Information
-
Audit Title
-
Plant
-
Conducted on
-
Prepared by
-
Department
-
Belt Photo
Conveyor Overview
Conveyor Overview
-
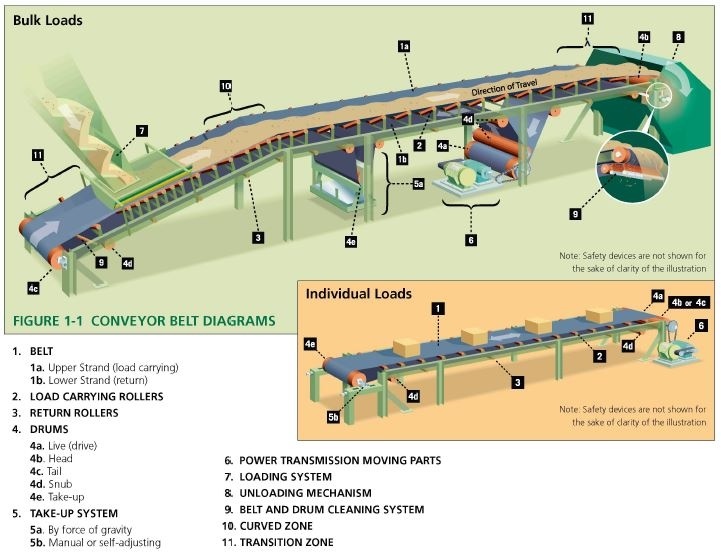
Typical Conveyor System
-
Functions
1) Belt: to convey or transport material
1a) Upper Belt: generally the load carrying belt
1b) Lower Belt: generally the return belt
2) Load Carrying Rollers: to support the belt and reduce its resistance to movement of the load.
3) Return Rollers: To support the belt and reduce resistance to movement.
4) Drums: To drive a belt or re-orient the direction of travel.
5) Take-Up System: To ensure proper belt tension
6) Power Transmission Moving Parts: To produce and transmit the required energy to the live drum for moving or restraining the belt.
7) Loading System: To guide and control the load feed on the belt.
8) Unloading Mechanism: To guide the load exiting the conveyor system.
9) Belt and Drum Cleaner: To remove material accumulation from belts and drums
10) Curved Zone: This is the area of the conveyor where the belt is vertically curved.
11) Transition Zone: Conveyor area where the profile (cross) of the belt changes from troughed to flattened and vice versa.
12) Shunting Mechanism: To change load direction.
Task/Equipment
Conveyor
-
Power transmission moving parts on conveyor guarded? If not, what needs to be accomplished to guard the moving parts.
-
These hazards are associated with the power transmission parts between the motor and the live drum. They are: shafts, couplings, pulley belts, chain and sprockets.
Hazard: Dragging, crushing, entanglement with rotating parts or pinch points. -
Other conveyor moving parts guarded? If not, what needs to be accomplished to guard the moving parts.
-
Nip and shear points shall be guarded. Typical locations are: 1) terminals, drives, take-ups, pulleys, snub rollers where the belt changes direction. 2) where belts wrap around pulleys. 3) at the discharge end of a belt conveyor. 4) on transfers and deflectors used with belt conveyors. 5) at take-ups. 6) idlers located underneath the skirt boards. 7) accessible return idlers on the inclined portion of a belt conveyor less than 2.44m (8feet) above the working surface. 8) accessible carrying and return idlers at convex and horizontal curves.
Hazard: Dragging into in-running nip points, abrasion and friction burns from rubbing against belt, injuries from being struck by a ruptured belt or falling roller. -
Are there any areas where confinement may pose a risk? If at risk, what needs to accomplished to decrease risk of injury.
-
These hazards are related to hoppers, skirt boards, skirt.
Hazard: Shearing or crushing between the load and a fixed object. -
Are there moving load hazards? If at risk, what needs to accomplished to decrease risk of injury.
-
Hazard: Shearing or crushing between the load and a fixed object, falling loads or impact with loads.
Electric Motors
-
Are there any risk of electrocution?
Belt Condition
-
Is the belt in good condition?
-
Hazard: Friction burns or abrasions.
-
Is the belt splice in good condition?
-
Hazard: Entanglement, burns, pokes, lacerations.
Emergency Stop Devices
-
Are there Emergency Stop devices in close approximation to the task?
-
All emergency stop devices shall be easily identifiable in the immediate vicinity of such locations unless guarded by location, position, or guards. Where the design, function, and operation of such conveyor clearly is not hazardous to personnel, an emergency stop device is not required.
Pass Overs, Aisles
-
Are any moving parts, not guarded, less than 8 feet from the walking/working surface?
-
ANSI B20-1 2012: When a conveyor passes over a walkway, roadway, or workstation, it is considered guarded by location if all moving parts are at least 2.44m (8feet) above the floor or walking surface r are otherwise located so that personnel cannot inadvertently come into contact with hazardous moving parts.