribute drinking water shall be clearly marked as to the nature of its contents and not used for any other purpose.
1926.51(a)(4) The common drinking cup is prohibited. -
Receptacle for disposing of used cups provided?
-
1926.51(a)(5) Where single service cups (to be used but once) are supplied, both a sanitary container for the unused cups and a receptacle for disposing of the used cups shall be provided.
-
Are adequate Toilets available for employees on-site?
-
1926.51(c)(1)
Toilets shall be provided for employees according to the following table:# of employees|# of toilets
< 20.................| 1
> 20.................| 1 toilet seat and 1 urinal/40 workers
> 200...............| 1 toilet seat and 1 urinal/50 workers -
1926.51(c)(2) Under temporary field conditions, provisions shall be made to assure not less than one toilet facility is available.
Personal Protective Equipment - Subpart E - 1926.95
-
Standard PPE - Safety Boots worn by everyone where required?
-
1926.96 Safety-toe footwear for employees shall meet the requirements and specifications in American National Standard for Men's Safety-Toe Footwear, Z41.1-1967.
-
Standard PPE - Hardhats worn by everyone where required?
-
1926.100(a)
Employees working in areas where there is a possible danger of head injury from impact, or from falling or flying objects, or from electrical shock and burns, shall be protected by protective helmets.
1926.100(b)
Criteria for head protection.
1926.100(b)(1)
The employer must provide each employee with head protection that meets the specifications contained in any of the following consensus standards:
1926.100(b)(1)(i)
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z89.1-2009, "American National Standard for Industrial Head Protection," incorporated by reference in §1926.6;
1926.100(b)(1)(ii)
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z89.1-2003, "American National Standard for Industrial Head Protection," incorporated by reference in §1926.6; or
1926.100(b)(1)(iii)
American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z89.1-1997, "American National Standard for Personnel Protection-Protective Headwear for Industrial Workers-Requirements," incorporated by reference in §1926.6.
1926.100(b)(2)
The employer must ensure that the head protection provided for each employee exposed to high-voltage electric shock and burns also meets the specifications contained in Section 9.7 ("Electrical Insulation") of any of the consensus standards identified in paragraph (b)(1) of this section.
1926.100(b)(3)
OSHA will deem any head protection device that the employer demonstrates is at least as effective as a head protection device constructed in accordance with one of the consensus standards identified in paragraph (b)(1) of this section to be in compliance with the requirements of this section. -
Standard PPE - Safety Vests worn by everyone where required?
-
PPE in good working condition? Compliant with appropriate ANSI Standard (Z89/Z87)?
-
1926.95(a) Protective equipment, including personal protective equipment for eyes, face, head, and extremities, protective clothing, respiratory devices, and protective shields and barriers, shall be provided, used, and maintained in a sanitary and reliable condition wherever it is necessary by reason of hazards of processes or environment, chemical hazards, radiological hazards, or mechanical irritants encountered in a manner capable of causing injury or impairment in the function of any part of the body through absorption, inhalation or physical contact
-
Additional PPE is being utilized as necessary (Hearing Protection, gloves, welding hoods, cutting goggles, face shields)?
-
Proper clothing being worn by all employees (shirts w/ sleeves, work boots, pants)?
-
Respirators required?
-
All users have current Fit Test(s)?
-
Respirators are being worn correctly, where required?
-
Respirators are being stored properly?
Fire Safety - Subpart F - 1926.150
-
Fire Extinguishers on site?
-
1926.150(a)(1) The employer shall be responsible for the development of a fire protection program to be followed throughout all phases of the construction and demolition work, and he shall provide for the firefighting equipment as specified in this subpart. As fire hazards occur, there shall be no delay in providing the necessary equipment.
1926.150(a)(2) Access to all available firefighting equipment shall be maintained at all times.
1926.150(a)(3) All firefighting equipment, provided by the employer, shall be conspicuously located. -
Fire Extinguisher Rated no less than 2A, 55 Gallon drum of water with 2 fire pails, or 1/2 inch garden hose with 100-foot length provided for every 3000 square feet and with a distance of fewer than 100 feet from the task?
-
1926.150(c)(1)(i) A fire extinguisher, rated not less than 2A, shall be provided for each 3,000 square feet of the protected building area, or major fraction thereof. Travel distance from any point of the protected area to the nearest fire extinguisher shall not exceed 100 feet.
1926.150(c)(1)(ii) One 55-gallon open drum of water with two fire pails may be substituted for a fire extinguisher having a 2A rating.1926.150(c)(1)(iii)
A 1/2-inch diameter garden-type hose line, not to exceed 100 feet in length and equipped with a nozzle, may be substituted for a 2A-rated fire extinguisher, providing it is capable of discharging a minimum of 5 gallons per minute with a minimum hose stream range of 30 feet horizontally. The garden-type hose lines shall be mounted on conventional racks or reels. The number and location of hose racks or reels shall be such that at least one hose stream can be applied to all points in the area. -
A fire extinguisher, rated not less than 10B, provided within 50 feet of wherever more than 5 gallons of flammable or combustible liquids or 5 pounds of flammable gas?
-
1926.150(c)(1)(vi) A fire extinguisher, rated not less than 10B, shall be provided within 50 feet of wherever more than 5 gallons of flammable or combustible liquids or 5 pounds of flammable gas are being used on the jobsite. This requirement does not apply to the integral fuel tanks of motor vehicles.
-
Fire Extinguisher has up to date annual inspection completed?
-
1926.150(c)(1)(viii) Portable fire extinguishers shall be inspected periodically and maintained in accordance with Maintenance and Use of Portable Fire Extinguishers, NFPA No. 10A-1970.
-
Fire Extinguisher has up to date monthly inspection completed?
-
1926.150(c)(1)(viii) Portable fire extinguishers shall be inspected periodically and maintained in accordance with Maintenance and Use of Portable Fire Extinguishers, NFPA No. 10A-1970.
-
Fire extinguisher rated 20-B located 25'-75' from outside fuel storage?
-
1926.152(d)(2) At least one portable fire extinguisher having a rating of not less than 20-B units shall be located not less than 25 feet, nor more than 75 feet, from any flammable liquid storage area located outside.
-
Portable fire extinguisher, having a rating of not less than 20-B units, located outside of, but not more than 10 feet from, the door opening into any room used for storage of more than 60 gallons of flammable liquids?
-
1926.152(d)(1) At least one portable fire extinguisher, having a rating of not less than 20-B units, shall be located outside of, but not more than 10 feet from, the door opening into any room used for storage of more than 60 gallons of flammable liquids.
-
Smoking in authorized area's only?
-
1926.151(a)(3) Smoking shall be prohibited at or in the vicinity of operations which constitute a fire hazard, and shall be conspicuously posted: "No Smoking or Open Flame."
-
Metal gas cans properly labeled with flame arrestor? (Plastic cans are not allowed)
-
29 CFR 1926.155(l) an approved closed container, of not more than 5 gallons capacity, having a flash arresting screen, spring-closing lid and spout cover and so designed that it will safely relieve internal pressure when subjected to fire exposure
-
Flammable liquids are being stored properly (Less than 25 gallons of flammable liquids stored outside of metal cabinet)?
-
1926.152(a)(1) Only approved containers and portable tanks shall be used for storage and handling of flammable liquids. Approved safety cans or Department of Transportation approved containers shall be used for the handling and use of flammable liquids in quantities of 5 gallons or less, except that this shall not apply to those flammable liquid materials which are highly viscid (extremely hard to pour), which may be used and handled in original shipping containers. For quantities of one gallon or less, the original container may be used, for storage, use and handling of flammable liquids.
-
LPG is stored outside?
-
1926.153(k)(1) Storage outside of buildings, for containers awaiting use, shall be located from the nearest building or group of buildings, in accordance with the following:
TABLE F-3
_______________________________________
Quantity of LP-Gas stored | Distance
| (feet)
_____________________________|_________
500 lbs. or less............ | 0
501 to 6,000 lbs............ | 10
6,001 to 10,000 lbs......... | 20
Over 10,000 lbs............. | 25
_____________________________|_________
1926.153(k)(2) Containers shall be in a suitable ventilated enclosure or otherwise protected against tampering.
1926.153(l) Fire protection. Storage locations shall be provided with at least one approved portable fire extinguisher having a rating of not less than 20-B:C. -
Weeds and grass kept down to prevent fires?
-
1926.151(c)(3) The entire storage site shall be kept free from accumulation of unnecessary combustible materials. Weeds and grass shall be kept down and a regular procedure provided for the periodic cleanup of the entire area.
-
1926.152(c)(5) Storage areas shall be kept free of weeds, debris, and other combustible material not necessary to the storage.
Signs, Signals, and Barricades- Subpart G - 1926.200
-
Danger signs in use where there is an immediate hazard?
-
1926.200(b)(1)Danger signs shall be used only where an immediate hazard exists, and shall follow the specifications illustrated in Figure 1 of ANSI Z35.1-1968 or in Figures 1 to 13 of ANSI Z535.2-2011, incorporated by reference in §1926.6.
-
Are Danger signs predominating red with a black outline?
-
1926.200(b)(2) Danger signs shall have red as the predominating color for the upper panel; black outline on the borders; and a white lower panel for additional sign wording.
-
Caution signs used to warn against potential hazards or to caution against unsafe practices
-
1926.200(c)(1) Caution signs shall be used only to warn against potential hazards or to caution against unsafe practices, and shall follow the specifications illustrated in Figure 4 of ANSI Z35.1-1968 or in Figures 1 to 13 of ANSI Z535.2-2011, incorporated by reference in §1926.6.
-
Caution signs have yellow as the predominating color; black upper panel and borders: yellow lettering of "caution" on the black pane?
-
1926.200(c)(2) Caution signs shall have yellow as the predominating color; black upper panel and borders: yellow lettering of "caution" on the black panel; and the lower yellow panel for additional sign wording. Black lettering shall be used for additional wording.
1926.200(c)(3) The standard color of the background shall be yellow; and the panel, black with yellow letters. Any letters used against the yellow background shall be black. The colors shall be those of opaque glossy samples as specified in Table 1 of ANSI Z53.1-1967 or in Table 1 of ANSI Z535.1-2006(R2011), incorporated by reference in §1926.6. -
Traffic Control Signs and Devices in use?
-
Are construction areas posted with legible traffic control signs and protected by traffic control devices?
-
1926.200(g)(1) At points of hazard, construction areas shall be posted with legible traffic control signs and protected by traffic control devices.
1926.200(g)(2) The design and use of all traffic control devices, including signs, signals, markings, barricades, and other devices, for protection of construction workers shall conform to Part 6 of the MUTCD (incorporated by reference, see §1926.6).
Material Handling & Storage - Subpart H - 1926.250
-
Material Handling and Storage on location?
-
All materials are stacked so as to prevent sliding, falling, or collapse?
-
1926.250(a)(1) All materials stored in tiers shall be stacked, racked, blocked, interlocked, or otherwise secured to prevent sliding, falling or collapse.
1926.250(a)(2)(i) The weight of stored materials on floors within buildings and structures shall not exceed maximum safe load limits. -
Conspicuously posted maximum safe load limits of floors within buildings and structures, in pounds per square foot, in all storage areas, except when the storage area is on a floor or slab on grade?
-
1926.250(a)(2)(ii) Employers shall conspicuously post maximum safe load limits of floors within buildings and structures, in pounds per square foot, in all storage areas, except when the storage area is on a floor or slab on grade. Posting is not required for storage areas in all single-family residential structures and wood-framed multi-family residential structures.
-
Material stored in walk paths, on stairs, or on scaffolds?
-
1926.250(a)(3) Aisles and passageways shall be kept clear to provide for the free and safe movement of material handling equipment or employees. Such areas shall be kept in good repair.
1926.250(b)(1) Material stored inside buildings under construction shall not be placed within 6 feet of any hoistway or inside floor openings, nor within 10 feet of an exterior wall which does not extend above the top of the material stored.
1926.250(b)(5) Materials shall not be stored on scaffolds or runways in excess of supplies needed for immediate operations. -
Bricks are not stacked higher than 7' and masonry block does not exceed 6'?
-
1926.250(b)(6) Brick stacks shall not be more than 7 feet in height. When a loose brick stack reaches a height of 4 feet, it shall be tapered back 2 inches in every foot of height above the 4-foot level.
1926.250(b)(7) When masonry blocks are stacked higher than 6 feet, the stack shall be tapered back one-half block per tier above the 6-foot level. -
Nails,screws, and staples have all been removed from all stored lumber or bent over?
-
1926.250(b)(8)(i) Used lumber shall have all nails withdrawn before stacking.
-
Materials staged a safe distance from leading edge?
-
Rigging equipment in use?
-
No employees are under suspended loads?
-
Tag lines being used?
-
All rigging equipment is being inspected daily?
-
1926.251(a)(1) Rigging equipment for material handling shall be inspected prior to use on each shift and as necessary during its use to ensure that it is safe. Defective rigging equipment shall be removed from service
-
All rigging equipment being stored properly?
-
Tags/labels present and legible?
-
1926.251(a)(2)(i) Has permanently affixed and legible identification markings as prescribed by the manufacturer that indicate the recommended safe working load;
1926.251(a)(2)(iii) Not be used without affixed, legible identification markings, required by paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section.
1926.251(a)(4) Special custom design grabs, hooks, clamps, or other lifting accessories, for such units as modular panels, prefabricated structures and similar materials, shall be marked to indicate the safe working loads and shall be proof-tested prior to use to 125 percent of their rated load.
Tools (Hand and Power) - Subpart I - 1926.300
-
All tools being inspected prior to use and are in good working condition?
-
1926.300(a) Condition of tools. All hand and power tools and similar equipment, whether furnished by the employer or the employee, shall be maintained in a safe condition.
-
Power tools are grounded or double insulated and cord is in good condition?
-
Tools are properly guarded per manufacturer's requirements?
-
1926.300(b)(1) When power operated tools are designed to accommodate guards, they shall be equipped with such guards when in use.
1926.300(b)(2) Belts, gears, shafts, pulleys, sprockets, spindles, drums, fly wheels, chains, or other reciprocating, rotating or moving parts of equipment shall be guarded if such parts are exposed to contact by employees or otherwise create a hazard. Guarding shall meet the requirements as set forth in American National Standards Institute, B15.1-1953 (R1958), Safety Code for Mechanical Power-Transmission Apparatus. -
Fuel Powered tools?
-
Fuel powered tools are shut off prior to refueling?
-
Fuel powered equipment used indoors have adequate ventilation?
-
Powder actuated tools in use?
-
Powder actuated tools are being used by properly trained employees?
-
Powder actuated tools are attended at all times?
-
Lasers & powder actuated signs posted and users trained?
-
Do tools have a magnetic switch?
Cutting and Welding - Subpart J - 1926.350
-
Welding / Cutting operations?
-
Hot works permit complete?
-
Back flow preventers in place?
-
Valves closed and capped when not in use?
-
Fire extinguisher present during hot works operation? Up to date inspection? Immediately available?
-
Properly trained fire watch being used where required?
-
Welding is being done on substances with known toxic properties?
-
Gas cylinders stored properly? (20' apart, 1/2 hour fire wall, and secured)
-
Adequate ventilation is being used?
-
Air quality has been evaluated as needed?
Electrical - Subpart K - 1926.400
-
Assured grounding program in place, or GFCI's used and checked?
-
Permanent power is GFCI protected?
-
Cords, plugs in good condition? Protected from traffic and damage?
-
Temporary lighting - Properly set up, in good condition, protected from damage?
-
Task lighting properly set up?
-
Panels marked and/or labeled, secured, and weather resistant?
-
All live wiring properly guarded or protected from employee exposure?
-
Lock out/tag out being used where required?
Scaffold - Subpart L -1926.450
-
Scaffolding in use?
-
Employees properly trained on scaffolding?
-
Scaffolding being inspected each day by a Competent Person and documented?
-
Planking meets OSHA requirements and is in good condition?
-
Working level is fully planked?
-
Planking properly installed? (Overlap or cleats)
-
Guardrails and toe boards (as necessary) in place?
-
Tie-ins, pins, braces installed as required?
-
Footing (cribbing, mudsills, screw-jacks, and baseplates/wheels) properly installed?
-
Proper access provided?
-
Height exceeds a 4:1 ratio without proper restraint to prevent tipping, 2:1 if using wheels?
-
All wheels locked?
-
Proper tie backs on suspended scaffolding?
-
Are the appropriate amount of counterweights being used with suspended scaffolding?
-
Each employee is using independent anchor point for fall protection?
-
Aerial lifts are working within their limits?
-
Gates are closed or chains are in place on all aerial lifts?
-
Proper PPE being used on aerial/scissor lifts?
-
Employees in aerial lifts have their feet firmly on the ground?
Fall Protection - Subpart M - 1926.500
-
Fall protection required?
-
Employee properly trained in fall protection?
-
All floor and/or roof openings adequately protected or covered and marked accordingly?
-
Overhead protection provided where necessary?
-
Employees exposed to falls are properly trained in fall protection and rescue?
-
Perimeter cable installed and flagged every 6'?
-
Perimeter Posts are installed correctly?
-
Perimeter cable has proper connection (Never saddle a dead horse)?
-
Guardrails in place and able to withstand 200# of outward downward force?
-
Guardrails consist of a top rail, mid rail, and a toe board, installed at proper height?
-
Guardrails are smooth and there is no potential of snags, cuts, or punctures?
-
Horizontal lifeline is inspected by a competent person and designed by a qualified person?
-
All employees are using 100% fall protection above 6'?
-
Proper anchor points are being utilized? Overhead? Rated for 5000#?
-
Fall protection equipment is being inspected daily by the end user?
Hoists, elevators, and conveyors - Subpart N - 1926.550
-
Hoists, Elevators, and Conveyors in use?
-
Rated load capacity is posted?
-
Personnel hoist has doors in good working order and will not operate while open?
-
Emergency stop button is on the hoist and clearly marked "STOP"?
-
Weekly inspection and maintenance is being conducted?
-
Operator properly trained and certified to operate the hoist/elevator?
-
Overhead Protection?
Motor vehicles, Mechanized equipment - Subpart O - 1926.600
-
Motor vehicles, Mechanized equipment in use?
-
Daily Inspection is complete and on the equipment?
-
Operator's all have their certification cards on them (fork, aerial/scissor lifts)?
-
All equipment - Level/stable work pad, proper distance from excavations/trenches?
-
Is there a working fire extinguisher on all pieces of equipment, as required?
-
Equipment back-up alarms functional and audible?
-
All equipment is equipped with an audible warning device (Horn)?
-
Work zone protection - Traffic Control Plan (Proper Reflective Vest/Materials/Signs/Cones & Barricades)?
-
Reflective devices are clean and working?
-
Barriers set up to avoid blunt impacts?
-
Flaggers are trained and certified?
-
Equipment turned off and parking brake set while unattended.
-
All raise able implements lowered to the ground prior to operator leaving it unattended.
-
Equipment is equipped with seat belt(s) and operator is using?
Excavations - Subpart P - 1926.650
-
Are excavations present?
-
Daily excavations and trenching inspection completed by Competent Person prior to each shift and after any weather event?
-
Trench box safety procedures in place (tabulated data available)?
-
Utilities located (current and documented)?
-
Ramps/Ladders every 50' (25' either direction) when 4' or deeper?
-
Existing utilities shored/supported properly?
-
Trenches 20' or deeper have engineering and certificate?
-
Trenches/excavation deeper than 5', cave in protection provided (trench box, shoring, sloping, benching).
-
Open excavations, road drop offs, trenches, manholes, uneven surfaces - barricaded and have proper notification?
-
Spoil piles at least 2' away from edge of excavation?
Concrete and Masonry Construction - Subpart Q - 1926.700
-
Concrete and Masonry work being performed?
-
Concrete is able to support all loads placed upon it?
-
Rebar protection (e.g. caps) used?
-
Rebar stakes are not impalement hazard?
-
Shoring/bracing properly installed?
-
Batching stations have proper access?
-
Post tension/pre stress cables are present?
Steel Erection - Subpart R 1926.750
-
Steel Erection being performed?
-
Site Layout: Adequate access roads, firm properly graded, and barricaded?
-
Site specific erection plan on site?
-
Approval to begin steel erection has been obtained and is in writing?
-
Controlled access to erection work area in place?
-
Proper bracing/guying?
-
Adequate bridging in place?
-
Anchor rod/bolt repair has been approved in writing by engineer of record?
-
Loose decking has been secured from displacement?
-
All employees properly trained in Subpart R?
-
Concrete has achieved 75% cure strength prior to setting posts or columns?
Underground Construction - Subpart S 1926.800
-
Underground Construction? (Note this does not cover Excavation & Trenching or Electrical Transmission & Distribution lines)
-
Safe means of access and egress?
-
Maintain a check in/check out procedure?
-
Employees Trained?
Demolition - Subpart T 1926.850
-
Demolition work being performed?
-
Prior to start, engineering survey (demolition plan) conducted by a competent person?
-
All utilities, controlled or disconnected?
-
Material not dropped greater than 20' without an enclosed chute?
-
Employees and the general public, are protected from falling objects and other hazards?
-
Are dust control methods in place?
-
Truck routes have been established and marked?
Stairways - Ladders - Subpart X - 1926.1050
-
Stairways or Ladders in use?
-
Stairrails on stairs and exposed edges?
-
Stairwells clear and unobstructed?
-
Stairs with >4 risers or >30" high, equipped with stairrails?
-
All elevation changes of 19" or more have a ladder, ramp, or stair?
-
Ladders extend 3' above landing?
-
Ladders secured from movement?
-
Ropes or other means provided for material/tool retrieval?
-
Ladders are being inspected prior to each use?
-
Ladders properly set up?
-
All required labels/tags are on the ladders?
Toxic and Hazardous Substances - Subpart Z
-
Employees have the proper level of asbestos training?
-
Employees have the proper level of lead training?
-
Have necessary medical evaluations been completed for all exposed employees?
-
Employees have the proper level of silica awareness training?
-
Air monitoring conducted when necessary?
-
Do subs on site have updated silica policy?
-
Is the silica policy up to date?
-
Are exposure control plans reviewed and current?
-
Has air monitoring data been collected if not using Table 1?
-
Are tools in good condition and connected to a HEPA filter when working on silica containing products?
Toxic and Hazardous Substances
-
Are there Above Ground Storage Tanks?
-
Are all ASTs observed during this survey properly labeled?
-
1910.1200(f)(6) Workplace labeling. The employer shall ensure that each container of hazardous chemicals in the workplace is labeled, tagged or marked.
-
Does each tank observed during this survey have appropriate secondary containment?
-
40 CFR 265.193(b) 40 CFR 265.193(c) 40 CFR 265.193(d)
-
Is all leak detection equipment observed during this survey in satisfactory condition?
-
40 CFR 265.193(c)(3) 40 CFR 265.193(e)(3)(iii)
-
Blood Borne Pathogens written exposure control plan been developed if required?
-
1910.1030(c)(1)(i) Each employer having an employee(s) with occupational exposure as defined by paragraph (b) of this section shall establish a written Exposure Control Plan designed to eliminate or minimize employee exposure.
-
Blood Borne Pathogens training records maintained for 3 years from the date on which the training occurred?
-
1910.1030(h)(2)(ii) Training records shall be maintained for 3 years from the date on which the training occurred.
-
Is blood borne pathogen training provided before or at the time of initial assignment where contact with blood or other potentially infectious materials is possible?
-
1910.1030(g)(2)(ii)(A) At the time of initial assignment to tasks where occupational exposure may take place
-
Is blood borne pathogen refresher training provided at least annually?
-
1910.1030(g)(2)(ii)(B) At least annually thereafter.
-
Does the company maintain all employee exposure and medical records for at least the duration of employment plus 30 years?
-
1910.1020(d)(1)(ii) "Employee exposure records." Each employee exposure record shall be preserved and maintained for at least thirty (30) years
-
Is each container/containers of hazardous chemicals in the workplace observed during this survey labeled, tagged or marked identifying the chemical it contains? HAZCOM
-
1910.1200(f)(6) Workplace labeling. The employer shall ensure that each container of hazardous chemicals in the workplace is labeled, tagged or marked
-
Are copies of the required safety data sheets for each hazardous chemical in the workplace observed during this survey readily accessible to employees in the work area during each work shift?
-
1910.1200(g)(8) The employer shall maintain in the workplace copies of the required safety data sheets for each hazardous chemical, and shall ensure that they are readily accessible during each work shift to employees when they are in their work area(s). (Electronic access and other alternatives to maintaining paper copies of the safety data sheets are permitted as long as no barriers to immediate employee access in each workplace are created by such options.)
-
Has a written Hazard Communication program been developed?
-
1910.1200(e)(1) Employers shall develop, implement, and maintain at each workplace, a written hazard communication program which at least describes how the criteria specified in paragraphs (f), (g), and (h) of this section for labels and other forms of warning, safety data sheets, and employee information and training will be met.
-
Asbestos and lead assessment have been completed?
-
Abatement certificate is on hand and available for review?
Confined Space - Subpart AA
-
Confined Space Work?
-
Confined spaces - Identified, evaluated, and classified (permitted/non-permitted)?
-
Are all required warning signs posted?
-
Communication between host, controlling, and exposing employers has been conducted?
-
Has a permit required confined space policy been established?
-
Employees properly trained (entry, attendant, rescue)?
-
Air monitoring conducted, documented, and results available for review?
-
Has an early warning system been established?
-
Have welding requirements been reviewed and established? 1926.353(b)
-
Are all required LOTO steps being followed?
-
Emergency services and rescue are in place?
-
Has public protection been established and in place?
Cranes & Derricks - Subpart CC - 1926.1400
-
Cranes in use?
-
Controlling entity has provided all known ground condition information (utilities, site drawings, and soil analysis if available)?
-
All underground hazards have been identified (voids, tanks, utilities) and operator has been informed?
-
Operator properly trained and certified (NCCCO, NCCER, Union)?
-
DOT Physical up to date?
-
Required post assembly inspection has been completed?
-
Cranes flagged, swing radius protected?
-
Outriggers are fully extended?
-
Outriggers are on adequate pads?
-
Crane annual certification/inspection up to date on the crane?
-
Daily inspection are completed each shift?
-
All rigging operations conducted by a qualified rigger?
-
Crane and hoisting operations are sufficient distance from energized power lines (20' or more)?
-
The operator remains in the cab while load is suspended?
-
Proper distance maintained from all power lines?
-
All signaling operations conducted by qualified signalman (Hand signals, voice, audible, new)?
-
Hand signal charts are on the equipment or conspicuously posted in the vicinity of the hoisting operations?
-
Hooks have appropriate latches and are in good working order?
-
Is there a lift plan in place?
-
Wind meter is in use?
Audit Summary
-
Training Recommendations:
-
undefined
-
Corrective Action Recommendations:
-
undefined